Introduction: Safeguarding Young Athletes’ Future
Youth sports participation has reached unprecedented levels, with millions of children and adolescents engaging in competitive athletics annually. While physical activity promotes healthy development, the intensification of training regimens and early sport specialization have contributed to alarming increases in pediatric sports injuries. The intersection of immature musculoskeletal systems, growth-related vulnerabilities, and repetitive stress creates unique challenges requiring specialized intervention approaches that prioritize long-term health over short-term athletic performance.
Why Pediatric Sports Injuries Require Special Attention
- Children’s musculoskeletal systems are still developing, making them more vulnerable to injury.
- Active growth plates (physes) are susceptible to damage from repetitive stress and acute trauma.
- Growth plate injuries, if mishandled, can lead to limb length discrepancies or angular deformities.
- Bones grow faster than tendons and ligaments during growth spurts, increasing injury risk.
- Immature neuromuscular coordination elevates susceptibility to both acute and overuse injuries.
- Psychological factors, such as fear of disappointing coaches or reluctance to report pain, can delay injury detection.
Risks of Long-Term Damage from Untreated Injuries
- Untreated overuse injuries can lead to chronic tendinopathies with permanent tendon degeneration.
- Growth plate injuries may cause skeletal deformities affecting limb alignment and joint biomechanics.
- Persistent inflammation accelerates cartilage degradation and promotes joint stiffness.
- Compensatory movement patterns can create secondary injuries and maladaptive neuromuscular habits.
- Chronic pain and functional limitations can reduce physical activity, impact athletic aspirations, and harm psychological development.
How Innovative, Non-Invasive Therapies Are Changing Recovery
Recent advances in regenerative medicine have transformed pediatric sports medicine by providing effective, non-surgical treatments that target tissue pathology while minimizing risks. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a breakthrough approach that stimulates the body’s natural healing mechanisms without drugs or invasive procedures. By applying acoustic pressure waves, ESWT triggers cellular mechanotransduction, enhancing metabolism, promoting angiogenesis, supporting tissue regeneration, and modulating pain. Unlike traditional treatments that rely on prolonged rest, anti-inflammatory medications, or surgery, shockwave therapy accelerates recovery while enabling age-appropriate activity. Its non-invasive nature avoids surgical risks, anesthesia, and lengthy downtime, protecting children’s musculoskeletal, academic, and social development during critical growth periods.
Comprendre la thérapie par ondes de choc
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy has evolved from its origins in urological lithotripsy to become a sophisticated treatment modality for diverse musculoskeletal conditions. Understanding the fundamental principles, biological mechanisms, and clinical applications of this technology provides essential context for appreciating its role in pediatric sports medicine.
What Shockwave Therapy Is and How It Works
Utilisations de la thérapie par ondes de choc ondes acoustiques de haute énergie—rapid pressure pulses with unique physical properties—that create mechanical stress and microtrauma at the cellular level. These waves feature nonlinearity, high peak pressure followed by low tensile amplitude, rapid rise time, short duration (~10 microseconds), and a broad frequency spectrum (0–20 MHz). Applied to injured tissues, shockwaves deliver focused mechanical energy to precise depths without penetrating the skin or harming superficial structures. There are two main types: focused shockwaves, which concentrate energy at a small focal point deep in tissue, and radial shockwaves, which disperse energy over larger surface areas with shallower penetration. Treatment protocols typically involve multiple pulses per brief session, repeated weekly. This controlled tissue stimulation triggers mechanotransduction, converting mechanical signals into biochemical responses that activate cellular repair and enhance healing.
Biological Mechanisms: Tissue Repair and Pain Reduction
The therapeutic effects of shockwave therapy arise from complex biological responses triggered when acoustic energy interacts with tissues. Acting as a mechanical stimulus, extracorporeal shockwave therapy promotes healing via mechanotransduction, inducing tissue regeneration, wound repair, angiogenesis, bone remodeling, and anti-inflammation. At the cellular level, shockwaves activate mechanoreceptors, initiating signaling cascades that increase growth factors such as VEGF, TGF-β, and BMPs. These factors stimulate fibroblast proliferation, collagen synthesis, and extracellular matrix remodeling, essential for tendon and ligament repair. Shockwaves also enhance neovascularization by promoting endothelial cell proliferation, improving perfusion and nutrient delivery to ischemic tissue. Pain reduction occurs through hyperstimulation analgesia, substance P depletion, and modulation of inflammatory cytokines, reducing pain signal transmission and local inflammation. Collectively, these mechanisms accelerate tissue healing, restore function, and alleviate pain in injured musculoskeletal structures.
