Lower back pain affects millions of people worldwide, significantly impacting quality of life and daily functioning. While traditional treatments often provide temporary relief, innovative approaches like shockwave therapy are revolutionizing how we address chronic musculoskeletal conditions. This comprehensive guide explores the science, benefits, and clinical applications of shockwave therapy for managing lower back pain and spinal stiffness.
Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Shockwave Therapy in Lower Back Pain Management
The prevalence of lower back pain continues to rise globally, creating an urgent need for effective, non-invasive treatment modalities. Traditional approaches, while beneficial for some patients, often fall short in providing long-term relief for chronic conditions. This gap in conventional treatment has led healthcare professionals to explore alternative therapeutic interventions, with shockwave therapy emerging as a promising solution.
What Is Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain, medically termed lumbar pain or lumbago, represents a complex musculoskeletal disorder affecting the lumbar spine region. This condition encompasses various pathophysiological processes, including inflammatory responses, nociceptive sensitization, and biomechanical dysfunction. Chronic lower back pain, persisting beyond twelve weeks, involves neuroplastic changes in pain processing pathways, making traditional analgesic approaches less effective. The etiology often includes degenerative disc disease, facet joint arthropathy, myofascial trigger points, and sacroiliac joint dysfunction, requiring comprehensive therapeutic interventions.
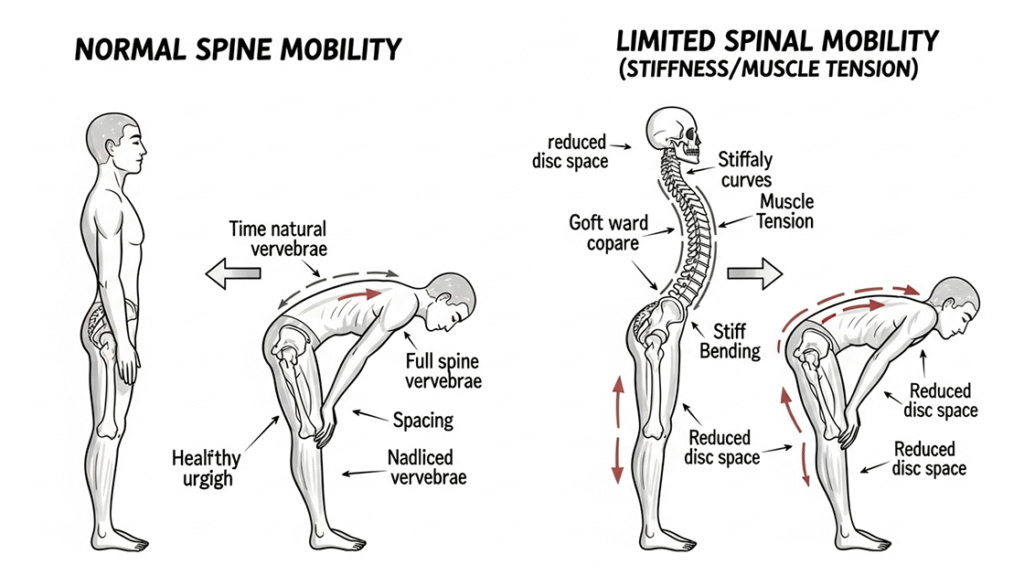
What Is Spinal Stiffness and Its Impact on Mobility?
Spinal stiffness, or vertebral rigidity, manifests as restricted range of motion in spinal segments due to various pathological processes. This condition involves decreased viscoelastic properties of perivertebral tissues, including ligamentous structures, paraspinal musculature, and fascial planes. Biomechanically, spinal stiffness results from increased muscle tension, fascial restrictions, and altered proprioceptive feedback mechanisms. The consequences include compensatory movement patterns, reduced functional capacity, and progressive deterioration of spinal health. Advanced cases may develop into ankylosing conditions, severely limiting daily activities and occupational performance.
Why Traditional Treatments Often Fall Short for Lower Back Pain
Conventional therapeutic modalities, including pharmacological interventions and passive physical therapy, often provide only symptomatic relief without addressing underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may cause gastrointestinal complications and cardiovascular risks with prolonged use. Opioid analgesics present significant addiction potential and tolerance development. Manual therapy techniques, while beneficial, require frequent sessions and may not penetrate deep tissue layers effectively. These limitations necessitate innovative treatment approaches that target cellular regeneration, tissue remodeling, and neuroplasticity restoration for sustainable pain management outcomes.
