Introduction: Basketball Injuries and the Need for Effective Treatment
Basketball’s explosive nature—characterized by rapid directional changes, high-velocity jumps, and intense physical contact—creates a perfect storm for musculoskeletal injuries. From recreational players to professional athletes, the pursuit of peak performance often comes at the cost of increased injury susceptibility. As sports medicine continues to evolve, innovative therapeutic modalities like extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) are revolutionizing how we approach basketball-related injuries, offering athletes faster recovery times and improved long-term outcomes.
The High-Risk Nature of Basketball Injuries
Basketball presents unique biomechanical challenges that predispose players to specific injury patterns. The sport’s plyometric demands, including repetitive jumping and landing sequences, place enormous stress on the kinetic chain. Research indicates that basketball players experience injury rates of approximately 9.9 per 1,000 athlete exposures during games and 4.3 per 1,000 during practice sessions. The lower extremities bear the brunt of these forces, with ankle sprains accounting for nearly 25% of all basketball injuries. The combination of neuromuscular fatigue, inadequate proprioception, and suboptimal landing mechanics creates a cascade of risk factors that traditional treatment methods often struggle to address comprehensively.
The Rise of Shockwave Therapy in Sports Medicine
The emergence of shockwave therapy represents a paradigm shift in sports medicine rehabilitation protocols. Originally developed for lithotripsy procedures in urology, this acoustic wave technology has found remarkable applications in orthopedic and sports medicine settings. The mechanotransduction principles underlying shockwave therapy—whereby mechanical stimuli are converted into cellular responses—align perfectly with the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Professional sports organizations and rehabilitation centers worldwide are increasingly incorporating ESWT into their treatment algorithms, recognizing its potential to accelerate tissue regeneration, reduce inflammatory cascades, and restore functional movement patterns in injured athletes.
Understanding Basketball Injuries: From Sprains to Strains
The complexity of basketball-related injuries extends far beyond simple acute trauma, encompassing a spectrum of pathophysiological processes that affect multiple tissue types. Understanding the intricate relationship between biomechanical stressors and tissue adaptation is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies that address both immediate symptoms and long-term athletic performance.
Common Basketball Injuries
Basketball’s multidirectional movement patterns and high-impact nature create specific injury profiles that sports medicine practitioners encounter regularly. Lateral ankle sprains dominate the injury landscape, typically involving the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) and calcaneofibular ligament (CFL) due to inversion mechanisms during cutting maneuvers. Patellar tendinopathy, colloquially known as “jumper’s knee,” affects the extensor mechanism through repetitive eccentric loading cycles. Achilles tendon disorders, ranging from tendinosis to partial tears, develop through cumulative microtrauma and inadequate recovery periods. Additionally, metatarsal stress fractures emerge from repetitive loading and insufficient bone remodeling capacity, particularly affecting the second and third metatarsals.
Why These Injuries Happen
Anatomical Variations: Differences in body structure that can affect movement mechanics.
Neuromuscular Imbalances: Weaknesses or dysfunctions in the muscles and nerves that can lead to improper movement patterns.
Previous Injury History: Past injuries can alter movement patterns and increase the risk of re-injury.
Hip Abductor Weakness: Weakness in the hip abductors and diminished gluteal activation disrupt the kinetic chain, causing added stress on lower body joints.
Training Load Errors: Overtraining or improper load management that exceeds the body’s recovery capacity.
Inadequate Recovery Protocols: Failure to allow sufficient time for muscles and tissues to recover between training sessions or games.
Environmental Conditions: Court surface characteristics, weather, and other external factors that can increase injury risk.
Injuries occur when the cumulative stress placed on tissues exceeds their adaptive capacity, leading to structural breakdown and inflammatory responses.
The Long-Term Impact of Untreated Injuries
Inadequately managed basketball injuries often progress to chronic conditions that significantly impact athletic performance and quality of life. Untreated ankle sprains frequently develop into chronic ankle instability (CAI), characterized by recurrent episodes of the ankle “giving way” and diminished proprioceptive function. This creates a cycle of reinjury and progressive joint degeneration. Similarly, neglected patellar tendinopathy can evolve into tendinosis, involving degenerative changes within the tendon matrix that become increasingly resistant to conservative treatment approaches. The development of compensatory movement patterns to avoid painful structures often leads to secondary injuries in adjacent joints, creating a cascade of dysfunction throughout the kinetic chain.