Advantages Over Traditional Pediatric Injury Treatments
- Non-invasive, avoiding surgical risks and anesthesia.
- It reduces the need for prolonged rest, allowing children to maintain age-appropriate activity.
- Pain relief occurs without reliance on medications and their potential side effects.
- Treatment accelerates tissue healing and regeneration compared to conventional therapies.
- Focused energy delivery targets injured tissues precisely without harming surrounding structures.
- It promotes long-term injury prevention by stimulating repair and strengthening tissues.
- Recovery periods are shorter, minimizing disruption to academic and social development.
- Suitable for chronic, acute, and overuse injuries that may respond poorly to traditional methods.
Common Pediatric Sports Injuries Treated with Shockwave Therapy
Young athletes experience distinctive injury patterns reflecting their developmental stage, sport participation patterns, and unique anatomical vulnerabilities. Shockwave therapy has demonstrated efficacy across various pediatric musculoskeletal conditions, offering targeted intervention for both overuse and acute injuries.
Overuse Injuries: Tendinitis, Osgood-Schlatter, Sever’s Disease
Overuse injuries are the most common in youth sports, caused by repetitive stress exceeding tissue repair capacity. Patellar tendinitis, or jumper’s knee, affects young athletes in jumping sports, causing anterior knee pain and limited function. Osgood-Schlatter disease involves painful inflammation of the tibial tuberosity apophysis during adolescent growth spurts, while Sever’s disease (calcaneal apophysitis) causes heel pain from traction on the Achilles tendon growth plate. These apophyseal injuries involve inflammation, microavulsion, and potential growth plate disturbance if untreated. Traditional rest-based treatments are often ineffective for active youth. Focused extracorporeal shockwave therapy addresses the underlying pathology by stimulating tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and promoting remodeling at the affected growth plate interfaces, facilitating early return to sport and preventing long-term complications.
Acute Injuries: Sprains, Muscle Strains, Ligament Tears
Acute pediatric sports injuries result from collisions, falls, or sudden directional changes exceeding tissue tolerance. Ankle sprains of the lateral ligament complex are most common, with incomplete healing predisposing to chronic instability. Muscle strains, often in hamstrings, quadriceps, or gastrocnemius, can form scar tissue that reduces elasticity. Partial ligament tears, such as ACL injuries, require optimal repair to maintain joint stability. Traditional RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) management may not fully restore function. Shockwave therapy enhances healing by aligning collagen fibers during scar maturation, reducing adhesion formation, accelerating inflammation resolution, and improving tissue tensile strength. These effects support functional recovery, minimize re-injury risk, and produce mechanically superior repair compared to passive healing, enabling safer return to activity for young athletes.
Chronic or Recurring Conditions: Growth Plate Stress, Persistent Pain
Some pediatric injuries progress into chronic conditions with persistent symptoms despite conventional treatment, often involving growth plate stress. Chronic apophysitis may affect sites like the medial epicondyle, olecranon, or iliac crest, resulting from cumulative microtrauma. Untreated cases risk permanent growth plate damage or complete avulsion requiring surgery. Persistent pain and degenerative tissue changes, including neovascularization, nerve ingrowth, calcification, and fibrosis, perpetuate dysfunction. Shockwave therapy is effective for these chronic scenarios by disrupting pathological neovascular-nerve complexes, stimulating regeneration of healthy tissue, reversing maladaptive remodeling, and normalizing pain processing. This promotes tissue repair, restores biomechanical function, and enables athletes to return to activity without compensatory movement patterns, addressing both symptoms and underlying pathology.
How Shockwave Therapy Prevents Long-Term Damage in Each Condition
Shockwave therapy prevents long-term damage by altering injury healing trajectories toward optimal recovery. In overuse apophyseal injuries, it accelerates inflammation resolution, promotes organized collagen deposition, and supports normal growth plate maturation, avoiding premature closure. For acute injuries, it enhances primary healing, optimizes collagen fiber orientation, reduces fibrosis and adhesion, and restores tissue architecture, minimizing functional deficits. In chronic conditions, shockwave therapy eliminates degenerative tissue, stimulates regeneration of healthy structures, modulates nerve endings to reduce pain, and restores biomechanics. This comprehensive approach addresses not only current symptoms but also underlying pathological processes, preventing permanent damage, improving tissue quality, and enabling safe return to sports without compensatory patterns.