Introduction to Shockwave Therapy: A Non-invasive Treatment Approach
Thérapie extracorporelle par ondes de choc (ESWT) represents an advanced non-invasive therapeutic modality utilizing high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate tissue repair and pain reduction. This technology, originally developed for urological lithotripsy, has evolved into a sophisticated treatment for musculoskeletal disorders. Shockwave therapy delivers controlled mechanical energy to targeted tissues, initiating biological responses including neovascularization, collagen synthesis, and neuroplastic modulation. The treatment offers significant advantages over invasive procedures, including minimal side effects, outpatient administration, and rapid recovery times, making it an attractive option for chronic pain management.
The Science Behind Shockwave Therapy and Its Effectiveness for Lower Back Pain
Understanding the scientific foundation of shockwave therapy is crucial for appreciating its therapeutic potential in managing lower back pain. The technology’s effectiveness stems from its ability to generate specific acoustic wave patterns that interact with biological tissues at the cellular and molecular levels, triggering cascades of healing responses.
How Shockwave Therapy Works: The Basics of Acoustic Waves
Shockwave therapy generates high-amplitude pressure waves with characteristic steep rise times and short durations, typically lasting microseconds. These acoustic waves possess unique physical properties, including high peak pressures exceeding 100 megapascals and rapid energy dissipation patterns. The waves propagate through tissues with minimal energy loss until reaching interfaces between materials of different acoustic impedances. Upon impact, the waves create cavitation bubbles, microstreaming effects, and mechanical stress concentrations. This acoustic-mechanical coupling initiates cellular signaling cascades, membrane permeabilization, and mechanotransduction pathways essential for therapeutic effects.
Mechanisms of Action: How Shockwaves Target Pain and Stiffness
The therapeutic mechanisms of shockwave therapy involve multiple biological pathways affecting pain perception and tissue mechanics. Acoustic waves stimulate mechanosensitive ion channels, particularly calcium and potassium channels, altering neuronal excitability and pain transmission. The therapy induces substance P depletion in nerve terminals, reducing nociceptive signaling intensity. Additionally, shockwaves trigger release of endogenous opioids, including β-endorphins and enkephalins, providing natural analgesic effects. For stiffness reduction, the mechanical energy disrupts pathological cross-linkages in collagen fibers, improves tissue extensibility, and enhances fascial mobility through myofascial release mechanisms.
Shockwave Therapy’s Effect on Tissue Repair and Inflammation
Shockwave therapy demonstrates potent effects on tissue regeneration and inflammatory modulation through various molecular mechanisms. The treatment upregulates expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), promoting angiogenesis and improving tissue perfusion. Shockwaves stimulate proliferation of tenocytes, fibroblasts, and osteoblasts, enhancing extracellular matrix synthesis and tissue remodeling. The therapy modulates inflammatory cascades by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1β, while promoting anti-inflammatory mediators. These combined effects accelerate healing processes, reduce chronic inflammation, and restore normal tissue architecture in affected spinal structures.
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Managing Lower Back Pain
The therapeutic advantages of shockwave therapy extend beyond simple pain relief, offering comprehensive benefits that address multiple aspects of lower back dysfunction. These benefits make it an increasingly popular choice among healthcare providers and patients seeking effective, non-pharmacological treatment options.
Immediate Pain Relief and Reduced Inflammation
Shockwave therapy provides rapid analgesic effects through multiple neurophysiological mechanisms, offering immediate relief for acute pain episodes. The treatment activates descending inhibitory pathways, including the periaqueductal gray matter and rostral ventromedial medulla, suppressing nociceptive transmission at spinal levels. Acoustic waves create temporary hyperstimulation analgesia, overwhelming pain receptors and providing immediate symptomatic relief. Simultaneously, the therapy reduces inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, indicating systemic anti-inflammatory effects. These immediate benefits allow patients to engage more effectively in rehabilitation activities and improve functional outcomes.
Improved Blood Circulation and Tissue Healing
Enhanced vascular perfusion represents a fundamental benefit of shockwave therapy, directly impacting tissue healing and regeneration capabilities. The treatment stimulates nitric oxide production in vascular endothelium, promoting vasodilation and improving microcirculatory flow patterns. Shockwaves trigger release of angiogenic factors, including basic fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor, facilitating new blood vessel formation. Improved circulation enhances oxygen delivery, nutrient transport, and metabolic waste removal from affected tissues. These vascular improvements accelerate healing processes, reduce tissue hypoxia, and promote optimal conditions for cellular regeneration and repair mechanisms.
