Introducción
Delivery workers face unique physical challenges that put constant stress on their lower limbs. Daily walking, stair climbing, and heavy lifting strain the Achilles tendon, making chronic injuries like Achilles tendinopathy common. Terapia de ondas de choque has emerged as a non-invasive, evidence-based solution to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and promote tendon healing.
Traditional methods such as rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy may provide temporary relief but often fail to address the underlying tendon degeneration. This article explores how shockwave therapy works, its benefits for delivery workers, treatment protocols, and common misconceptions, offering a comprehensive guide for maintaining long-term Achilles tendon health.
1. Why Achilles Tendinopathy is Common in Delivery Workers
Achilles tendinopathy is prevalent among delivery workers due to the combination of repetitive stress, heavy lifting, and insufficient recovery time. Unlike casual walking or occasional stair climbing, the occupational demands placed on delivery personnel involve prolonged, repeated strain on the tendon. Over time, micro-tears and degenerative changes accumulate, leading to chronic inflammation and pain.
Understanding the occupational causes is critical for implementing effective therapies. Without addressing the underlying repetitive strain, conservative treatments may provide only temporary relief. Shockwave therapy offers a targeted approach, stimulating tissue repair directly at the cellular level and improving long-term tendon resilience.
1.1 Repetitive Strain from Walking and Climbing
Daily walking and stair climbing increase the mechanical load on the Achilles tendon. The tendon experiences high tensile stress with each step, which, over time, results in microtrauma and chronic inflammation. Continuous overloading without adequate recovery can lead to thickening of the tendon, pain, and functional limitation.
Shockwave therapy targets these damaged areas by delivering high-energy acoustic waves that penetrate deep into tendon tissue. The mechanical stimulation triggers cellular repair, enhances microcirculation, and promotes collagen remodeling, helping restore tendon elasticity. For delivery workers, this means reduced pain, improved mobility, and better tolerance for the physical demands of their job.
1.2 Heavy Lifting and Load Management
Delivery workers frequently lift and carry packages, often weighing tens of pounds, which places additional strain on the Achilles tendon. Heavy loads increase the risk of tendon micro-tears and aggravate pre-existing degenerative changes, making chronic tendinopathy more likely.
Shockwave therapy addresses these micro-injuries by mechanically stimulating fibroblasts within the tendon, promoting collagen production and realignment of fibers. Enhanced blood flow to the tendon region also accelerates healing and reduces inflammation. Incorporating shockwave therapy alongside proper lifting techniques and load management strategies helps delivery workers prevent further degeneration while maintaining occupational performance.
1.3 Sedentary Recovery and Inadequate Stretching
Despite high activity levels during work hours, delivery workers often have limited recovery time and may neglect stretching or strengthening exercises. A sedentary period following a physically demanding shift can lead to tendon stiffness and reduced flexibility, compounding injury risk.
Combining shockwave therapy with daily stretching and eccentric strengthening exercises provides a comprehensive approach. Shockwave therapy primes the tendon for tissue repair, while stretching maintains elasticity and range of motion. This combination ensures that recovery is effective, reducing recurrence risk and helping delivery workers stay pain-free throughout their shifts.
2. Understanding Terapia de ondas de choque
Shockwave therapy, or extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive technique that delivers high-energy acoustic waves to targeted tissue. It is used extensively to treat musculoskeletal conditions, including tendinopathies, plantar fasciitis, and chronic muscle pain.
The therapy works by inducing microtrauma in the affected tissue, which stimulates the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Increased blood flow, activation of fibroblasts, and collagen synthesis collectively contribute to tendon repair. ESWT differs from traditional treatments by directly addressing degenerative tissue rather than merely alleviating symptoms, making it highly effective for chronic Achilles tendinopathy.
2.1 Mechanism of Action: Tissue Repair and Blood Flow
Shockwave therapy’s efficacy lies in its ability to stimulate biological responses at the cellular level. The mechanical stress delivered by acoustic waves triggers fibroblast activation, promoting collagen synthesis and tendon remodeling. This enhances tissue strength and elasticity over time.