How Early Treatment Makes a Difference
Prompt intervention during the acute phase of injury leverages the body’s natural healing processes and prevents the transition to chronic pathological states. Early mobilization and appropriate loading protocols stimulate collagen synthesis and promote optimal tissue remodeling. The inflammatory response, while initially protective, can become detrimental if prolonged, leading to excessive scar tissue formation and altered tissue mechanics. Evidence-based early intervention strategies focus on controlling inflammation while maintaining tissue mobility and preventing muscle atrophy. This approach significantly reduces the risk of chronic complications and accelerates return-to-sport timelines, ultimately preserving long-term athletic careers and functional capacity.
Shockwave Therapy Explained: A Game-Changer for Athletes
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy represents a sophisticated technological advancement that harnesses the power of acoustic waves to stimulate cellular repair mechanisms at the molecular level. This non-invasive therapeutic modality has emerged as a cornerstone treatment option for various musculoskeletal conditions affecting basketball players, offering unique advantages over traditional rehabilitation approaches through its ability to target specific tissues with precise energy delivery.
衝撃波治療とは?
Shockwave therapy utilizes high-energy acoustic pulses generated through electromagnetic, pneumatic, or piezoelectric mechanisms to deliver controlled energy to targeted tissues. These acoustic waves create rapid pressure changes within the tissue matrix, generating cavitation bubbles that subsequently collapse and create secondary mechanical effects. The therapy exists in two primary forms: focused shockwave therapy (F-SWT), which concentrates energy at specific depths, and radial shockwave therapy (R-SWT), which disperses energy across broader tissue areas. The energy flux density, typically measured in millijoules per square millimeter (mJ/mm²), determines the therapy’s penetration depth and biological effects, allowing clinicians to customize treatment parameters based on specific pathological conditions and tissue characteristics.
How Shockwave Therapy Works for Injury Recovery
The therapeutic mechanisms of shockwave therapy involve complex cellular and molecular cascades that promote tissue regeneration and pain modulation. Mechanotransduction pathways are activated when acoustic waves create mechanical stress within cells, triggering the release of growth factors including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). These signaling molecules stimulate angiogenesis, enhancing blood supply to injured tissues and facilitating nutrient delivery for optimal healing. Additionally, shockwave therapy modulates nociceptive pathways through the gate control theory of pain, effectively reducing pain perception while promoting endogenous opioid release. The therapy also influences nitric oxide synthesis, improving endothelial function and promoting vasodilation within the treated tissue region.
Why Shockwave Therapy is Effective for Basketball Injuries
Basketball-specific injuries respond particularly well to shockwave therapy due to the treatment’s ability to address the underlying pathophysiological processes common in these conditions. The therapy’s capacity to break down calcific deposits makes it invaluable for treating chronic tendinopathies that often plague basketball players. Its anti-inflammatory properties help resolve persistent inflammatory states that characterize overuse injuries, while its ability to stimulate collagen synthesis promotes proper tissue remodeling in healing tendons and ligaments. The treatment’s neuroplastic effects on pain processing pathways provide significant symptomatic relief, allowing athletes to engage more effectively in rehabilitation exercises. Furthermore, shockwave therapy’s ability to improve tissue extensibility and reduce muscle tension addresses the biomechanical dysfunctions that often contribute to injury recurrence in basketball players.
Evidence and Studies Supporting Shockwave Therapy
Robust scientific evidence supports the efficacy of shockwave therapy for various basketball-related injuries, with multiple randomized controlled trials demonstrating superior outcomes compared to conventional treatments. A systematic review examining shockwave therapy for patellar tendinopathy revealed significant improvements in pain scores and functional outcomes, with success rates exceeding 80% in many studies. Research investigating Achilles tendinopathy treatment showed that focused shockwave therapy produced statistically significant improvements in pain reduction and functional scores compared to eccentric exercise alone. Studies evaluating lateral ankle sprain recovery demonstrated accelerated healing times and improved proprioceptive function when shockwave therapy was incorporated into rehabilitation protocols. Meta-analyses consistently support the use of shockwave therapy as a first-line treatment option for chronic tendinopathies, with effect sizes often exceeding those of other conservative treatment modalities.
Shockwave Therapy in Action: Treating Specific Basketball Injuries
The versatility of shockwave therapy becomes evident when examining its application across the spectrum of basketball-related injuries. Each injury type presents unique pathophysiological characteristics that require specific treatment approaches, and shockwave therapy’s adaptable parameters make it an ideal therapeutic tool for addressing these diverse conditions with precision and effectiveness.
