Introduction to Shockwave Therapy for Neck and Shoulder
Chronic neck and shoulder pain affects millions of individuals worldwide, significantly impacting quality of life and workplace productivity. Traditional treatment approaches often provide temporary relief, leaving patients seeking more effective, long-lasting solutions. Enter shockwave therapy—a revolutionary non-invasive treatment modality that’s transforming how medical professionals approach musculoskeletal pain management.
Qu'est-ce que la thérapie par ondes de choc ?
Shockwave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), utilizes high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate healing processes within damaged tissues. This FDA-approved treatment delivers controlled mechanical energy pulses to specific anatomical regions, promoting cellular regeneration and pain reduction. The therapy employs either radial or focused shockwaves, each targeting different tissue depths and pathological conditions. Modern shockwave devices generate pressure waves ranging from 1-5 bar, creating cavitation bubbles that enhance tissue metabolism and accelerate healing cascades.
The Growing Prevalence of Neck and Shoulder Pain
Contemporary lifestyle factors have significantly contributed to escalating rates of cervical and shoulder disorders. Sedentary occupations, prolonged computer use, and smartphone dependency create postural imbalances leading to myofascial pain syndromes. Epidemiological studies indicate that approximately 67% of adults experience neck pain annually, with 54% reporting concurrent shoulder discomfort. The economic burden exceeds $45 billion annually in healthcare costs and lost productivity, highlighting the urgent need for effective therapeutic interventions.
La science derrière la thérapie par ondes de choc
Understanding the physiological mechanisms underlying shockwave therapy illuminates why this treatment modality demonstrates superior efficacy compared to conventional approaches. The therapy’s multifaceted biological effects target various pathophysiological processes simultaneously, creating synergistic healing responses that address both acute inflammation and chronic degenerative changes.
How Shockwaves Stimulate Blood Flow and Tissue Regeneration
Shockwave application induces immediate vasodilation through nitric oxide release and endothelial cell activation. This enhanced perfusion delivers essential nutrients, oxygen, and growth factors to hypoxic tissues. Simultaneously, mechanical stimulation promotes angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels—through vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) upregulation. Improved microcirculation facilitates waste product removal, reducing metabolic acidosis and inflammatory mediators that perpetuate chronic pain states.
Breaking Down Scar Tissue and Calcifications
Mechanical energy from shockwaves disrupts pathological tissue formations, including fibrotic adhesions and calcium deposits. The controlled cavitation effect creates microtrauma that activates matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes responsible for breaking down excessive collagen and scar tissue. This process, termed mechanotransduction, converts mechanical stimuli into biochemical signals that promote tissue remodeling. Calcific deposits undergo fragmentation, enabling gradual resorption through macrophage activation and phagocytosis.
Neuromodulation: Reducing Pain Signaling in Nerves
Shockwave therapy exerts analgesic effects through multiple neurological pathways. The gate control theory explains immediate pain relief, where mechanical stimulation of large-diameter nerve fibers inhibits nociceptive transmission in the spinal cord. Additionally, shockwaves modulate substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) levels, reducing peripheral sensitization. Hyperstimulation analgesia occurs through endorphin release, providing sustained pain reduction lasting weeks to months post-treatment.
Collagen Stimulation and Musculoskeletal Healing
Controlled mechanical stress triggers fibroblast proliferation and enhanced collagen synthesis, particularly Type I collagen crucial for tendon strength. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) activation promotes organized tissue repair, improving tensile strength and functional capacity. Tenocyte migration and proliferation accelerate, replacing degenerative tissue with healthy, well-organized collagen matrices. This regenerative process typically requires 6-12 weeks for complete tissue maturation and functional restoration.
Common Neck and Shoulder Conditions Treated with Shockwave Therapy
The versatility of shockwave therapy extends across numerous musculoskeletal pathologies affecting the cervical spine and shoulder girdle. Clinical evidence supports its application for both acute injuries and chronic degenerative conditions, making it an invaluable tool in modern rehabilitation medicine.
