1. Introduction
Frozen shoulder (also known as adhesive capsulitis) is a painful and debilitating condition where the shoulder joint becomes stiff and inflamed. The pain and limited range of motion it causes can significantly affect a person’s ability to perform daily tasks. Traditional treatments for frozen shoulder often involve a combination of physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, injections or surgery. However, in recent years, shockwave therapy has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment for patients suffering from this condition.
In this blog, we will explore shockwave therapy as an alternative treatment option for frozen shoulder, its effectiveness, how it works, the benefits, and possible risks. By the end, we will answer the key question: Can shockwave therapy be a viable solution for frozen shoulder relief?
2. Understanding Frozen Shoulder
2.1 What is Frozen Shoulder?
Frozen shoulder is a condition where the capsule of the shoulder joint becomes thickened and tight, restricting the movement of the shoulder. The joint’s natural range of motion is significantly reduced, and it often leads to chronic pain and stiffness. The exact cause of frozen shoulder remains unclear, but it is believed to be associated with inflammation, injury, or extended periods of immobility.
There are three primary stages of frozen shoulder: the freezing stage, where pain begins and the shoulder becomes stiff; the frozen stage, where pain may lessen, but stiffness remains; and the thawing stage, where range of motion gradually returns.
2.2 Diagnosing Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations and imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs. During the physical exam, doctors test the range of motion in the shoulder and check for areas of tenderness. Imaging tests can help rule out other conditions like التهاب المفاصل or rotator cuff tears, which may present similar symptoms.
2.3 Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of frozen shoulder remains elusive, several factors can contribute to its development. These include diabetes, thyroid disorders, and shoulder injuries. Individuals who experience prolonged periods of immobility, such as after surgery or injury, are also at an increased risk. Additionally, women and people between the ages of 40 and 60 are more likely to develop this condition.
3. Shockwave Therapy for Frozen Shoulder
3.1 What is Shockwave Therapy?
العلاج بالموجات الصدمية (also known as extracorporeal shock wave therapy or ESWT) involves the use of high-energy sound waves to stimulate healing in damaged tissue. These shockwaves are delivered to the affected area via a device that generates waves of energy that penetrate deep into the tissues.
Shockwave therapy can be radial or focused, depending on the severity of the condition and the depth of the tissue needing treatment. Radial shockwaves are more superficial, whereas focused shockwaves target deeper structures. This non-invasive therapy has been increasingly used for various musculoskeletal disorders, including frozen shoulder, tendonitis, and calcific tendinopathy.
3.2 How Shockwave Therapy Works for Frozen Shoulder
Shockwave therapy works by generating mechanical pressure that travels through the tissues to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. The shockwaves increase blood flow to the affected area, reduce inflammation, and break down any scar tissue that might be restricting movement.
For frozen shoulder, shockwave therapy targets the shoulder joint capsule and surrounding tissues. This treatment helps improve the flexibility of the capsule, which reduces stiffness and alleviates pain. As a result, patients often experience improved mobility and pain relief following treatment.
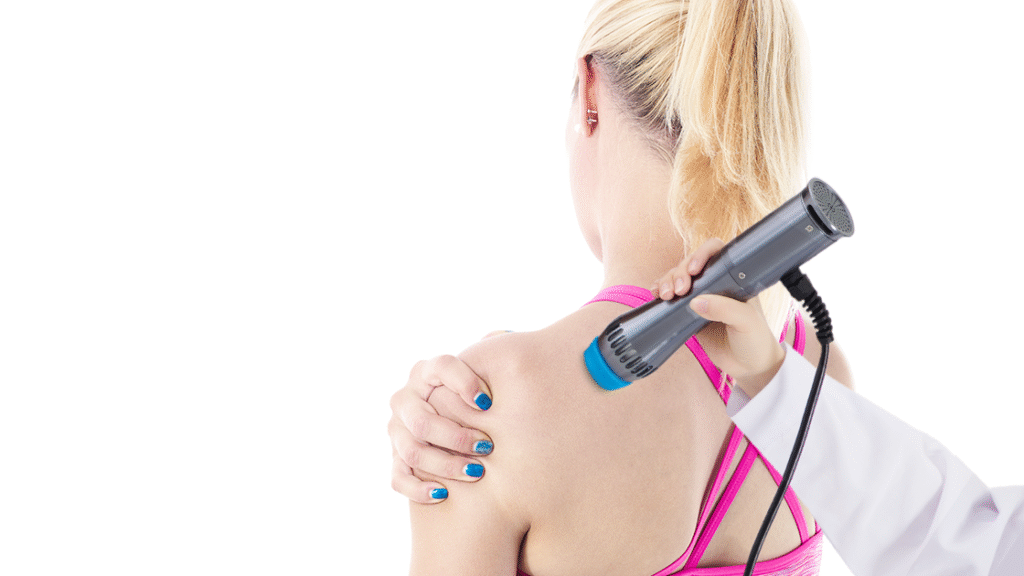
3.3 Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Frozen Shoulder
3.3.1 Non-Invasive Pain Relief
Shockwave therapy provides effective pain relief without the need for invasive procedures such as surgery or injections. By targeting the root cause of the pain, shockwaves reduce inflammation, helping to manage and alleviate chronic shoulder pain. This makes it an attractive option for patients who wish to avoid long-term reliance on medications or invasive treatments.
3.3.2 Improved Shoulder Mobility
One of the most significant benefits of shockwave therapy is the improvement in shoulder mobility. By stimulating collagen production and reducing tissue stiffness, shockwaves help restore the natural movement of the shoulder joint. This is especially important for patients who have limited range of motion due to frozen shoulder.
