Introduction
The demands placed on modern performance horses have never been higher, with athletic expectations spanning disciplines from racing and jumping to dressage and endurance riding. As these magnificent athletes push the boundaries of equine performance, maintaining optimal joint health becomes paramount to their success and longevity. Joint-related injuries represent one of the most significant challenges facing equine practitioners today, often determining whether a horse can continue competing at peak performance levels or face early retirement.
Overview of Joint Health Challenges in Active Horses
Active horses face a complex array of joint health challenges that stem from both their athletic demands and inherent anatomical vulnerabilities. The repetitive stress placed on synovial joints, particularly in the distal limbs, creates a cascade of biomechanical forces that can lead to cartilage degeneration, subchondral bone remodeling, and synovial inflammation. Competition horses experience loading forces that can exceed eight times their body weight during galloping, creating microtrauma within articular cartilage that accumulates over time. Additionally, the limited regenerative capacity of hyaline cartilage means that even minor injuries can progress to significant degenerative joint disease if left untreated.
Importance of Maintaining Mobility and Preventing Injuries
Maintaining optimal joint mobility is crucial not only for athletic performance but also for the overall welfare and quality of life of active horses. Joint stiffness and decreased range of motion can create compensatory movement patterns that redistribute stress to adjacent structures, potentially leading to secondary injuries in tendons, ligaments, and other joints. Early intervention and proactive joint health management can prevent the progression of mild synovitis to irreversible osteoarthritis, preserving the horse’s career longevity. Furthermore, maintaining proper joint function ensures efficient biomechanical movement patterns, reducing energy expenditure and improving overall performance efficiency while minimizing the risk of catastrophic injuries during high-intensity activities.
Brief Introduction to Shockwave Therapy for Horses
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) represents a revolutionary advancement in equine veterinary medicine, utilizing focused acoustic waves to stimulate cellular regeneration and tissue healing at the molecular level. Originally developed for human lithotripsy procedures, this non-invasive therapeutic modality has been successfully adapted for veterinary applications, offering significant benefits for treating musculoskeletal conditions in horses. The therapy delivers controlled acoustic energy pulses that penetrate deep into tissues, triggering mechanotransduction pathways that promote neovascularization, collagen synthesis, and anti-inflammatory responses. This innovative approach has gained widespread acceptance among equine practitioners due to its proven efficacy and minimal side effects.
How Shockwave Therapy Fits into Modern Equine Care
Modern equine care has evolved to embrace evidence-based, multimodal treatment approaches that prioritize both performance optimization and animal welfare. Shockwave therapy seamlessly integrates into comprehensive treatment protocols, complementing traditional therapies such as anti-inflammatory medications, controlled exercise programs, and physiotherapy interventions. This integration reflects the veterinary profession’s shift toward regenerative medicine approaches that harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms rather than simply masking symptoms. The therapy’s non-invasive nature aligns with current trends toward minimally invasive treatments that reduce recovery time and allow horses to maintain training schedules with minimal interruption, making it an ideal component of modern performance horse management programs.
Understanding Joint Health in Horses
To appreciate the therapeutic benefits of shockwave therapy, it’s essential to understand the complex anatomy and physiology of equine joints, as well as the pathological processes that can compromise their function. Equine joints represent sophisticated biomechanical structures that must withstand enormous forces while maintaining precise movement patterns required for athletic performance.
Anatomy of Equine Joints: Key Components and Functions
Equine synovial joints consist of several interconnected components working in harmony to facilitate smooth, pain-free movement. The articular cartilage, composed primarily of type II collagen and proteoglycans, provides a smooth, low-friction surface that distributes load forces across the joint. The synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid, a viscous lubricant rich in hyaluronic acid that nourishes the avascular cartilage and reduces friction during movement. Joint capsules and supporting ligaments provide structural stability while allowing appropriate range of motion. The subchondral bone beneath the cartilage absorbs and dissipates impact forces, while the joint’s proprioceptive innervation provides crucial feedback for coordinated movement patterns essential for athletic performance.