Clinical Benefits for Young Athletes
The application of shockwave therapy in pediatric sports medicine yields multifaceted benefits that extend beyond the treated injury to influence overall athletic development, psychological wellbeing, and long-term musculoskeletal health. Understanding these diverse benefits contextualizes the therapy’s value within comprehensive youth athlete care.
Accelerated Healing and Tissue Regeneration
Shockwave therapy accelerates healing by enhancing cellular and biochemical repair processes. Mechanotransduction stimulates fibroblast and tenocyte proliferation through activation of mitogenic pathways. Growth factors such as PDGF, IGF, and TGF-β increase, creating an optimal environment for tissue synthesis and regeneration. Enhanced mitochondrial function raises ATP production, fueling energy-intensive repair mechanisms. Neovascularization improves oxygen and nutrient delivery while clearing metabolic waste. Organized collagen deposition replaces disorganized scar tissue, producing stronger, more functional structures. Clinical studies show recovery time reductions of 30–50% compared with conventional care. This acceleration allows young athletes to return to training sooner while achieving superior tissue quality—particularly valuable during competitive seasons when extended downtime could impede skill development and athletic progression.
Pain Reduction Without Medications or Invasive Procedures
Shockwave therapy provides effective, drug-free pain relief through multiple biological and neurological mechanisms. Immediate analgesia occurs via hyperstimulation, where intense sensory input temporarily overrides pain signaling. Substance P depletion further reduces nociceptive transmission, diminishing pain perception over time. Pathological neovascular-nerve complexes common in chronic tendinopathies are disrupted, eliminating persistent pain sources. Anti-inflammatory effects lower cytokine activity, reducing local irritation and swelling. As tissue healing progresses, restored homeostasis supports sustained pain reduction without medication. Avoiding pharmacological agents eliminates risks associated with NSAID use—such as impaired bone healing or gastrointestinal effects—while the non-invasive nature removes anesthesia and procedural anxiety concerns. These combined effects provide safe, lasting relief for pediatric patients, supporting continued physical activity and psychological well-being throughout recovery.
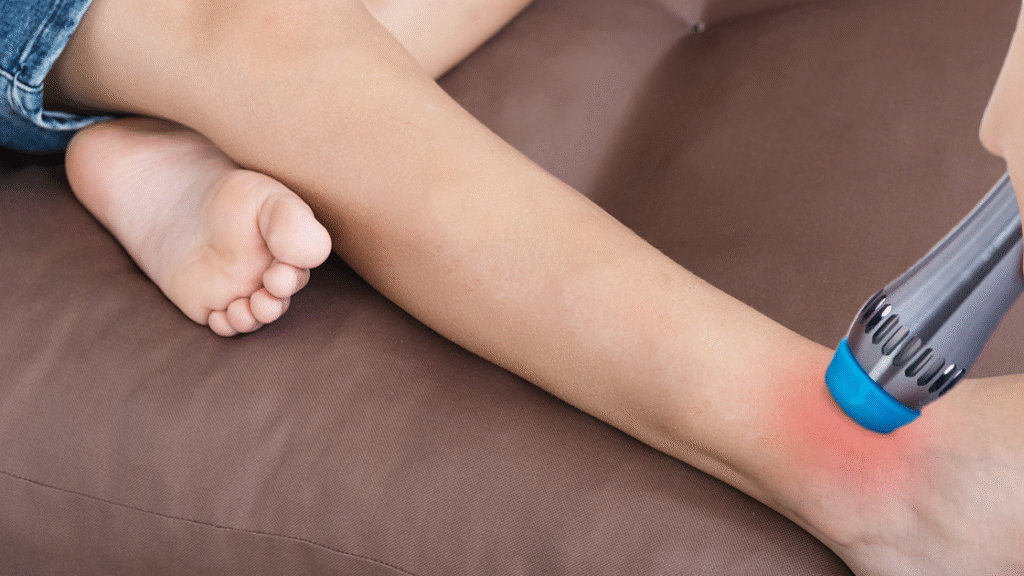
Improved Mobility and Athletic Performance
Shockwave therapy restores and enhances functional mobility, often improving performance beyond pre-injury levels. As inflammation subsides and fibrosis resolves, range of motion increases and pain-free movement returns. Normalized muscle activation restores coordination and strength, while improved proprioception enhances balance and control. Early reloading stimulates muscle hypertrophy and neuromuscular adaptation, accelerating strength recovery. Enhanced vascularization boosts oxygen delivery, improving endurance and tissue resilience. Restored biomechanics eliminate compensatory patterns, increasing efficiency and reducing energy expenditure during motion. Many young athletes report feeling stronger and more stable after therapy, reflecting optimal tissue remodeling and maintained conditioning from continued modified training. These cumulative effects extend beyond recovery, contributing to long-term athletic improvement through superior tissue integrity and functional performance.
