Introduction: Revolutionizing Calf Injury Recovery
Calf injuries represent one of the most frustrating setbacks for athletes and active individuals, often requiring extended recovery periods that interrupt training schedules and diminish performance capacity. Traditional rehabilitation approaches, while effective, sometimes fall short in addressing persistent pain and incomplete tissue healing. This comprehensive guide explores how shockwave therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment modality that accelerates calf muscle recovery through scientifically validated mechanisms, offering hope to those struggling with stubborn lower leg injuries.
The Prevalence of Calf Injuries in Athletes and Active Individuals
Calf muscle injuries represent a significant portion of sports-related musculoskeletal problems, accounting for roughly 12–15% of all such injuries. Athletes engaged in running, basketball, tennis, soccer, and sprint-based sports are particularly prone due to the explosive acceleration, sudden deceleration, and jumping movements these activities demand. The gastrocnemius and soleus muscles bear the majority of stress, with the medial gastrocnemius head being the most commonly injured, often at the myotendinous junction where muscle fibers transition into tendon. Injuries range from mild grade I strains, causing minor discomfort and temporary limitation, to severe grade III ruptures that may require surgical intervention. Early identification and tailored rehabilitation are crucial to minimize downtime, prevent recurrent injury, and maintain performance levels. Understanding the prevalence and risk factors helps athletes, trainers, and healthcare providers implement targeted prevention and recovery strategies.
Common Challenges in Calf Muscle Healing
Limited blood flow slows nutrient delivery and tissue repair.
Scar tissue and fibrosis reduce muscle elasticity.
Persistent inflammation prolongs pain and stiffness.
Reduced range of motion limits functional recovery.
Premature loading increases reinjury risk.
Complex physiology makes healing slower than other muscles.
¿Qué son las ondas de choque?
Before examining shockwave therapy’s specific applications in calf injury rehabilitation, it’s essential to understand the fundamental principles and biological mechanisms underlying this innovative treatment approach. This section provides a comprehensive overview of how shockwave therapy works at cellular and tissue levels to promote healing.
What Is Shockwave Therapy? Mechanism and Science
Terapia de ondas de choque, also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive treatment that delivers high-energy acoustic waves to injured tissues via a specialized transducer. These pressure waves generate mechanical stress that triggers mechanotransduction, activating cellular pathways including growth factors and inflammatory mediators that facilitate tissue repair. There are two main types: focused shockwave therapy, which delivers concentrated energy to deeper tissues, and radial shockwave therapy, which disperses energy over broader, more superficial areas. The therapy works through mechanisms such as cavitation, microtrauma induction, and stimulation of neovascularization, which collectively alter the tissue microenvironment to favor regeneration over degeneration. By targeting both cellular and vascular processes, shockwave therapy accelerates repair, reduces pain, and improves function in muscles, tendons, and ligaments, making it an increasingly popular modality in sports medicine and orthopedic rehabilitation.
How Shockwave Therapy Targets Muscle, Tendon, and Ligament Repair
Shockwave therapy is versatile, promoting healing across muscles, tendons, and ligaments through similar biological pathways. In muscle tissue, acoustic waves stimulate satellite cell proliferation and differentiation, which are essential for regenerating damaged myofibers after injury. In tendons, shockwaves enhance tenocyte activity and extracellular matrix remodeling, improving tensile strength and alleviating tendinopathy symptoms. Ligament recovery is supported through fibroblast activation, which accelerates collagen synthesis and cross-linking, restoring tissue stability. Additionally, shockwave therapy modulates blood vessel formation by disrupting pathological neovascularization while promoting healthy angiogenesis, creating optimal conditions for structural repair. This multi-target approach is particularly effective for complex calf injuries, where muscle, tendon, and ligament tissues are often simultaneously affected. Overall, ESWT fosters a coordinated regenerative environment, reduces inflammation, and accelerates functional recovery.
How Shockwave Therapy Supports Calf Muscle Healing
The therapeutic benefits of shockwave therapy extend across multiple physiological domains, each contributing to comprehensive calf injury recovery. Understanding these specific mechanisms helps patients and practitioners optimize treatment protocols for maximum effectiveness. Let’s explore the primary ways shockwave therapy facilitates healing in injured calf muscles.