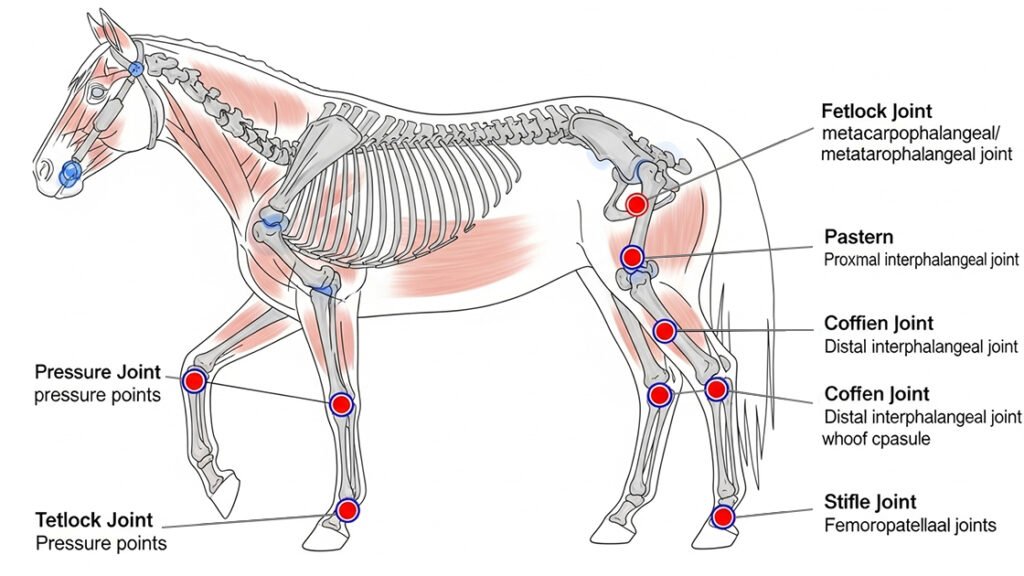
Common Joint Problems in Active Horses
Active horses commonly develop several categories of joint pathology that can significantly impact their performance and welfare. Osteoarthritis, characterized by progressive cartilage degradation and subchondral bone remodeling, represents the most prevalent joint disease in performance horses. Synovitis, inflammation of the synovial membrane, often precedes cartilage damage and manifests as joint effusion and pain. Osteochondral fragmentation, particularly in high-motion joints like the fetlock, creates mechanical irritation and progressive joint damage. Capsulitis and periarticular soft tissue inflammation can restrict joint mobility and cause compensatory movement patterns. Additionally, age-related changes in cartilage composition and synovial fluid quality can predispose older horses to degenerative joint disease even with appropriate management.
How Joint Problems Impact Performance and Mobility
Joint pathology creates a complex cascade of performance-limiting factors that extend far beyond the affected joint itself. Pain and inflammation reduce the horse’s willingness to engage fully in athletic activities, leading to shortened stride length, reduced impulsion, and altered gait patterns. Decreased joint mobility restricts range of motion, particularly affecting collection and extension in dressage horses or jumping technique in sport horses. Compensatory movement patterns develop as horses attempt to minimize discomfort, often leading to secondary injuries in other limbs or back pain. Chronic joint inflammation can cause progressive muscle atrophy and weakness, further compromising athletic performance. The psychological impact of persistent pain can also affect the horse’s attitude and willingness to work, creating training difficulties that persist even after successful treatment.
Preventive Measures for Maintaining Joint Health
Effective joint health maintenance requires a comprehensive approach that addresses multiple risk factors throughout the horse’s career. Proper conditioning programs that gradually increase workload allow tissues to adapt to increasing demands while minimizing injury risk. Maintaining optimal body weight reduces loading forces on joints, particularly important for horses with conformational predispositions to joint problems. High-quality footing that provides appropriate cushioning and traction helps absorb impact forces and prevents excessive joint stress. Regular veterinary monitoring, including periodic joint flexion tests and diagnostic imaging when indicated, enables early detection and intervention before irreversible damage occurs. Nutritional support with appropriate joint supplements, particularly glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help maintain cartilage health and reduce inflammatory responses throughout the horse’s competitive career.