Ankle Sprains: Accelerating Recovery and Reducing Swelling
Lateral ankle sprains, the most prevalent injury in basketball, benefit significantly from shockwave therapy’s multi-modal effects on tissue healing and inflammation resolution. The acoustic waves promote lymphatic drainage, effectively reducing post-traumatic edema that often impedes recovery. Treatment parameters typically involve low-energy protocols (0.08-0.25 mJ/mm²) applied to the anterior talofibular and calcaneofibular ligaments to stimulate collagen synthesis without causing additional tissue trauma. The therapy’s ability to modulate inflammatory mediators accelerates the transition from the inflammatory phase to the proliferative phase of healing. Concurrently, shockwave therapy enhances proprioceptive recovery by stimulating mechanoreceptors within the ligamentous structures, addressing the neuromuscular deficits that contribute to chronic ankle instability. This comprehensive approach results in faster return-to-sport times and reduced reinjury rates compared to traditional rehabilitation methods.
Patellar Tendonitis: Healing the Jumpers’ Knee
膝蓋腱症 represents one of the most challenging conditions affecting basketball players, with traditional treatments often providing limited long-term success. Shockwave therapy addresses the degenerative changes within the tendon matrix by stimulating neovascularization and promoting proper collagen remodeling. High-energy protocols (0.28-0.60 mJ/mm²) are typically employed to penetrate the thick patellar tendon and create sufficient mechanical stimulation for therapeutic effects. The treatment targets the characteristic hypoechoic regions visible on ultrasound imaging, which represent areas of tendon degeneration. Research demonstrates that shockwave therapy significantly reduces neovascularization within the tendon, which correlates with pain reduction and functional improvement. The therapy’s ability to modulate substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) levels contributes to its analgesic effects, allowing athletes to participate more effectively in eccentric strengthening protocols that form the cornerstone of tendinopathy rehabilitation.
Achilles Tendon Injuries: Boosting Strength and Flexibility
Achilles tendon pathology in basketball players ranges from acute paratenonitis to chronic tendinosis, each requiring tailored shockwave therapy approaches. The treatment’s capacity to stimulate tenocyte proliferation and enhance collagen synthesis makes it particularly effective for addressing the degenerative changes characteristic of Achilles tendinosis. Medium-energy protocols (0.20-0.35 mJ/mm²) are applied to both the insertion site and mid-portion of the tendon, depending on the location of pathology. Shockwave therapy’s ability to break down calcific deposits within the tendon insertion proves invaluable for treating insertional Achilles tendinopathy. The treatment enhances tendon viscoelasticity by promoting proper collagen fiber orientation and reducing pathological cross-linking between collagen fibers. This results in improved tendon compliance and reduced injury risk during the explosive movements characteristic of basketball. Combined with eccentric exercise protocols, shockwave therapy produces synergistic effects that accelerate functional recovery and restore optimal force transmission through the Achilles tendon complex.
Stress Fractures: Speeding Up Bone Healing
Metatarsal stress 骨折, common in basketball players due to repetitive loading patterns, represent another area where shockwave therapy demonstrates significant therapeutic potential. The treatment’s osteogenetic effects are mediated through the activation of osteoblasts and the stimulation of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) expression. Low-to-medium energy protocols (0.10-0.30 mJ/mm²) are applied directly over the fracture site to promote callus formation and accelerate bone remodeling. Shockwave therapy enhances angiogenesis within the fracture callus, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to support optimal healing. The treatment’s ability to stimulate the release of growth factors, including insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), creates an optimal biological environment for bone regeneration. Clinical studies demonstrate reduced healing times and improved bone density at fracture sites when shockwave therapy is incorporated into treatment protocols, allowing basketball players to return to competition sooner while reducing the risk of refracture.
バスケットボール選手に対する衝撃波治療の効果
The unique advantages of shockwave therapy extend beyond simple symptom resolution, encompassing comprehensive improvements in tissue quality, functional capacity, and long-term athletic performance. These benefits align perfectly with the demanding requirements of basketball players who need rapid recovery without compromising future performance potential or risking treatment-related complications.