Reduced Risk of Recurrence and Long-Term Damage
Shockwave therapy reduces recurrence risk and protects long-term musculoskeletal health by promoting superior tissue regeneration. The therapy improves collagen fiber alignment, mechanical strength, and integration with surrounding structures. It eliminates degenerative tissue and abnormal neovascularization that can trigger future injuries. Restoring normal architecture corrects biomechanical imbalances, preventing abnormal stress accumulation. Early controlled loading strengthens tissues beyond pre-injury levels, while avoiding immobilization prevents muscle atrophy and deconditioning. Growth plate injuries treated early with shockwave therapy heal completely, preventing premature closure or deformity. This proactive approach not only resolves current injury but also reduces susceptibility to future damage, supporting continued athletic participation and long-term functional stability in growing athletes.
Supporting Recovery with Lifestyle and Preventive Strategies
While shockwave therapy provides powerful direct therapeutic effects, optimal outcomes require integration within comprehensive treatment plans addressing multiple factors influencing healing and injury prevention. Supporting lifestyle modifications and preventive strategies create synergistic effects that maximize recovery and minimize future injury risk.
Nutrition and Hydration for Healing and Growth
Optimal nutrition supports the elevated metabolic demands of tissue repair stimulated by shockwave therapy. Adequate protein intake (1.2–1.6 g/kg/day) provides amino acids for collagen synthesis and muscle regeneration. Vitamin C aids collagen hydroxylation, while vitamin D and calcium strengthen bone integrity—critical during growth and apophyseal injury recovery. Omega-3 fatty acids exert anti-inflammatory effects complementing therapy-induced healing. Antioxidants such as vitamins E and A protect tissues from oxidative stress, while zinc and copper serve as enzymatic cofactors for repair. Sufficient carbohydrates supply energy for metabolically active processes, and hydration ensures perfusion, nutrient delivery, and waste removal. Together, these factors create the biochemical environment necessary for efficient cellular activity, enabling shockwave therapy to achieve maximal regenerative outcomes and sustain healthy growth in young athletes.
Stretching, Strengthening, and Conditioning Programs
Progressive rehabilitation programs enhance the regenerative effects of shockwave therapy through controlled mechanical loading. Early gentle range-of-motion exercises prevent adhesions and maintain mobility. Gradual stretching restores flexibility, while progressive resistance training promotes collagen alignment, rebuilds strength, and improves tissue mechanics. Proprioceptive and balance exercises restore neuromuscular control, reducing reinjury risk. Sport-specific drills are reintroduced gradually to maintain skills and confidence during recovery. Core stability and kinetic-chain strengthening correct biomechanical imbalances that contributed to the original injury. Functional movement assessments identify residual deficits requiring continued focus. This systematic, progressive loading approach supports tissue adaptation, reinforces structural integrity, and enables safe return to full athletic participation while optimizing the biological benefits initiated by shockwave therapy.
Rest, Sleep, and Recovery Monitoring
Despite enabling continued activity, shockwave therapy outcomes depend on adequate recovery and rest. Structured training modifications preserve conditioning while protecting healing tissues from re-injury. Deep sleep is essential for growth hormone release and cellular repair, with adolescents requiring 8–10 hours nightly. Scheduled rest days prevent cumulative fatigue and overtraining. Active recovery, such as low-intensity movement, enhances circulation and tissue metabolism. Monitoring training load, pain levels, and functional progress ensures balanced recovery pacing. Objective measures—such as pain scales or imaging—guide safe advancement. Coordinated communication among athletes, parents, coaches, and clinicians helps align healing priorities with performance goals. This integrated approach ensures optimal recovery, sustained conditioning, and long-term musculoskeletal health.
Educating on Safe Sports Practices to Minimize Long-Term Injury Risk
Education is critical to reducing injury risk and promoting a culture of safety in youth sports. Athletes learn proper technique and body mechanics to distribute forces evenly and avoid overloading tissues. Dynamic warm-ups and gradual intensity increases prepare muscles and joints for activity. Cool-down routines aid recovery and waste clearance. Correctly fitted equipment—especially footwear—reduces external risk factors. Training volume and intensity must progress gradually, particularly during growth spurts. Encouraging multisport participation and structured rest periods prevents overuse injuries. Early recognition and reporting of discomfort prevent minor issues from becoming chronic. Educating parents and coaches fosters realistic expectations, prompt response to injury signs, and prioritization of long-term health over short-term performance outcomes.