How Shockwave Therapy Works at a Cellular Level
The therapeutic efficacy of shockwave therapy stems from its ability to trigger complex cellular and molecular responses that promote tissue healing and regeneration. Understanding these mechanisms provides insight into why this therapy has become such a valuable tool in equine medicine.
Mechanism of Action: Stimulating Tissue Repair
Shockwave therapy initiates tissue repair through mechanotransduction, a process whereby mechanical energy is converted into biochemical signals that activate cellular healing pathways. The acoustic waves create cavitation bubbles within tissues, generating localized stress that stimulates fibroblast proliferation and differentiation. This mechanical stimulation upregulates growth factor expression, including transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The therapy also activates nitric oxide synthase pathways, promoting vasodilation and improved tissue oxygenation. Additionally, shockwaves stimulate the release of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide, which contribute to neurogenic inflammation and subsequent tissue remodeling. These cellular responses collectively enhance the body’s natural healing capacity, accelerating recovery from both acute injuries and chronic degenerative conditions.
Improving Blood Circulation and Nutrient Delivery
Enhanced vascularization represents one of the most significant benefits of shockwave therapy, particularly important in treating relatively avascular tissues like tendons and cartilage. The acoustic energy stimulates angiogenesis through upregulation of VEGF and angiopoietin expression, promoting the formation of new capillary networks within treated tissues. This neovascularization improves oxygen and nutrient delivery to metabolically active cells involved in tissue repair processes. The therapy also causes temporary vasodilation of existing blood vessels, immediately improving perfusion to treated areas. Enhanced circulation facilitates the removal of metabolic waste products and inflammatory mediators that can impede healing. In joints specifically, improved synovial circulation enhances the delivery of nutrients to avascular articular cartilage, supporting chondrocyte metabolism and matrix synthesis essential for maintaining cartilage integrity and function.
Reducing Inflammation and Promoting Collagen Production
Shockwave therapy exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects through multiple pathways that help resolve both acute and chronic inflammatory processes. The treatment modulates inflammatory cell migration and activation, reducing the accumulation of neutrophils and macrophages in treated tissues. It also influences cytokine production, decreasing pro-inflammatory mediators like interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) while promoting anti-inflammatory cytokines. The therapy stimulates collagen synthesis by activating fibroblasts and promoting the expression of collagen types I and III genes. This enhanced collagen production improves tissue tensile strength and structural integrity, particularly beneficial for healing tendon and ligament injuries. Additionally, shockwave therapy promotes the organization of newly synthesized collagen fibers, ensuring proper tissue architecture that can withstand the mechanical demands placed on active horses during training and competition.
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Joint Health
The application of shockwave therapy in equine joint health management offers numerous advantages that make it an invaluable tool in the modern veterinary arsenal. These benefits extend beyond simple pain relief to encompass comprehensive tissue healing and long-term joint preservation.
Accelerated Healing of Tendons and Ligaments
Shockwave therapy significantly accelerates the healing process in periarticular tendons and ligaments through stimulation of cellular proliferation and enhanced collagen synthesis. The treatment promotes the formation of functionally oriented collagen fibers, improving the biomechanical properties of healing tissues compared to conventional rest-only approaches. Research demonstrates that shockwave-treated tendon injuries show improved tensile strength and reduced scar tissue formation, leading to better long-term outcomes. The therapy also enhances the integration of healing tissues with surrounding structures, reducing the risk of re-injury during return to athletic activity. This acceleration in healing time allows horses to resume training sooner while achieving superior tissue quality, making it particularly valuable for high-level performance horses where extended layoffs can significantly impact competitive careers.