Additionally, shockwave therapy increases local blood flow, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to the affected tendon. This accelerated microcirculation reduces inflammation, facilitates the removal of metabolic waste, and supports tissue regeneration. For delivery workers, these physiological changes translate to faster recovery, less pain, and improved tendon function.
2.2 Types of Shockwave Therapy
There are two main types of shockwave therapy: focused and radial. Focused shockwave therapy delivers energy to a specific depth, suitable for deep-seated tendon injuries. Radial shockwave therapy disperses energy over a broader area, targeting superficial tissues and reducing localized discomfort.
For Achilles tendinopathy, focused shockwaves are often preferred due to their ability to penetrate the dense tendon structure. Selection depends on tendon thickness, injury severity, and patient tolerance. Understanding these differences allows clinicians to customize treatment for maximum effectiveness and minimal discomfort.
2.3 Safety and Proper Application
Shockwave therapy is generally safe when administered by trained professionals. Non-invasive and well-tolerated, the procedure requires proper parameter selection, including energy level, frequency, and number of pulses. Protective measures, such as padding and positioning, ensure patient comfort and safety.
Contraindications are minimal but include active infection, coagulation disorders, or severe vascular compromise. When combined with appropriate stretching, eccentric loading exercises, and load management, shockwave therapy provides a safe, effective solution for chronic Achilles tendon injuries in delivery workers.
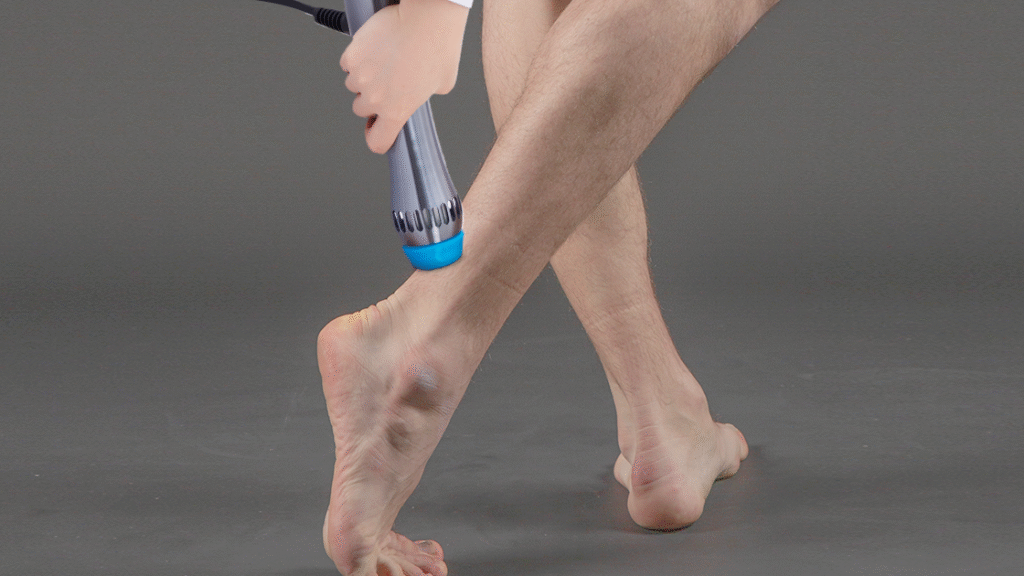
3. Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Achilles Tendinopathy
Shockwave therapy offers multiple advantages over traditional interventions, particularly for delivery workers who rely on consistent lower limb function. The therapy addresses both structural and symptomatic aspects of tendinopathy, promoting faster recovery and functional restoration.
3.1 Pain Relief and Reduced Inflammation
One of the most immediate benefits of shockwave therapy is pain relief. Acoustic waves reduce inflammation by modulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting tissue repair. Patients often experience decreased tenderness, swelling, and stiffness after several sessions.
For delivery workers, pain relief is crucial for maintaining productivity and reducing reliance on analgesic medications. By targeting the root cause of inflammation, shockwave therapy provides longer-lasting relief compared to temporary symptom-focused treatments.
3.2 Improved Tendon Elasticity and Function
Chronic tendinopathy often leads to thickened, less flexible tendons. Shockwave therapy promotes collagen remodeling, improving tendon elasticity and functional capacity. Over time, this enhances the tendon’s ability to withstand repetitive stress from walking, climbing stairs, and lifting.