Stimulating Collagen Production and Tissue Regeneration
Shockwave therapy significantly upregulates collagen synthesis by activating transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression within damaged tissue. This biochemical cascade promotes type I collagen deposition, which provides superior tensile strength compared to the type III collagen formed during unassisted healing. Enhanced fibroblast proliferation creates a robust extracellular matrix scaffold that supports myocyte regeneration. Research demonstrates that ESWT-treated tissues exhibit improved collagen fiber alignment and organization, resulting in biomechanically superior healed muscle with reduced scar tissue formation and better functional outcomes compared to conventional rehabilitation approaches.
Reducing Post-Injury Inflammation and Swelling
While acute inflammation serves protective functions, prolonged inflammatory responses impede healing and perpetuate pain in calf injuries. Shockwave therapy modulates inflammatory pathways by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, including interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, while simultaneously promoting anti-inflammatory mediator release. This immunomodulatory effect accelerates transition from inflammatory to proliferative healing phases. Additionally, shockwaves enhance lymphatic drainage through mechanical stimulation, reducing interstitial edema and tissue pressure. Decreased swelling improves oxygen diffusion to injured cells and facilitates metabolic waste removal, creating optimal conditions for tissue repair while simultaneously alleviating discomfort associated with inflammation.
Enhancing Blood Flow for Accelerated Recovery
Neovascularization represents one of shockwave therapy’s most significant contributions to calf muscle healing. Acoustic waves trigger endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation, promoting vasodilation and increasing regional blood flow to hypoxic injured tissues. The therapy stimulates angiogenic growth factor expression, particularly VEGF, which initiates new capillary formation through endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Improved microcirculation ensures adequate oxygen and nutrient delivery to metabolically active healing tissues while efficiently removing metabolic byproducts. Enhanced perfusion also supports satellite cell function and myogenesis, essential processes for muscle fiber regeneration. This vascular remodeling creates a sustainable blood supply network supporting long-term tissue health.
Pain Relief Without Medications
Shockwave therapy provides analgesic effects through multiple neurophysiological mechanisms, offering medication-free pain management for calf injury patients. The treatment induces hyperstimulation analgesia by overstimulating nociceptors, effectively raising pain thresholds through gate control theory principles. Shockwaves also degrade substance P, a key neurotransmitter involved in pain signal transmission, reducing pain perception at spinal cord levels. Additionally, endorphin release triggered by mechanical stimulation creates natural analgesia. The therapy addresses pain generators by breaking down calcifications and reducing muscle tension through fascial release. These combined mechanisms provide both immediate and cumulative pain reduction, allowing patients to participate more effectively in rehabilitation exercises without pharmaceutical interventions.
Clinical Applications and Case Examples
Shockwave therapy’s versatility enables its application across various calf injury presentations, from acute muscle strains to chronic tendinopathies. This section examines specific clinical scenarios where ESWT demonstrates particular effectiveness, supported by real-world outcomes that illustrate the therapy’s practical benefits for diverse patient populations.
Treatment for Calf Strains and Tears
Grade I and II calf strains respond exceptionally well to shockwave therapy protocols, with research indicating 30-40% faster return-to-activity times compared to conventional treatment. The therapy is particularly effective when initiated during the proliferative phase, typically 48-72 hours post-injury after acute inflammation subsides. For grade III complete ruptures requiring surgical intervention, ESWT serves as valuable adjunctive therapy during post-operative rehabilitation. Treatment parameters typically involve 2000-3000 shockwaves at 0.10-0.25 mJ/mm² energy density per session, administered weekly over four to six weeks. Patients report significant pain reduction and improved functional mobility following treatment protocols, with objective measurements showing enhanced muscle strength recovery.
Rehabilitation of Achilles Tendon and Gastrocnemius Injuries
The calf complex’s intimate relationship with the Achilles tendon means many injuries involve both structures simultaneously. Insertional and mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy demonstrates excellent response to focused shockwave therapy, with studies showing 60-80% success rates in chronic cases resistant to conservative management. Gastrocnemius myotendinous junction injuries, commonly termed “tennis leg,” benefit from radial shockwave applications targeting the musculotendinous interface. Combined treatment addressing both proximal gastrocnemius and distal Achilles components yields superior outcomes for patients with kinetic chain dysfunction. The therapy effectively addresses scar tissue adhesions and fascial restrictions that commonly develop following these injuries, restoring optimal tissue gliding and biomechanical function.