Pain Relief and Reduced Inflammation
The analgesic effects of shockwave therapy provide significant pain relief through multiple mechanisms, including the gate control theory of pain transmission and direct effects on nociceptors. The treatment reduces substance P levels in treated tissues, diminishing pain signal transmission to the central nervous system. Additionally, shockwave therapy promotes the release of endorphins and other endogenous pain-relieving compounds, providing sustained pain relief that extends beyond the immediate treatment period. The anti-inflammatory effects help reduce joint effusion, synovial thickening, and periarticular soft tissue swelling that contribute to discomfort and restricted mobility. This dual action of pain relief and inflammation reduction creates a positive feedback loop that facilitates improved joint function and allows for more effective rehabilitation exercises, ultimately leading to better treatment outcomes and faster return to athletic performance.
Improved Range of Motion and Flexibility
Shockwave therapy effectively addresses the mechanical restrictions that limit joint range of motion in horses with chronic joint problems. The treatment reduces fibrotic tissue formation and adhesions within joint capsules and surrounding soft tissues that can mechanically limit joint mobility. By promoting proper collagen remodeling and tissue elasticity, the therapy helps restore normal joint mechanics and movement patterns. The reduction in pain and inflammation allows horses to move more freely, which in turn helps maintain joint mobility through natural movement. Studies have shown significant improvements in joint flexion angles and stride length following shockwave therapy protocols. This enhanced mobility is particularly important for performance horses, as restricted range of motion can significantly impact athletic performance and increase the risk of compensatory injuries in other limbs or the axial skeleton.
Enhanced Performance in Active Horses
The performance benefits of shockwave therapy extend beyond simple injury treatment to encompass overall athletic enhancement and career longevity. By addressing subclinical joint inflammation and early degenerative changes, the therapy helps maintain optimal joint function before performance-limiting symptoms develop. Horses treated with shockwave therapy often demonstrate improved stride quality, increased willingness to work, and enhanced overall athletic ability. The therapy’s ability to reduce recovery time between training sessions allows for more consistent conditioning programs, leading to improved fitness levels and competitive performance. Additionally, the treatment’s preventive benefits help maintain joint health throughout the horse’s competitive career, reducing the likelihood of career-ending injuries. This comprehensive approach to joint health management has made shockwave therapy an essential component of performance horse care protocols in many top-level equine facilities worldwide.
Long-Term Joint Preservation and Prevention of Degenerative Conditions
One of the most valuable aspects of shockwave therapy is its ability to slow or prevent the progression of degenerative joint disease when applied proactively. The treatment stimulates cartilage matrix synthesis and helps maintain chondrocyte viability, essential factors in preventing osteoarthritis progression. By improving synovial fluid quality and reducing inflammatory mediators within joints, shockwave therapy helps preserve the joint’s natural lubricating and nourishing mechanisms. The therapy also promotes proper subchondral bone remodeling, preventing the formation of abnormal bone densities that can contribute to cartilage breakdown. Regular shockwave therapy sessions as part of a comprehensive joint health program can significantly extend the competitive careers of performance horses while maintaining their quality of life into their senior years. This preventive approach represents a paradigm shift from reactive treatment to proactive joint health management.
Non-Invasive Nature and Minimal Recovery Time
The non-invasive nature of shockwave therapy makes it an ideal treatment option for valuable performance horses who cannot afford extended periods away from training. Unlike surgical interventions or invasive procedures, shockwave therapy requires no anesthesia, surgical sites, or prolonged recovery periods that can lead to deconditioning. Most horses can resume normal training activities within 24-48 hours following treatment, with some protocols allowing immediate return to work. The minimal side effects and low complication rates make the therapy suitable for frequent use as part of ongoing joint maintenance programs. This convenience factor has contributed significantly to the widespread adoption of shockwave therapy in the performance horse industry, where maintaining training schedules is crucial for competitive success. The ability to provide effective treatment without disrupting training routines makes shockwave therapy an invaluable tool for trainers and veterinarians working with high-level equine athletes.