Enhanced Mobility and Flexibility for Spinal Stiffness
Shockwave therapy significantly improves spinal mobility through mechanical and biological mechanisms affecting tissue flexibility and range of motion. The acoustic energy disrupts adhesions and scar tissue formation, reducing mechanical restrictions in fascial planes and joint capsules. Treatment enhances viscoelastic properties of soft tissues, improving their ability to stretch and deform under physiological loads. Shockwaves stimulate proprioceptive receptors, enhancing neuromuscular coordination and movement quality. These improvements result in increased lumbar flexion, extension, and rotational movements, allowing patients to perform daily activities with greater ease and reduced discomfort.
Non-invasive and Drug-free Alternative to Surgery
The non-invasive nature of shockwave therapy offers significant advantages over surgical interventions and long-term medication use for chronic back pain management. Treatment eliminates surgical risks, including infection, bleeding, and anesthetic complications, while avoiding lengthy recovery periods associated with invasive procedures. The therapy requires no pharmaceutical agents, eliminating concerns about drug interactions, side effects, and dependency issues. Patients can return to normal activities immediately after treatment, maintaining work productivity and lifestyle continuity. These advantages make shockwave therapy particularly attractive for patients seeking conservative treatment options or those who are poor surgical candidates.
The Role of Shockwave Therapy in Treating Spinal Stiffness
Spinal stiffness presents unique challenges in clinical management, requiring targeted approaches that address both mechanical restrictions and underlying pathophysiological processes. Shockwave therapy offers specific advantages in treating this complex condition through its unique ability to affect tissue mechanics and cellular function simultaneously.
Understanding Spinal Stiffness and Its Causes
Spinal stiffness develops through complex interactions between mechanical, inflammatory, and neurological factors affecting spinal segment mobility. Common etiologies include degenerative changes in intervertebral discs, facet joint osteoarthritis, and ligamentous hypertrophy leading to spinal stenosis. Myofascial dysfunction, characterized by trigger point formation and fascial restrictions, contributes significantly to movement limitations. Neurological factors, including altered motor control patterns and protective muscle guarding, perpetuate stiffness through maladaptive movement strategies. Age-related changes in collagen cross-linking and decreased tissue hydration further compromise spinal flexibility. Understanding these multifactorial causes enables targeted therapeutic interventions for optimal treatment outcomes.
How Shockwave Therapy Relieves Muscle Tightness and Increases Flexibility
Shockwave therapy addresses muscle tightness through direct mechanical effects on muscle fibers and indirect neurological modulation of muscle tone. The acoustic energy disrupts abnormal cross-bridges in contracted muscle filaments, allowing for improved sarcomere length and muscle extensibility. Treatment stimulates Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles, resetting abnormal muscle tension patterns through reflex inhibition mechanisms. Shockwaves enhance fascial mobility by breaking down pathological adhesions and improving sliding between tissue layers. The therapy promotes collagen remodeling, replacing rigid, cross-linked fibers with more flexible, functional collagen structures. These combined effects result in improved muscle flexibility, reduced tension, and enhanced range of motion.
Combining Shockwave Therapy with Other Therapies for Spinal Health
Integrative treatment approaches combining shockwave therapy with complementary modalities often yield superior outcomes compared to monotherapy. Physical therapy exercises, including core stabilization and flexibility training, synergize with shockwave effects to maintain and enhance treatment benefits. Manual therapy techniques, such as spinal manipulation and soft tissue mobilization, can be performed more effectively following shockwave treatment due to improved tissue compliance. Therapeutic modalities like ultrasound and electrical stimulation may enhance shockwave penetration and cellular responses. This multimodal approach addresses different aspects of spinal dysfunction, providing comprehensive care that maximizes functional improvements and long-term outcomes.
Case Studies and Success Stories of Shockwave Therapy for Spinal Stiffness
Clinical evidence demonstrates significant improvements in spinal mobility and functional outcomes following shockwave therapy interventions. A representative case involved a 45-year-old construction worker with chronic lumbar stiffness and limited forward flexion. After six shockwave therapy sessions, objective measurements showed 40% improvement in lumbar flexion range and significant reduction in disability scores. Another case featured a 52-year-old office worker with thoracolumbar stiffness who achieved 60% improvement in rotational movements following treatment. These success stories, supported by objective functional assessments and patient-reported outcomes, demonstrate shockwave therapy’s effectiveness in restoring spinal mobility and improving quality of life.