Post-Surgical Calf Recovery and Scar Tissue Management
Following surgical repair of complete calf muscle ruptures or Achilles tendon reconstructions, shockwave therapy accelerates rehabilitation by addressing post-operative complications. The treatment effectively breaks down excessive scar tissue and adhesions that limit range of motion and compromise functional outcomes. ESWT promotes proper collagen remodeling during the maturation phase, typically beginning 6-8 weeks post-surgery once incisions have adequately healed. The therapy reduces keloid formation risk and improves surgical scar pliability through mechanical disruption of disorganized collagen fibers. Patients undergoing post-surgical shockwave protocols demonstrate improved dorsiflexion range, enhanced proprioception, and earlier return to pre-injury activity levels compared to those receiving standard rehabilitation alone.
Real-World Patient Outcomes and Success Stories
A 32-year-old marathon runner with recurrent medial gastrocnemius strains achieved complete symptom resolution after four shockwave therapy sessions, returning to competitive running within six weeks. A 45-year-old recreational basketball player suffering from chronic Achilles tendinopathy unresponsive to 18 months of conventional treatment experienced 85% pain reduction following six-week ESWT protocol, avoiding planned surgical intervention. Professional soccer player recovered from grade II calf tear in seven weeks using combined shockwave therapy and progressive loading, compared to typical 10-12 week recovery timelines. These cases exemplify shockwave therapy’s effectiveness across diverse injury presentations and patient populations, consistently delivering accelerated healing and functional restoration.
Integrating Shockwave Therapy into Calf Injury Rehab
Successful calf injury rehabilitation requires strategic integration of shockwave therapy within comprehensive treatment protocols. This section provides practical guidance on patient selection, optimal timing, and synergistic combinations with other therapeutic modalities to maximize recovery outcomes and minimize recurrence risk.
Candidatos ideales para la terapia con ondas de choque
Subacute or chronic calf injuries lasting over six weeks.
Athletes needing faster return-to-sport timelines.
Recurrent calf strains due to incomplete healing.
Chronic Achilles tendinopathy resistant to eccentric training.
Persistent pain, stiffness, or limited range of motion.
Active infection, malignancy, or coagulation disorders are contraindications.
Pregnancy is a contraindication.
Avoid treatment over epiphyseal plates in children.
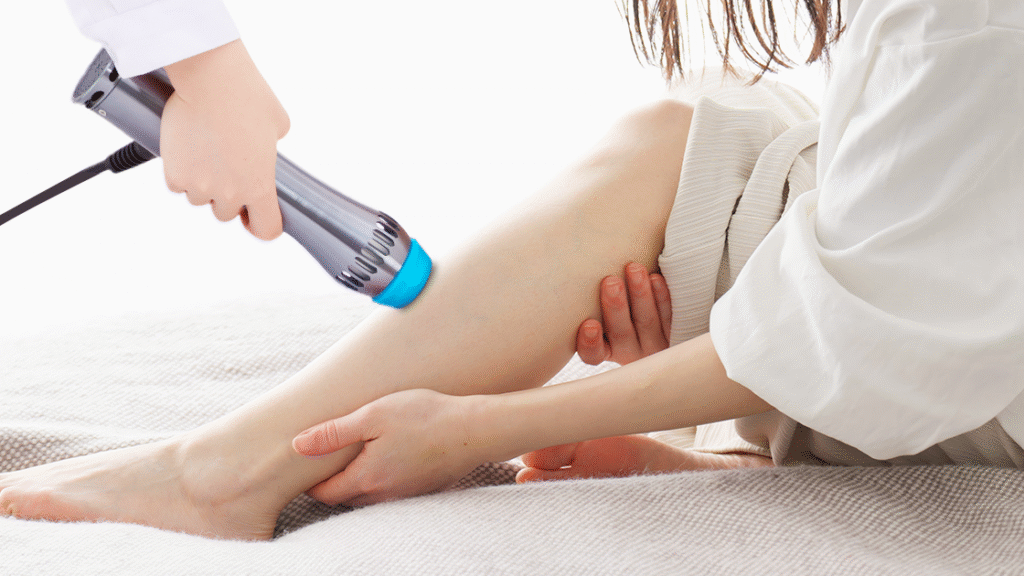
Timing: Acute and Chronic Calf Injury Applications
Treatment timing significantly influences shockwave therapy outcomes in calf injury rehabilitation. For acute injuries, ESWT typically begins 48-96 hours post-injury once initial inflammatory phase subsides, allowing mechanical stimulation without exacerbating acute inflammation. Early intervention during proliferative phase optimizes collagen remodeling and prevents excessive scar tissue formation. Chronic injuries benefit from shockwave therapy regardless of injury duration, though earlier intervention generally yields superior outcomes. Delayed-onset treatment effectively addresses long-standing tendinopathies, calcifications, and adhesions resistant to other interventions. Treatment frequency varies based on injury severity and chronicity, typically ranging from weekly sessions for four to eight weeks in acute cases to biweekly protocols extending twelve weeks for chronic conditions.