Chronic Neck Pain and Cervical Myofascial Syndrome
Myofascial pain syndrome characterized by trigger points in cervical musculature responds exceptionally well to shockwave intervention. Treatment targets hyperirritable muscle bands within the upper trapezius, levator scapulae, and suboccipital muscles. Mechanical disruption of trigger points releases contracted sarcomeres, normalizing muscle length and reducing referred pain patterns. Clinical protocols typically involve 3-6 sessions at weekly intervals, with significant pain reduction observed within 2-3 treatments.
Shoulder Tendinitis and Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff tendinopathy, including supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis involvement, demonstrates excellent response rates to shockwave therapy. Treatment addresses both inflammatory and degenerative components of tendinosis, promoting collagen reorganization and reducing neovascularity. Eccentric loading combined with shockwave application enhances treatment outcomes, with success rates exceeding 80% in clinical trials. Patients typically experience functional improvement within 4-6 weeks of treatment initiation.
Calcific Tendinopathy of the Shoulder
Calcium hydroxyapatite deposits within rotator cuff tendons create severe pain and functional limitation. Shockwave therapy demonstrates superior efficacy in fragmenting calcifications compared to traditional approaches. High-energy focused shockwaves penetrate deep tissues, disrupting calcium crystals through cavitation effects. Subsequent inflammatory response facilitates deposit resorption, with complete resolution achieved in 60-90% of patients within 3-6 months post-treatment.
Postural Strain from Desk Work and Tech Neck
Forward head posture and rounded shoulder syndrome prevalent in office workers create chronic muscular imbalances and myofascial restrictions. Shockwave therapy addresses shortened anterior cervical muscles, hypertonic upper trapezius, and restricted thoracic fascia. Treatment protocols focus on restoring optimal cervical lordosis and scapular positioning. Combined with ergonomic modifications and postural retraining, patients experience significant symptom resolution and improved workplace comfort.
Frozen Shoulder and Stiffness-Related Disorders
Adhesive capsulitis, characterized by progressive shoulder stiffness and pain, benefits from shockwave therapy’s ability to address capsular restrictions and inflammatory processes. Treatment targets the joint capsule, coracohumeral ligament, and surrounding soft tissues. Mechanical disruption of adhesions combined with pain modulation facilitates improved range of motion. Clinical outcomes demonstrate accelerated recovery compared to conventional physiotherapy alone, with patients achieving functional restoration 3-6 months earlier.
Clinical Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Neck and Shoulder Pain
The therapeutic advantages of shockwave therapy extend beyond simple pain reduction, encompassing comprehensive improvements in tissue quality, functional capacity, and patient satisfaction. Evidence-based outcomes demonstrate consistent, lasting benefits that surpass traditional treatment modalities in both effectiveness and patient convenience.
Pain Reduction and Improved Range of Motion
Shockwave therapy achieves significant pain reduction through multiple mechanisms, including immediate analgesic effects and long-term tissue healing. Visual analog scale (VAS) scores typically decrease by 60-80% within 6-8 weeks of treatment completion. Concurrent improvements in cervical rotation, lateral flexion, and shoulder abduction enhance functional capacity and quality of life. Goniometric measurements demonstrate 30-50% increases in active range of motion across multiple movement planes.
Accelerated Healing Without Surgery
Non-invasive shockwave treatment eliminates surgical risks while achieving comparable outcomes to operative interventions. Patients avoid anesthesia complications, infection risks, and prolonged recovery periods associated with surgical procedures. Treatment sessions typically last 10-15 minutes, allowing immediate return to daily activities. Success rates for avoiding surgery range from 70-85% depending on condition severity and patient compliance with post-treatment protocols.
Reducing Muscle Tension and Trigger Points
Mechanical disruption of myofascial trigger points provides immediate muscle relaxation and improved tissue compliance. Pressure pain thresholds increase significantly, indicating reduced tissue sensitivity and improved pain tolerance. Muscle tone normalization occurs through restoration of optimal sarcomere length and improved neuromuscular control. Electromyographic studies demonstrate reduced resting muscle activity and improved activation patterns following shockwave treatment.