Real-World Outcomes and Patient Success Stories
Clinical evidence and patient experiences provide essential validation of shockwave therapy’s efficacy and safety in pediatric populations, offering concrete examples of how this technology translates from theoretical mechanisms to meaningful improvements in young athletes’ lives.
Case Studies Demonstrating Long-Term Injury Prevention
Clinical cases illustrate how shockwave therapy prevents chronic complications and restores full function in young athletes. A 14-year-old soccer player with refractory Osgood-Schlatter disease achieved complete pain resolution after four weekly sessions, maintaining symptom-free performance and normal tibial growth at two-year follow-up. A 16-year-old pitcher with chronic medial epicondyle apophysitis avoided growth plate closure after shockwave therapy and biomechanical correction, returning to competition without recurrence. A 12-year-old gymnast with bilateral Sever’s disease resumed training pain-free within three weeks, demonstrating normal heel development at follow-up. Across cases, therapy accelerated recovery, eliminated chronic pain risk, and preserved normal skeletal maturation. These examples underscore shockwave therapy’s preventive capacity—addressing not only immediate symptoms but also mitigating the long-term deformities, surgical interventions, and functional losses often seen with inadequately managed pediatric sports injuries.
Testimonials from Parents and Coaches
Parent and coach feedback highlights the real-world benefits of shockwave therapy beyond clinical outcomes. Families value a non-surgical, drug-free treatment that relieves pain without disrupting school or sports participation. Children tolerate sessions well, with minimal discomfort and no downtime, improving compliance. Parents report reduced stress and greater optimism as their children recover quickly without medication concerns. Coaches appreciate earlier returns to play, lower recurrence rates, and improved awareness of injury prevention through education accompanying treatment. Athletes describe increased confidence, restored motivation, and a renewed sense of physical capability. The therapy’s non-invasive, efficient nature fosters positive psychological and social outcomes, reducing isolation and frustration common in prolonged recovery. Collectively, these testimonials emphasize shockwave therapy’s holistic impact—enhancing physical healing, emotional wellbeing, and the overall athletic experience for young patients and their support networks.
Evidence-Based Research Supporting Pediatric Shockwave Therapy
Emerging research supports shockwave therapy as a safe and effective intervention for pediatric musculoskeletal injuries. Clinical trials report significant pain reduction, faster healing, and earlier return to sport compared to standard care. Studies of apophyseal and overuse conditions demonstrate improvements within one to three months with minimal treatment sessions. Safety analyses show negligible adverse effects, typically transient soreness, and no evidence of growth plate disturbance or developmental impact. Systematic reviews conclude that shockwave therapy represents a viable, evidence-based option for pediatric sports injuries when appropriately applied. Its non-invasive nature and minimal recovery time align with the unique needs of growing athletes. Ongoing research continues refining optimal treatment parameters, strengthening clinical confidence and guiding future best-practice recommendations for pediatric sports medicine applications.
Conclusion: Protecting Young Athletes with Science-Backed, Non-Invasive Care
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy marks a major advancement in pediatric sports medicine by promoting safe, effective healing while safeguarding long-term musculoskeletal health. Unlike traditional treatments requiring rest, medication, or surgery, it accelerates recovery, reduces pain naturally, and restores superior tissue quality without disrupting growth. Through mechanotransduction, shockwave therapy activates biological repair—stimulating angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, and anti-inflammatory responses—addressing injury causes rather than symptoms. Its integration into holistic care plans combining nutrition, rehabilitation, and education enhances recovery and prevents recurrence. Research confirms strong safety and efficacy, positioning it as a leading non-invasive option for common youth sports injuries. By enabling continued healthy participation and reducing chronic damage, shockwave therapy empowers young athletes to heal fully, grow stronger, and pursue their athletic goals safely—representing the future of science-driven, preventive pediatric sports medicine.
Références
- Focused extracorporeal shockwave therapy for youth sports-related apophyseal injuries: case series
- Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for orthopedic conditions: a systematic review on studies listed in the PEDro database
- Age-related changes in mechanical properties of the Achilles tendon
- Mécanismes de la thérapie extracorporelle par ondes de choc dans la médecine régénérative musculo-squelettique
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Calcifying Tendonitis of the Rotator Cuff