Delivery workers benefit from improved mobility and reduced risk of reinjury. Enhanced tendon function supports proper biomechanics during work activities, minimizing compensatory strain on surrounding joints and muscles.
3.3 Faster Recovery Compared to Traditional Methods
Compared to conservative treatments like rest, oral anti-inflammatories, or superficial physiotherapy, shockwave therapy accelerates tendon healing. Studies show improved structural tendon integrity and functional outcomes within weeks, allowing patients to return to work sooner.
For delivery workers, a faster recovery means less downtime, fewer missed shifts, and reduced long-term complications. Integrating shockwave therapy into a comprehensive rehabilitation plan ensures both symptom relief and functional restoration.
4. Treatment Protocols for Delivery Workers
Treatment protocols for delivery workers must consider the physical demands of the occupation and chronicity of injury. Frequency, session duration, and combination with rehabilitation exercises are critical for optimal results.
4.1 Typical Session Duration and Frequency
A standard shockwave therapy session lasts 10–20 minutes, depending on tendon thickness and pain severity. Initial protocols usually involve 2–3 sessions per week over a period of 3–6 weeks. The number of pulses and energy settings are individualized based on patient response.
Regular monitoring ensures that the tendon is responding appropriately and prevents overtreatment. Delivery workers often notice pain reduction after the first few sessions, with progressive improvement in function over subsequent treatments.
4.2 Combining Therapy with Stretching and Strengthening
Shockwave therapy is most effective when combined with targeted stretching and strengthening exercises. Eccentric loading exercises for the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles improve tendon elasticity and reduce recurrence risk. Proper stretching maintains range of motion, while strengthening exercises enhance load-bearing capacity.
Additionally, occupational adjustments such as lifting techniques, footwear optimization, and pacing of deliveries complement the therapy. This multimodal approach maximizes recovery and supports long-term tendon health.
4.3 Home Care Tips
Delivery workers can enhance treatment outcomes with simple home strategies. Cold or warm compresses may reduce residual soreness, while daily stretching maintains tendon flexibility. Using supportive footwear or orthotics minimizes stress on the Achilles tendon during work hours.
Gradual reintroduction of heavy lifting and stair climbing, along with hydration and proper nutrition, supports tissue regeneration. Consistent home care reinforces clinical therapy, ensuring sustained recovery and preventing relapse.
5. Common Observations and Misconceptions
While shockwave therapy is highly effective, misconceptions persist. Some believe that one session will cure chronic tendinopathy, or that the therapy might damage the tendon. In reality, multiple sessions are typically required, and proper administration is safe and non-invasive.
Delivery workers often observe gradual improvements: reduced pain, improved tendon flexibility, and enhanced functional capacity. Understanding realistic expectations and combining therapy with rehabilitation ensures optimal outcomes and long-term tendon health.
FAQ
How many sessions are needed to see results?
Typically, 6–10 sessions are required, depending on severity and individual response.
Is shockwave therapy painful?
Most patients report only mild discomfort or tingling during treatment; topical anesthetics can be used if needed.
Can it fully replace physical therapy or medication?
Shockwave therapy is best used as part of a comprehensive rehabilitation plan, including exercises and ergonomic adjustments.
Are there risks of long-term use for delivery workers?
When properly administered, shockwave therapy is safe, non-invasive, and free from systemic side effects.
Conclusión
Shockwave therapy offers a powerful, non-invasive solution for chronic Achilles tendinopathy in delivery workers. By promoting collagen remodeling, enhancing microcirculation, and reducing inflammation, it addresses both structural damage and symptomatic pain.
When combined with targeted stretching, strengthening exercises, and occupational modifications, delivery workers can achieve faster recovery, improved tendon function, and reduced risk of recurrence. For busy delivery professionals, this therapy provides an effective pathway to regain mobility, reduce pain, and maintain long-term occupational performance.
Referencias
American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society – Achilles Tendinopathy
Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopathy – PubMed
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed
PhysioAdvisor – Shockwave Therapy