Non-Invasive, Drug-Free Pain Relief
Shockwave therapy offers a drug-free solution for pain management in basketball players, eliminating concerns about drug interactions or anti-doping violations. It works by stimulating large-diameter afferent fibers, reducing pain transmission through gate control theory. Additionally, the therapy promotes the release of endogenous opioids and reduces substance P in nerve endings, providing long-lasting relief. This non-invasive approach is especially valuable for athletes who require sharp mental focus and optimal performance during competition. Unlike long-term pharmaceutical pain management, shockwave therapy avoids systemic side effects, such as gastrointestinal issues, cardiovascular risks, and dependency. It’s a safe, effective method that ensures athletes stay at the top of their game without compromising their health or eligibility.
Quick Recovery Time: Getting Back in the Game Faster
Shockwave therapy accelerates recovery, allowing basketball players to return to competition faster while maintaining peak performance. Within 3-6 sessions, athletes often experience significant symptomatic improvement and functional gains. The therapy stimulates healing pathways like collagen synthesis, improved blood flow, and reduced inflammation, leading to quicker tissue remodeling. This is particularly beneficial during competitive seasons when any downtime can affect individual performance and team outcomes. With minimal downtime and continued training, athletes avoid the deconditioning that often accompanies prolonged rehabilitation. Shockwave therapy helps players heal faster, return to action sooner, and get back to peak form, ultimately improving their career longevity and competitive edge.
Enhancing Performance: Preventing Future Injuries
Shockwave therapy not only speeds up recovery but also prevents future injuries by improving tissue quality and movement patterns. It enhances tissue extensibility and neuromuscular function, optimizing biomechanics and reducing the risk of injuries like ankle sprains. The therapy improves proprioception, enhancing joint position sense and neuromuscular control, crucial in preventing basketball-related injuries. By addressing subclinical tissue changes before they become symptomatic, shockwave therapy acts as a preventive tool. Its effects on tissue perfusion and cellular metabolism create stronger, more resilient tissues, better equipped to handle the repetitive stress of basketball. This preventive aspect is cost-effective, potentially saving athletes from long-term injuries and expensive healthcare costs.
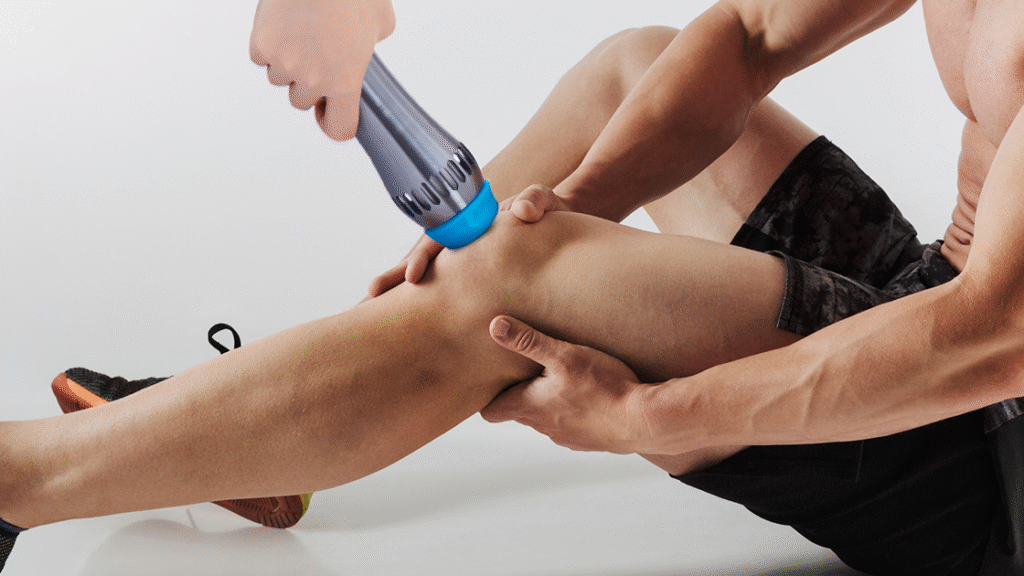
衝撃波治療で期待されること
Understanding the treatment process helps basketball players approach shockwave therapy with appropriate expectations and optimal preparation for successful outcomes. The comprehensive treatment experience encompasses pre-treatment assessment, the actual therapy session, and post-treatment care protocols that collectively contribute to therapeutic success.
The Treatment Process: What Happens in a Session?