Combining Shockwave Therapy with Physical Therapy and Strengthening
Shockwave therapy achieves optimal results when integrated within comprehensive rehabilitation programs incorporating progressive loading and neuromuscular re-education. Following ESWT sessions, patients should engage in controlled eccentric strengthening exercises targeting gastrocnemius and soleus muscles to promote functional adaptation. Manual therapy techniques, including soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation, complement shockwave effects by addressing compensatory movement patterns and adjacent joint restrictions. Proprioceptive training restores neuromuscular control essential for preventing re-injury during return-to-activity progression. Timing exercise interventions relative to shockwave sessions matters; high-intensity loading should occur 48-72 hours post-treatment, allowing tissues to respond optimally to mechanical stimulation while avoiding excessive stress during acute inflammatory responses.
Expected Recovery Timelines and Milestones
Recovery trajectories following shockwave therapy vary based on injury severity, chronicity, and individual healing capacity. Grade I calf strains typically resolve within 3-4 weeks with ESWT, compared to 5-6 weeks with conventional treatment. Grade II injuries demonstrate significant improvement after 6-8 weeks of combined shockwave and rehabilitation protocols. Chronic tendinopathies show progressive symptom reduction, with patients experiencing 30-50% improvement after initial treatment series and continued gains over subsequent 3-6 months as tissue remodeling continues. Key milestones include pain reduction within 2-3 treatments, improved range of motion by week 4, and progressive strength gains throughout 8-12 week rehabilitation period. Individual variations necessitate personalized timeline adjustments based on objective functional assessments.
Evidence-Based Insights
The growing body of scientific literature examining shockwave therapy’s effectiveness provides valuable insights into treatment mechanisms, optimal protocols, and expected outcomes. This section synthesizes current research findings, expert perspectives, and important considerations for evidence-informed clinical decision-making regarding ESWT for calf injuries.
Peer-Reviewed Studies on Shockwave Therapy for Calf Injuries
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses consistently demonstrate shockwave therapy’s superiority over placebo and conventional treatments for muscle and tendon injuries. A 2023 randomized controlled trial published in the American Journal of Sports Medicine showed focused ESWT reduced recovery time for gastrocnemius strains by 38% compared to standard care. Research in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research documented significant improvements in Achilles tendon structure using ultrasound imaging following shockwave protocols, with increased tendon thickness and improved fiber organization. Multiple studies report 65-85% success rates for chronic Achilles tendinopathy treatment, with outcomes sustained at two-year follow-up evaluations. Evidence quality ranges from high-quality randomized trials to observational studies, collectively supporting ESWT integration into evidence-based practice.
Orthopedic Specialists’ Perspectives
Leading sports medicine physicians and orthopedic surgeons increasingly incorporate shockwave therapy into treatment algorithms for calf injuries based on clinical experience and research evidence. Specialists emphasize ESWT’s value as conservative intervention potentially avoiding surgical procedures for chronic tendinopathies and recalcitrant muscle injuries. Orthopedic consensus statements recommend shockwave therapy as second-line treatment following failed conservative management or as adjunctive therapy for complex cases. Experts highlight the importance of proper patient selection, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment parameters for optimal outcomes. Many specialists advocate for earlier ESWT integration rather than prolonged unsuccessful conservative treatment, preventing chronicity development and associated functional limitations that complicate rehabilitation.