Optimizing Treatment with Shockwave Therapy for Lower Back Pain
Successful shockwave therapy outcomes depend on proper treatment optimization, including appropriate frequency, combination with complementary therapies, and comprehensive patient management. Understanding these factors ensures maximum therapeutic benefit and patient satisfaction.
How Often Should You Receive Shockwave Therapy for Lower Back Pain?
Treatment frequency for shockwave therapy follows evidence-based protocols tailored to individual patient characteristics and condition severity. Standard protocols typically involve weekly sessions over 3-6 weeks, allowing adequate time for tissue healing between treatments. Acute conditions may require more frequent initial sessions, while chronic cases benefit from extended treatment courses. Session intervals must consider tissue recovery time, as excessive frequency may cause treatment fatigue and reduced therapeutic response. Follow-up treatments may be necessary at 3-6 month intervals for maintenance of benefits. Individual factors, including age, comorbidities, and treatment response, influence optimal scheduling decisions for personalized care approaches.
Combining Shockwave Therapy with Physical Therapy for Enhanced Results
Integration of shockwave therapy with structured physical therapy programs significantly enhances treatment outcomes through synergistic therapeutic mechanisms. Pre-treatment physical therapy assessment identifies specific movement dysfunctions and muscle imbalances requiring targeted interventions. Shockwave therapy sessions should precede therapeutic exercises, as improved tissue compliance enhances exercise effectiveness and range of motion gains. Post-treatment exercise protocols focus on maintaining flexibility improvements and strengthening supporting musculature. Core stabilization exercises, performed after shockwave treatment, benefit from reduced muscle tension and improved neuromuscular coordination. This combined approach addresses both symptomatic relief and functional restoration for comprehensive patient care.
Understanding the Full Treatment Process: What to Expect
The shockwave therapy treatment process involves systematic evaluation, treatment delivery, and ongoing assessment to ensure optimal outcomes. Initial consultation includes comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and imaging review to determine treatment candidacy. Pre-treatment preparation involves positioning, skin preparation, and coupling gel application for optimal wave transmission. During treatment, patients experience controlled discomfort as acoustic waves penetrate tissues, with intensity adjusted based on tolerance levels. Session duration typically ranges from 15-20 minutes, depending on treatment area size and protocol requirements. Post-treatment monitoring includes immediate assessment for adverse reactions and scheduling of subsequent sessions based on individual response patterns.
Post-Treatment Care: How to Maximize Recovery and Maintain Results
Effective post-treatment care significantly influences treatment outcomes and long-term benefit maintenance following shockwave therapy. Immediate post-treatment recommendations include gentle mobility exercises to prevent stiffness and promote circulation in treated areas. Patients should avoid strenuous activities for 24-48 hours while allowing initial healing responses to occur. Application of ice may help manage temporary discomfort, while heat therapy should be avoided initially. Progressive return to normal activities is encouraged based on symptom improvement and functional capacity. Long-term maintenance strategies include regular exercise, proper ergonomics, and periodic follow-up evaluations to monitor treatment durability and identify needs for additional interventions.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Shockwave Therapy for Lower Back Pain and Spinal Stiffness
The growing body of scientific literature provides compelling evidence for shockwave therapy’s effectiveness in treating lower back pain and spinal stiffness. This research foundation strengthens clinical confidence and guides evidence-based treatment decisions.
Review of Clinical Studies and Research Findings
Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses demonstrate significant evidence supporting shockwave therapy for musculoskeletal conditions, including lower back pain. A comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials showed statistically significant pain reduction and functional improvement compared to placebo treatments. Studies report effect sizes ranging from moderate to large for pain reduction, with Cohen’s d values exceeding 0.8 in several investigations. Functional outcome measures, including Oswestry Disability Index and Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire scores, show clinically meaningful improvements. Long-term follow-up studies indicate sustained benefits at 6-12 months post-treatment, demonstrating treatment durability. These findings provide robust evidence for clinical effectiveness and support wider adoption.
