Introduction
Thérapie par ondes de choc, also known as extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), has emerged as a popular non-invasive treatment for a variety of musculoskeletal conditions, including tendinopathies, plantar fasciitis, and chronic soft tissue injuries. While its efficacy has been documented in numerous clinical studies, the success of shockwave therapy depends not only on the technology itself but also on how well patients understand the procedure. Patient education plays a crucial role in managing expectations, enhancing treatment adherence, and ensuring safety. This article explores the importance of educating patients prior to shockwave therapy, discussing key topics to cover, methods of effective communication, and how education contributes to overall clinical outcomes.
1. Why Patient Education Matters
Educating patients is not just an administrative step; it directly impacts treatment effectiveness and patient satisfaction. Proper education allows patients to understand the rationale behind the therapy, anticipate potential sensations during treatment, and actively participate in their recovery. This section explores three primary reasons why patient education is essential.
1.1 Improving Treatment Outcomes
A patient’s understanding of shockwave therapy directly affects compliance and engagement. When patients are well-informed about the mechanism of action, expected outcomes, and the importance of adhering to treatment schedules, they are more likely to complete recommended sessions and follow post-treatment guidelines. Studies indicate that patients who comprehend the purpose and benefits of therapy report higher satisfaction and demonstrate improved functional recovery. Moreover, knowledge about the biological effects, such as stimulation of collagen synthesis and enhanced microcirculation, helps patients appreciate the gradual nature of healing, reducing premature disappointment.
1.2 Reducing Patient Anxiety and Fear
Many patients experience apprehension before undergoing shockwave therapy due to unfamiliarity with the procedure or fear of pain. Educating patients about what to expect—such as mild tingling, warmth, or a sensation of pressure at the treatment site—can significantly alleviate anxiety. Understanding the safety profile and non-invasive nature of shockwave therapy allows patients to feel more comfortable and cooperative during sessions. Reducing fear also minimizes involuntary muscle tension, which can otherwise interfere with energy transmission and reduce treatment efficacy.
1.3 Enhancing Safety and Compliance
Proper patient education ensures safety by informing patients about contraindications, potential side effects, and precautions. Patients are advised to disclose underlying conditions such as coagulation disorders, infections, or malignancies, which could affect treatment eligibility. Additionally, understanding pre- and post-treatment care—like avoiding anti-inflammatory medications or refraining from intense physical activity immediately after therapy—supports adherence and prevents complications. Educated patients are more likely to follow recommendations consistently, directly influencing both short-term and long-term therapeutic outcomes.
2. Core Topics to Cover in Patient Education
Effective patient education involves structured communication covering multiple aspects of shockwave therapy. From explaining the mechanism to discussing post-treatment care, each topic ensures patients are adequately prepared for the procedure.
2.1 What is Shockwave Therapy
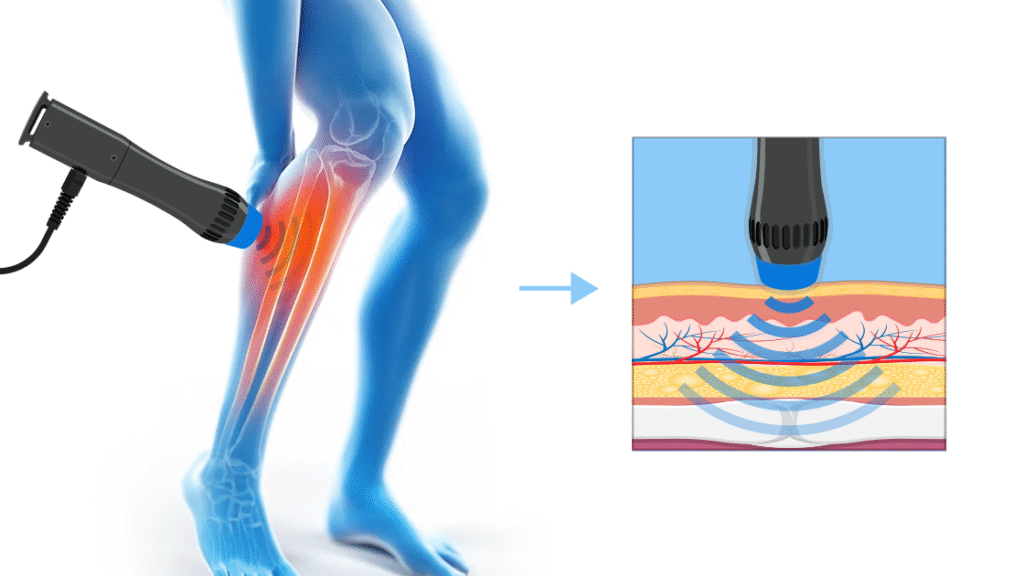
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive procedure that delivers high-energy acoustic waves to targeted tissues. These waves stimulate cellular responses, promoting angiogenesis, collagen remodeling, and tissue regeneration. It is commonly used to treat chronic tendinopathies, plantar fasciitis, myofascial pain, and musculoskeletal disorders. For patients, understanding that the therapy is designed to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, rather than providing instant relief, helps set realistic expectations and promotes engagement throughout the rehabilitation process.
2.2 Expected Benefits and Realistic Outcomes
Patient education should clearly outline the anticipated benefits of shockwave therapy while also emphasizing that results may take several weeks. Benefits often include reduced pain, improved mobility, and accelerated tissue healing. Realistic outcome discussions prevent misunderstandings and help patients appreciate gradual improvements. Sharing evidence from clinical studies, including success rates and typical timelines for functional recovery, reinforces trust and encourages adherence to follow-up sessions, ultimately supporting long-term therapeutic success.