Conditions Where Shockwave Therapy Is Effective
The versatility of shockwave therapy makes it effective for treating a wide range of joint and soft tissue conditions commonly encountered in performance horses. Understanding the specific applications and expected outcomes helps veterinarians and horse owners make informed treatment decisions.
Arthritis and Osteoarthritis in Horses
Shockwave therapy has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in managing both acute arthritis and chronic osteoarthritis in equine patients. The treatment addresses multiple pathological processes involved in joint degeneration, including synovial inflammation, cartilage matrix degradation, and subchondral bone sclerosis. In acute arthritis cases, shockwave therapy rapidly reduces inflammatory cell infiltration and cytokine production, preventing the progression to chronic degenerative changes. For established osteoarthritis, the therapy stimulates remaining chondrocytes to increase matrix synthesis while improving the mechanical properties of existing cartilage. Clinical studies have shown significant improvements in lameness scores, joint flexion tests, and radiographic changes following shockwave therapy protocols. The treatment is particularly effective when combined with appropriate exercise modification and joint supplementation, providing a comprehensive approach to arthritis management that can maintain horses in active work for extended periods.
Tendon and Ligament Injuries Around Joints
Periarticular tendon and ligament injuries respond exceptionally well to shockwave therapy due to the treatment’s ability to enhance healing in these typically challenging tissues. The therapy’s promotion of neovascularization is particularly beneficial for tendons and ligaments, which have limited natural blood supply and consequently poor healing capacity. Shockwave treatment accelerates the inflammatory phase of healing while promoting proper collagen fiber alignment during the remodeling phase, resulting in stronger, more functional scar tissue. Common conditions successfully treated include collateral ligament injuries, suspensory ligament insertional problems, and digital flexor tendon injuries near their joint attachments. The therapy’s ability to improve tissue elasticity and reduce adhesion formation helps restore normal biomechanical function, reducing the risk of re-injury during return to athletic activity. Research indicates that shockwave-treated tendon and ligament injuries have lower recurrence rates and superior long-term outcomes compared to conventional treatments alone.
Navicular Syndrome and Related Joint Stress
Navicular syndrome, a complex condition affecting the navicular bone, bursa, and associated soft tissues, represents one of the most successful applications of shockwave therapy in equine medicine. The condition’s multifactorial nature, involving poor circulation, chronic inflammation, and degenerative changes, aligns perfectly with shockwave therapy’s mechanisms of action. The treatment improves circulation to the relatively avascular navicular region, reducing ischemia-related pain and promoting healing of microfractures and erosive lesions. Shockwave therapy also addresses the soft tissue components of navicular syndrome, including navicular bursa inflammation and deep digital flexor tendon lesions. Clinical outcomes show significant improvement in heel pain, stride quality, and overall soundness in horses with navicular syndrome. The therapy’s effectiveness in this traditionally challenging condition has made it a cornerstone of navicular syndrome treatment protocols, often providing dramatic improvements in horses previously considered poor candidates for return to athletic activity.
Degenerative Joint Disease in Aging Performance Horses
Aging performance horses commonly develop degenerative joint disease as a result of cumulative wear and tear throughout their competitive careers. Shockwave therapy offers significant benefits for managing these age-related changes, helping to slow disease progression and maintain quality of life. The treatment stimulates the remaining viable chondrocytes to increase matrix synthesis, potentially slowing cartilage loss in affected joints. Additionally, the therapy’s anti-inflammatory effects help reduce the chronic low-grade inflammation that contributes to progressive joint degeneration in older horses. Shockwave therapy also improves synovial fluid quality by stimulating hyaluronic acid production and reducing inflammatory mediators that degrade synovial fluid viscosity. For senior horses, this therapy can significantly improve comfort levels and maintain mobility, allowing continued light exercise that benefits overall health and wellbeing. Many older horses show renewed enthusiasm for work following shockwave therapy treatment, highlighting its impact on pain relief and joint function.