A typical shockwave therapy session begins with comprehensive clinical assessment, including diagnostic imaging review and functional movement screening to precisely identify treatment targets. The practitioner applies coupling gel to the treatment area to ensure optimal acoustic wave transmission and minimize energy loss at tissue interfaces. Treatment parameters, including energy flux density, pulse frequency, and total pulse number, are customized based on the specific condition, tissue depth, and individual patient factors. The handheld applicator is positioned perpendicular to the tissue surface and moved systematically across the treatment area to ensure uniform energy distribution. Most sessions last 15-20 minutes, with the actual shockwave application comprising 5-10 minutes of the total treatment time. Real-time ultrasound guidance may be employed for deeper structures to ensure precise energy delivery to pathological tissues while minimizing effects on healthy surrounding structures.
Is It Painful? Understanding the Sensation
The sensory experience during shockwave therapy varies significantly based on individual pain tolerance, tissue sensitivity, and treatment parameters employed. Most patients describe the sensation as rhythmic tapping or pulsing pressure that may range from mildly uncomfortable to moderately intense. The acoustic waves create brief pressure changes that stimulate various mechanoreceptors, producing sensations that typically peak during pulse delivery and immediately subside. Treatment tolerance generally improves throughout each session as endogenous pain modulation mechanisms are activated. Topical anesthetic agents are rarely necessary and may actually interfere with the treatment’s neuroplastic effects on pain processing pathways. The temporary nature of treatment-related discomfort, typically resolving within minutes of session completion, makes the therapy highly tolerable for most basketball players. Post-treatment soreness may occur for 24-48 hours, similar to delayed-onset muscle soreness following intense exercise, and generally indicates appropriate tissue stimulation has occurred.
Post-Treatment Care: Maximizing Recovery
Apply ice for 10-15 minutes to reduce inflammation without affecting the therapy’s benefits on tissue metabolism.
Avoid anti-inflammatory medications for 48 hours to prevent interference with the natural healing process.
Engage in gentle movement and light activities to promote circulation and prevent stiffness. Avoid high-intensity activities for 24-48 hours, depending on the treatment intensity and individual response.
Drink plenty of water to aid in the elimination of metabolic byproducts produced during treatment. Proper hydration supports the lymphatic and vascular systems in clearing waste from the body.
Schedule follow-up visits weekly to monitor recovery progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Continue with prescribed therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, and biomechanical correction to address underlying issues and optimize long-term recovery outcomes.
FAQs About Shockwave Therapy for Basketball Injuries
衝撃波治療は治癒を早め、多くのアスリートがわずか数回のセッションで改善を実感しています。怪我の状態にもよりますが、従来の回復方法よりも記録的な速さでコートに復帰できるかもしれません。
Shockwave therapy is safe for most common basketball injuries, like sprains, tendonitis, and stress fractures. However, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it’s the right fit for your condition.
感覚は強く感じるかもしれないが、一般的には我慢できる程度だ。負傷箇所をターゲットにした深いマッサージのようなものだと考えてください。多くのアスリートは、一時的な不快感をはるかに上回る効果があると報告している。
Wondering if it’s just for recovery, or if it can keep you from getting hurt again? Shockwave therapy doesn’t just heal—it’s also a great preventive measure. By stimulating blood flow and collagen production, it helps strengthen tissues, reducing the likelihood of future injuries.
Final Thoughts on Why Shockwave Therapy is a Winning Choice for Basketball Players
衝撃波治療 is transforming sports medicine by meeting the unique needs of basketball players. It effectively targets inflammation, pain, tissue regeneration, and functional recovery all at once. Its non-invasive approach, fast results, and strong safety record make it an ideal treatment for both quick recovery and long-term career health. Research continues to validate shockwave therapy’s benefits, with advancements improving its precision for sport-specific injuries common in basketball. As our understanding of tissue mechanics grows, this therapy will become even more effective. For basketball players aiming to speed up recovery, prevent future injuries, and maintain peak performance, shockwave therapy offers a scientifically backed, clinically proven solution. It’s truly a slam dunk in injury management and athletic excellence.
参考文献
- How Shockwave Therapy Can Treat Basketball Injuries
- 運動後の筋肉回復を促進する衝撃波治療の方法
- 衝撃波治療の穏やかな波が足首の捻挫に快適さをもたらす
- The effectiveness of shockwave therapy on patellar tendinopathy, Achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The effectiveness of shockwave therapy on patellar tendinopathy, Achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