Expert Opinions on Shockwave Therapy for Chronic Back Pain
Leading spine specialists and pain management experts increasingly recognize shockwave therapy as a valuable treatment option for chronic back pain management. Professional organizations, including the International Association for the Study of Pain, acknowledge the therapy’s potential in multimodal treatment approaches. Expert consensus emphasizes the importance of proper patient selection, with best outcomes observed in cases with specific tissue pathology rather than purely neuropathic pain. Specialists recommend shockwave therapy as a second-line treatment following conservative management failure but before surgical intervention. Expert opinion supports the therapy’s role in reducing healthcare costs and improving patient satisfaction compared to traditional approaches.
Patient Testimonials: Real-world Results from Shockwave Therapy
Patient experiences provide valuable insights into real-world effectiveness and treatment satisfaction with shockwave therapy for back pain. Common themes include rapid pain reduction, improved sleep quality, and enhanced ability to perform daily activities. Patients frequently report decreased reliance on pain medications and improved mood related to better pain control. Many testimonials highlight the non-invasive nature as a significant advantage over surgical options. Patient satisfaction surveys consistently show high approval ratings, with most patients recommending the treatment to others with similar conditions. These positive experiences, combined with objective outcome measures, support the therapy’s clinical value and patient acceptance.
Risques et considérations potentiels de la thérapie par ondes de choc
While shockwave therapy demonstrates excellent safety profiles, understanding potential risks and contraindications ensures appropriate patient selection and optimal treatment outcomes. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate individual patient factors before recommending treatment.
Are There Any Side Effects or Risks Associated with Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy demonstrates excellent safety profiles with minimal adverse events reported in clinical studies and practice. Common temporary side effects include mild to moderate discomfort during treatment, localized skin redness, and occasional bruising at treatment sites. These effects typically resolve within 24-48 hours without intervention. Rare complications may include temporary numbness, skin irritation, or increased pain immediately following treatment. Serious adverse events are extremely uncommon when proper treatment protocols are followed. The therapy’s non-invasive nature eliminates risks associated with surgical interventions, including infection, bleeding, and anesthetic complications. Overall risk profiles compare favorably to alternative treatment modalities.
Who Should Avoid Shockwave Therapy for Lower Back Pain?
Specific contraindications limit shockwave therapy use in certain patient populations to ensure safety and prevent potential complications. Absolute contraindications include pregnancy, presence of pacemakers or other implantable electronic devices, and malignancy in or near treatment areas. Patients with bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications require careful evaluation due to potential bleeding risks. Active infections, severe cardiovascular disease, and neurological conditions affecting sensation may preclude treatment. Relative contraindications include severe osteoporosis, recent corticosteroid injections, and certain medications affecting bone metabolism. Thorough medical screening and risk assessment ensure appropriate patient selection and optimal safety outcomes.
Managing Expectations: When to See Results and How Long Treatment Lasts
Realistic expectation management is crucial for patient satisfaction and treatment success with shockwave therapy. Initial improvements may be noticed within 1-2 weeks following treatment initiation, though maximum benefits typically develop over 6-12 weeks. The gradual response pattern reflects underlying biological processes, including tissue healing and cellular regeneration. Treatment durability varies among individuals, with many patients experiencing sustained benefits for 6-12 months or longer. Factors influencing treatment longevity include severity of underlying pathology, patient compliance with post-treatment recommendations, and lifestyle factors. Some patients may require maintenance treatments to sustain optimal outcomes, while others achieve long-term benefit from initial treatment courses.
Final Thoughts: Why Shockwave Therapy Can Be a Game-Changer for Chronic Pain Sufferers
La thérapie par ondes de choc offre a groundbreaking solution for chronic pain, particularly for conditions like lower back pain and spinal stiffness. Its combination of immediate pain relief and long-term tissue healing makes it a valuable non-invasive alternative to surgery or long-term medication. By addressing root causes rather than just symptoms, shockwave therapy improves patient outcomes with minimal side effects. Supported by growing research and expert endorsements, it’s becoming a preferred choice for chronic pain sufferers. Healthcare providers are encouraged to incorporate this therapy into pain management programs, as it reduces costs and enhances quality of life. As technology advances, shockwave therapy will continue to evolve, offering even more benefits for those with chronic musculoskeletal conditions.
Références
- La thérapie par ondes de choc soulage les hernies discales
- Efficacité et sécurité de la thérapie extracorporelle par ondes de choc dans la lombalgie chronique : revue systématique et méta-analyse de 632 patients
- Focused extracorporeal shockwave therapy for the treatment of low back pain: a systematic review