Enhanced Circulation and Cellular Repair
Doppler ultrasound studies confirm increased tissue perfusion lasting 4-6 weeks post-treatment. Enhanced oxygen delivery and nutrient supply accelerate cellular metabolism and repair processes. Growth factor upregulation, including platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), promotes tissue regeneration. Inflammatory marker reduction, particularly interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α, indicates resolution of chronic inflammatory processes.
Long-Term Relief Compared to Conventional Treatments
Longitudinal studies demonstrate sustained benefits lasting 12-24 months post-treatment, significantly exceeding conventional therapy outcomes. Recurrence rates remain below 15% when combined with appropriate exercise protocols and lifestyle modifications. Cost-effectiveness analyses favor shockwave therapy over repeated injections or prolonged physiotherapy regimens. Patient satisfaction scores consistently exceed 85%, with high treatment recommendation rates among successful cases.
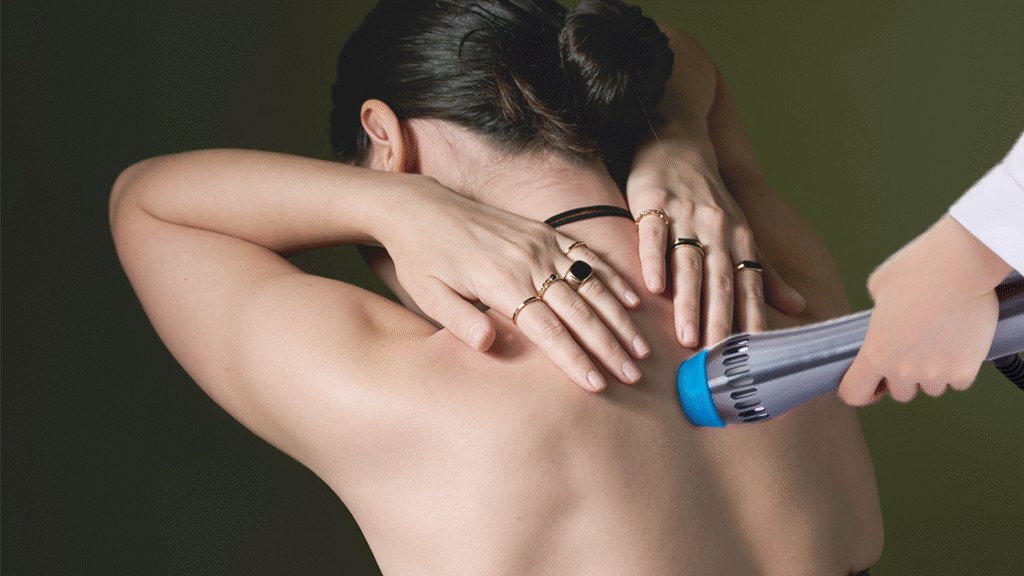
Evidence-Based Research on Shockwave Therapy
Scientific literature provides robust evidence supporting shockwave therapy’s efficacy for neck and shoulder pathologies. Systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and randomized controlled trials consistently demonstrate superior outcomes compared to placebo and alternative treatments, establishing shockwave therapy as an evidence-based intervention.
Studies on Shockwave Therapy for Neck Pain
Multiple randomized controlled trials have evaluated shockwave therapy for cervical spine disorders. A landmark study by Zhang et al. (2019) demonstrated 73% pain reduction in chronic neck pain patients following 6 treatment sessions. Comparative effectiveness research shows superior outcomes to ultrasound therapy and manual techniques. Long-term follow-up studies confirm sustained benefits at 12-month intervals, with minimal adverse effects reported across diverse patient populations.
Clinical Trials on Shoulder Tendon Healing and Function
Rotator cuff tendinopathy studies consistently demonstrate 65-85% success rates with shockwave therapy. Ultrasound imaging reveals improved tendon echogenicity and reduced neovascularization following treatment. Functional outcome measures, including the Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, show clinically significant improvements. Biomechanical testing confirms restored tendon strength and elasticity comparable to healthy tissue properties.