Soft Tissue Injuries and Muscle Strains
Muscle strains and soft tissue injuries around joints respond favorably to shockwave therapy through enhanced circulation and accelerated healing processes. The treatment is particularly effective for addressing muscle fibrosis and trigger points that can develop following acute injuries or chronic overuse. Shockwave therapy promotes the resolution of hematomas and reduces scar tissue formation, leading to more complete functional recovery. The treatment also addresses muscle tension and spasm patterns that can develop as compensation for joint problems, helping to restore normal movement patterns. Common applications include treatment of semimembranosus and semitendinosus muscle strains, gluteal muscle injuries, and cervical muscle tension associated with poll and neck problems. The therapy’s ability to improve tissue elasticity and reduce pain makes it valuable for maintaining muscle health in performance horses subjected to intensive training programs. Integration with appropriate stretching and strengthening exercises enhances treatment outcomes and reduces recurrence rates.
Chronic Joint Pain and Stiffness
Chronic joint pain and stiffness, often resulting from previous injuries or ongoing low-grade inflammation, represents a common indication for shockwave therapy in performance horses. These conditions frequently involve multiple joints and can significantly impact athletic performance and quality of life. Shockwave therapy addresses the underlying inflammatory processes that perpetuate chronic pain while promoting tissue remodeling that can restore joint function. The treatment’s neurological effects help break pain cycles that can become self-perpetuating in chronic conditions. Many horses with chronic joint problems show improvement in attitude and willingness to work following shockwave therapy, indicating significant pain relief. The therapy is particularly valuable for managing horses with multiple joint involvement, where systemic anti-inflammatory medications may not provide adequate relief. Regular maintenance protocols using shockwave therapy can help prevent acute flare-ups of chronic conditions while maintaining joint mobility and comfort levels necessary for continued athletic participation.

Tips for Maximizing Joint Health in Horses
Achieving optimal joint health in performance horses requires a comprehensive, multifaceted approach that extends beyond individual treatments to encompass all aspects of horse management. Successful joint health programs integrate various therapeutic modalities with sound management practices to create synergistic effects that maximize outcomes.
Combining Shockwave Therapy with Physical Therapy
The integration of shockwave therapy with targeted physical therapy protocols creates synergistic effects that enhance treatment outcomes significantly. Physical therapy modalities such as therapeutic ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and laser therapy complement shockwave treatment by addressing different aspects of the healing process. Controlled exercise programs following shockwave therapy help optimize tissue remodeling and maintain joint mobility during the healing process. Manual therapy techniques, including joint mobilization and soft tissue massage, enhance the circulation improvements initiated by shockwave treatment. Proprioceptive training exercises help restore normal movement patterns and reduce compensation mechanisms that can lead to secondary injuries. The timing and sequencing of combined treatments require careful coordination to maximize benefits while avoiding interference between modalities. This integrated approach often produces superior outcomes compared to individual treatments used in isolation.
Proper Nutrition and Joint Supplements
Nutritional support plays a crucial role in maintaining joint health and maximizing the benefits of shockwave therapy treatments. High-quality protein sources provide essential amino acids necessary for collagen synthesis and tissue repair processes stimulated by shockwave treatment. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, provide anti-inflammatory effects that complement the inflammation-reducing properties of shockwave therapy. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate supplements support cartilage matrix synthesis and may enhance the regenerative effects of shockwave treatment. Hyaluronic acid supplementation helps maintain synovial fluid quality, while MSM provides sulfur necessary for proper collagen cross-linking. Antioxidants such as vitamin E and selenium help protect tissues from oxidative damage during the healing process. The timing of nutritional interventions in relation to shockwave therapy can influence treatment outcomes, with some supplements showing enhanced effectiveness when administered in conjunction with therapy sessions.