2.3 Treatment Procedure and Sensations
Explaining the treatment procedure in detail prepares patients for what they will experience. Sessions usually last 10–20 minutes, depending on the condition and targeted area. Patients may feel a mild tingling, warmth, or pressure as acoustic waves penetrate the tissue. Clarifying these sensations reduces anxiety and prevents misinterpretation of normal treatment reactions as complications. Educating patients about the non-invasive nature of the procedure reinforces confidence and encourages relaxation, which is essential for optimal energy transmission and therapeutic effectiveness.
2.4 Pre-Treatment and Post-Treatment Guidelines
Patients should be instructed on behaviors that optimize therapy effectiveness and minimize adverse effects. Pre-treatment guidance may include avoiding anti-inflammatory medications that could interfere with tissue response. Post-treatment care often involves gentle activity modification, ice application, or light stretching as recommended. Understanding these instructions prevents complications and supports tissue repair. Well-informed patients are also more likely to communicate any unusual symptoms promptly, allowing clinicians to adjust treatment protocols safely.
3. Tools and Methods for Effective Patient Education
Delivering patient education requires thoughtful selection of methods and tools that suit different learning styles. Combining verbal explanations with visual aids and written materials enhances comprehension and retention.
3.1 Verbal Explanation and Consultation
Face-to-face consultations allow clinicians to assess patient understanding, answer questions, and provide personalized guidance. Clinicians can explain the procedure, expected outcomes, and potential side effects, adjusting their communication based on patient concerns. Interaction encourages engagement and ensures that misconceptions are addressed immediately, fostering a trusting therapeutic relationship that improves adherence and treatment success.
3.2 Educational Brochures and Digital Resources
Supplementing verbal explanations with brochures, infographics, or digital videos reinforces understanding. Visual aids can simplify complex concepts, such as tissue regeneration or acoustic wave mechanics. Providing take-home materials allows patients to revisit the information at their own pace, reinforcing key points and promoting compliance with pre- and post-treatment instructions.
3.3 Demonstrations and Visual Aids
Live demonstrations or illustrative diagrams showing device operation and targeted treatment areas help patients visualize the process. Simple models of tissue layers and shockwave penetration can clarify how therapy stimulates healing. Visual learning reduces fear of the unknown and improves patient confidence, which is essential for optimal engagement and relaxation during sessions.
3.4 FAQs and Common Misconceptions
Developing a FAQ section addressing common patient concerns—such as anticipated pain, session frequency, or immediate relief expectations—prevents misunderstandings. Misconceptions like “shockwave therapy always hurts” or “it works instantly” can be corrected. Clear, accurate information empowers patients to participate actively in their care and enhances overall treatment satisfaction.
4. Role of Patient Education in Clinic Success
Educating patients benefits not only individual outcomes but also clinic efficiency, patient retention, and professional reputation. Clinics that prioritize education see improved treatment adherence, fewer cancellations, and higher satisfaction scores.
4.1 Increasing Patient Satisfaction
Patients who understand the therapy process and realistic outcomes report higher satisfaction. Clear communication fosters trust and reduces anxiety, which translates into positive experiences. Satisfied patients are more likely to provide favorable reviews and recommend the clinic, strengthening its reputation in the competitive healthcare market.
4.2 Enhancing Treatment Efficiency
When patients follow pre- and post-treatment instructions accurately, clinicians can achieve consistent energy delivery and predictable outcomes. Education reduces treatment interruptions, late cancellations, and miscommunication, optimizing resource utilization. Clinics benefit from smoother workflow and enhanced treatment success rates, allowing practitioners to serve more patients effectively.
4.3 Building Trust and Retention
Effective education establishes a strong patient-provider relationship. Patients who feel informed are more confident in their care plan and more likely to adhere to follow-up sessions. This trust encourages long-term engagement, retention, and ongoing referrals, which are crucial for clinic growth and professional credibility.
FAQ
Will shockwave therapy be painful?
Most patients feel mild tingling or pressure, which is normal. Discomfort is minimal and usually well-tolerated.
How many sessions are needed?
Depending on the condition, 3–6 weekly sessions are typical. Individual response may vary.
What should I do before treatment?
Avoid anti-inflammatory medications unless directed, and inform the clinician of any medical conditions.
How soon can I return to normal activity?
Light activity is often allowed immediately; heavy activity should follow clinician guidance.
Who should avoid shockwave therapy?
Patients with bleeding disorders, infections, or malignancy at the treatment site should not undergo ESWT.
Conclusion
Patient education is an integral component of successful shockwave therapy. By informing patients about the procedure, expected outcomes, sensations, and pre- and post-treatment guidelines, clinicians enhance treatment adherence, reduce anxiety, and improve overall satisfaction. Educated patients are empowered to actively participate in their care, ensuring safety, optimizing results, and building trust. Clinics that prioritize patient education not only achieve better clinical outcomes but also strengthen patient retention, satisfaction, and professional reputation.
Références
Venn Healthcare. Importance of Patient Education Before Shockwave Therapy.
https://www.vennhealthcare.com/v-actor-vibration-therapy-how-it-enhances-shockwave-treatment/
RegenOMedix. Shockwave Therapy Category.
https://regenomedix.com/category/shockwave-therapy/
Storz Medical. Shockwave Therapy Overview.