Limitations, Considerations, and Safety Guidelines
While generally safe, shockwave therapy carries potential adverse effects including temporary pain exacerbation, skin redness, and localized swelling lasting 24-48 hours post-treatment. Rare complications include subcutaneous hematoma formation, particularly in patients with coagulation disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications. Treatment intensity requires careful calibration; excessive energy levels may cause tissue damage, while insufficient intensity produces subtherapeutic effects. The therapy’s effectiveness depends heavily on accurate diagnosis and anatomical targeting, necessitating qualified practitioner administration. Cost and insurance coverage limitations may restrict access for some patients. Additionally, research gaps remain regarding optimal treatment protocols for specific injury subtypes, long-term outcome data, and comparative effectiveness against emerging regenerative medicine approaches.
Practical Tips for Patients
Successful shockwave therapy outcomes depend not only on treatment administration but also on patient preparation, post-treatment care, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. This section provides actionable guidance empowering patients to maximize therapy benefits and optimize their calf injury recovery journey.
Preparing for a Shockwave Therapy Session
Wear loose, comfortable clothing for easy calf access.
Stop anti-inflammatory medications 48 hours before treatment.
Communicate pain tolerance and symptom history with your practitioner.
Light activity and gentle calf stretching may enhance treatment effectiveness.
Stay hydrated to support tissue healing.
Understand that mild discomfort during treatment is normal.
Post-Treatment Care: Maximize Your Calf Recovery at Home
Avoid intense activity for 48 hours after treatment.
Apply ice 15–20 minutes if soreness occurs, avoiding immediate icing within 6 hours.
Maintain hydration and nutrition, focusing on protein and vitamin C.
Perform gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness.
Follow prescribed home exercises, adjusting intensity as needed.
Track symptoms and functional improvements for follow-up visits.
Prioritize adequate sleep to support tissue repair and remodeling.
Monitoring Progress and When to Seek Medical Advice
Track pain, range of motion, and functional tests.
Expect gradual improvement with possible temporary setbacks.
Seek immediate care for severe pain, swelling, deformity, numbness, or inability to bear weight.
Contact providers if symptoms worsen or plateau beyond expected timelines.
Reassess regularly to adjust treatment and address complications.
Avoiding Re-Injury and Long-Term Prevention
Progress activity gradually following tissue healing.
Perform dynamic warm-ups and progressive intensity before training.
Correct biomechanical issues via gait, footwear, and movement adjustments.
Maintain consistent calf and lower limb strength training.
Schedule rest between high-intensity sessions for tissue adaptation.
Cross-train with low-impact activities to reduce stress.
Monitor early signs like tightness or discomfort and act promptly.
Summary and Takeaways
Shockwave therapy (ESWT) is an effective, evidence-based treatment for calf injury rehabilitation, targeting multiple healing pathways simultaneously. It stimulates tissue regeneration, reduces inflammation, improves blood flow, and provides medication-free pain relief, offering advantages over conventional rehab alone. ESWT is particularly effective for subacute or chronic calf strains, Achilles tendinopathy, and post-surgical recovery, with research showing faster return-to-function. Optimal results depend on integration with progressive loading, neuromuscular training, and manual therapy, alongside proper patient selection, accurate diagnosis, and treatment timing. Generally safe with minimal side effects, ESWT requires qualified practitioners and individualized protocols. Growing clinical adoption and supporting evidence highlight its role as a standard care option for challenging calf injuries. When implemented correctly, shockwave therapy helps patients achieve complete functional restoration and long-term injury resilience.
Referencias
- Vibration and pressure wave therapy for calf strains: a proposed treatment
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy treatment of painful hematoma in the calf: A case report
- Eficacia y seguridad del tratamiento con ondas de choque extracorpóreas para afecciones ortopédicas: revisión sistemática de los estudios incluidos en la base de datos PEDro
- Efectos biológicos de la terapia con ondas de choque extracorpóreas (eswt) en el tejido tendinoso
- Tratamiento con ondas de choque extracorpóreas para el dolor musculoesquelético: revisión narrativa