Regular Exercise and Conditioning Programs
Appropriate exercise programs are essential for maintaining joint health and optimizing the benefits of shockwave therapy treatments. Progressive conditioning protocols that gradually increase workload allow tissues to adapt to increasing demands while minimizing injury risk. Cross-training activities that vary movement patterns help prevent overuse injuries and maintain overall fitness during treatment periods. Swimming and aqua-therapy provide low-impact exercise options that maintain cardiovascular fitness while reducing joint stress during recovery periods. Hill work and cavaletti exercises promote proper biomechanical patterns while strengthening supporting musculature around treated joints. The integration of flexibility and stretching routines helps maintain range of motion improvements achieved through shockwave therapy. Regular assessment of exercise tolerance and performance helps guide program modifications and treatment scheduling. Consistency in exercise programs is crucial for maintaining the benefits of shockwave therapy over time.
Monitoring for Early Signs of Joint Problems
Early detection of joint problems is crucial for successful treatment outcomes and career longevity in performance horses. Daily observation of movement patterns, attitude changes, and performance indicators can reveal subtle signs of developing joint issues before they become performance-limiting. Regular veterinary examinations including joint flexion tests, palpation, and movement assessments help identify problems in their early stages when treatment is most effective. Baseline diagnostic imaging establishes reference points for monitoring disease progression and treatment response over time. Performance metrics such as stride length, timing, and biomechanical parameters can reveal functional changes that precede obvious lameness. Temperature monitoring of joints and surrounding tissues can indicate inflammatory processes before clinical signs develop. Gait analysis technology provides objective measurements of movement quality that can detect subtle changes in joint function. Early intervention with shockwave therapy and other treatments can prevent minor problems from progressing to career-threatening conditions.
Maintaining Optimal Weight to Reduce Joint Stress
Weight management represents a critical component of joint health maintenance, particularly important for horses receiving shockwave therapy treatments. Excess body weight significantly increases loading forces on joints, potentially overwhelming the healing benefits of therapeutic interventions. Regular body condition scoring helps maintain optimal weight ranges that minimize joint stress while supporting athletic performance. Dietary management strategies should balance energy requirements for athletic performance with weight control objectives to prevent excessive loading of healing joints. The relationship between body weight and joint loading is particularly important in horses with conformational predispositions to joint problems. Weight reduction programs may need to be implemented gradually to avoid compromising athletic performance while achieving joint health benefits. Regular monitoring of weight changes helps guide dietary adjustments and exercise modifications. The integration of weight management with shockwave therapy protocols often enhances treatment outcomes and reduces the frequency of maintenance treatments required.
Environmental and Stall Management for Joint Health
Environmental factors significantly influence joint health and can affect the outcomes of shockwave therapy treatments. Footing quality in both training areas and turnout paddocks should provide appropriate cushioning and traction while maintaining consistency to prevent joint stress from uneven surfaces. Stall design should encourage natural movement patterns and prevent prolonged periods of immobility that can contribute to joint stiffness. Temperature and humidity control help prevent environmental stressors that can exacerbate inflammatory conditions and interfere with healing processes. Bedding selection should provide adequate cushioning for recumbent positions while maintaining cleanliness to prevent infection risks. Turnout management should balance the benefits of natural movement with protection from injury risks, particularly during treatment and recovery periods. Facility design should minimize sharp turns and sudden elevation changes that can stress healing joints. Environmental enrichment that encourages natural behaviors and movement patterns supports overall joint health and wellbeing throughout the treatment process.
Conclusion
Shockwave therapy has transformed joint health management in performance horses, offering a scientifically-based, non-invasive treatment that promotes natural healing while reducing pain and inflammation. Beyond symptom relief, it supports true tissue regeneration, enhancing collagen synthesis, neovascularization, and modulating inflammatory responses to preserve joint function. Its versatility allows treatment of both acute injuries and chronic degenerative conditions, making it a valuable tool in equine medicine. When combined with proper nutrition, exercise management, and environmental care, shockwave therapy delivers synergistic benefits that optimize performance and welfare. As research advances, treatment protocols and applications will continue to improve. For horse owners, trainers, and veterinarians, this therapy provides a safe, effective, and evidence-based option to maintain joint health, enhance athletic performance, and support the long-term soundness and career longevity of equine athletes.