3.3.3 Faster Recovery Compared to Surgery
Unlike surgery, which requires significant downtime and rehabilitation, shockwave therapy offers a much shorter recovery period. Most patients report noticeable improvements in pain and mobility after just a few sessions, allowing them to return to their daily activities much sooner.
4. Risks and Side Effects of Shockwave Therapy for Frozen Shoulder
4.1 Common Side Effects
4.1.1 Mild Soreness and Discomfort
After a shockwave therapy session, it is common for patients to experience mild soreness or discomfort in the treated area. This is usually short-lived and similar to the sensation one might feel after an intense workout. The discomfort typically subsides within a day or two as the body adjusts to the treatment.
4.1.2 Temporary Redness or Swelling
Due to the increased blood circulation in the treated area, patients may experience temporary redness or mild swelling following shockwave therapy. This side effect is generally mild and should resolve on its own within a few hours to a day after the treatment.
4.1.3 Mild Bruising
In some cases, particularly with higher energy settings or in patients with more sensitive skin, mild bruising may occur. This is a normal reaction to the pressure applied during the shockwave therapy and typically fades within a few days.
4.2 Can Shockwave Therapy Cause Injury or Harm?
Shockwave therapy, when performed by a trained professional, is generally safe. However, there are risks associated with improper use or overuse of the therapy. High-energy shockwaves can cause damage to surrounding tissues if not carefully administered, leading to more harm than good.
It is crucial that shockwave therapy is only performed by qualified practitioners who understand the proper intensity and application for each condition. Overuse or incorrect treatment could lead to muscle strain or nerve irritation, though these side effects are rare.
4.3 Contraindications for Shockwave Therapy
4.3.1 Pregnancy
Shockwave therapy should not be used during pregnancy. The high-energy sound waves may have an unknown effect on the fetus, and it is generally advised to avoid this treatment during the prenatal period. Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider for alternative treatment options.
4.3.2 Cancer or Active Infections
Patients who have active cancer or infections in the area being treated should avoid shockwave therapy. The shockwaves can potentially exacerbate existing conditions, and the risk of complications may be higher. Always inform your healthcare provider about your medical history before undergoing shockwave therapy.
4.3.3 Blood Disorders or Heart Conditions
Individuals with blood disorders, such as hemophilia, or those with certain heart conditions may need to avoid shockwave therapy due to the potential for increased blood flow and clotting issues. In such cases, a medical professional will assess whether shockwave therapy is a safe option or if alternative treatments should be considered.https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jospt/49/4/49_3_256/_article
5. Alternative Non-Surgical Treatments for Frozen Shoulder
5.1 Corticosteroid Injections
For some patients with severe frozen shoulder pain, corticosteroid injections can be effective in reducing inflammation. These injections help provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation, enabling patients to engage in physical therapy and improve shoulder mobility.
However, corticosteroid injections have limitations, and long-term use can lead to side effects like weakened tendons or cartilage damage. When comparing shockwave therapy to corticosteroid injections, the key advantage of shockwave therapy is its ability to treat the root cause of frozen shoulder without the use of drugs.
5.2 Physical Therapy and Stretching Exercises
Physical therapy is one of the most common treatments for frozen shoulder. Stretching and strengthening exercises help restore movement and flexibility to the joint. When combined with shockwave therapy, physical therapy can be even more effective. Shockwave therapy alleviates pain and reduces inflammation, while physical therapy addresses the muscle stiffness and range of motion issues that are characteristic of frozen shoulder.
Patients often see significant improvements in both pain levels and mobility after a few sessions of shockwave therapy, followed by a structured physical therapy program.
5.3 Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Another emerging treatment for frozen shoulder is platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. This involves injecting a patient’s own concentrated platelets into the shoulder joint to promote tissue repair and healing. PRP therapy is particularly useful in treating tendon injuries and can be effective when combined with shockwave therapy.
The main advantage of PRP therapy over traditional treatments is its ability to harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms. However, it may be more expensive than shockwave therapy and requires multiple sessions to see results.
6. The Long-Term Effects of Shockwave Therapy for Frozen Shoulder
6.1 Patient Outcomes and Recovery Times
Most patients begin to experience pain relief after just a few sessions of shockwave therapy. While the results vary depending on the severity of the condition, many individuals report significant improvements in shoulder mobility within 3-6 weeks of treatment.
Recovery times are typically much shorter compared to surgical options, and patients can return to normal activities much faster. However, for best results, it is often recommended to combine shockwave therapy with a comprehensive physical therapy regimen.
6.2 Comparing Shockwave Therapy with Surgical Options
Surgery for frozen shoulder is usually considered a last resort when other treatments have failed. Arthroscopic surgery can help release tight tissue around the shoulder joint and restore movement. However, surgery comes with risks such as infection, longer recovery times, and potential complications.
Shockwave therapy, by contrast, is a minimally invasive procedure that can provide lasting relief without the need for cutting or stitches. For most patients with mild to moderate frozen shoulder, shockwave therapy can offer an effective and safer alternative to surgery.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, shockwave therapy is a promising non-invasive treatment for frozen shoulder that can provide significant pain relief, improve range of motion, and promote faster recovery compared to traditional methods. It is a safe and effective alternative for many patients, especially those seeking to avoid surgery.
While it is not a one-size-fits-all solution, shockwave therapy offers a viable option for managing frozen shoulder and improving quality of life. As with any treatment, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach based on individual needs.
8. References
Efficacy of Shockwave Therapy in Treating Frozen Shoulder: A Systematic Review
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6065153/)
Shockwave Therapy for Shoulder Pain: A Meta-Analysis
(https://www.journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/03057356211034561)
Clinical Applications of Shockwave Therapy for Frozen Shoulder Treatment (https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jospt/49/4/49_3_256/_article)