Comparative Studies: Shockwave vs. Cortisone Injections and Physical Therapy
Head-to-head comparisons reveal shockwave therapy’s superiority over corticosteroid injections for long-term outcomes. While injections provide immediate relief, shockwave therapy demonstrates sustained benefits without medication-related side effects. Combination studies suggest synergistic effects when shockwave therapy precedes structured exercise programs. Physical therapy alone shows inferior outcomes compared to shockwave-enhanced rehabilitation protocols.
Expert Opinions from Orthopedic and Physiotherapy Specialists
Leading orthopedic surgeons increasingly recommend shockwave therapy as first-line treatment for chronic tendinopathies. International consensus statements support its use for calcific tendinopathy and adhesive capsulitis. Physiotherapy specialists report enhanced treatment outcomes when incorporating shockwave therapy into comprehensive rehabilitation programs. Medical society guidelines now include shockwave therapy in evidence-based treatment algorithms for musculoskeletal disorders.
Shockwave Therapy in Holistic Pain Management Programs
Optimal treatment outcomes emerge when shockwave therapy integrates within comprehensive, multidisciplinary pain management approaches. This holistic perspective addresses underlying biomechanical dysfunctions, lifestyle factors, and patient-specific needs to maximize therapeutic benefits and prevent symptom recurrence.
Combining Shockwave Therapy with Physiotherapy and Massage
Synergistic treatment protocols combining shockwave therapy with manual techniques demonstrate enhanced outcomes compared to individual interventions. Pre-treatment massage improves tissue compliance and shockwave penetration, while post-treatment mobilization maintains newly achieved range of motion. Specific timing protocols optimize healing responses: shockwave therapy followed by gentle mobilization within 24-48 hours maximizes therapeutic gains. Evidence suggests 25-30% improvement in functional outcomes with combined approaches.
Posture Correction and Ergonomic Adjustments
Workplace ergonomic assessments identify contributing factors perpetuating neck and shoulder dysfunction. Monitor positioning, keyboard height, and seating arrangements require optimization to prevent symptom recurrence. Cervical support pillows, adjustable workstations, and regular movement breaks complement shockwave therapy outcomes. Studies demonstrate 40% reduction in symptom recurrence when ergonomic modifications accompany treatment protocols.
Stretching, Strengthening, and Mobility Exercises for Long-Term Results
Progressive exercise prescription following shockwave therapy maintains tissue health and prevents re-injury. Specific stretching protocols target shortened muscles including upper trapezius, levator scapulae, and pectoralis minor. Strengthening exercises focus on deep cervical flexors, rhomboids, and posterior deltoid muscles to restore optimal muscle balance. Mobility exercises emphasize thoracic extension and scapular retraction patterns essential for postural correction.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Factors Supporting Musculoskeletal Recovery
Anti-inflammatory nutrition protocols support tissue healing and reduce chronic pain states. Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and magnesium supplementation demonstrate benefits for musculoskeletal health. Hydration optimization ensures adequate tissue perfusion and waste product removal. Sleep hygiene improvements facilitate growth hormone release and tissue repair processes essential for recovery. Stress management techniques reduce cortisol levels that impair healing responses.
Who Can Benefit from Shockwave Therapy for Neck and Shoulder Pain
Shockwave therapy demonstrates broad applicability across diverse patient populations and pathological conditions. Understanding ideal candidate profiles helps clinicians optimize treatment selection and patient outcomes while identifying potential contraindications or modified protocols.
Office Workers with Postural Neck Pain
Sedentary professionals experiencing chronic cervical strain represent ideal candidates for shockwave therapy. Forward head posture and rounded shoulder syndrome respond exceptionally well to targeted treatment protocols. Typical presentations include suboccipital tension, upper trapezius trigger points, and cervical facet joint dysfunction. Treatment success rates exceed 80% when combined with ergonomic modifications and postural retraining. Symptoms typically resolve within 4-6 treatment sessions.
Athletes with Overuse Shoulder Injuries
Repetitive overhead activities in swimming, tennis, and baseball create specific injury patterns amenable to shockwave intervention. Rotator cuff tendinopathy, labral irritation, and shoulder impingement syndrome demonstrate excellent response rates. Treatment protocols accommodate training schedules with minimal activity restriction. Return-to-sport timelines accelerate by 30-40% compared to conventional rehabilitation alone. Professional athletes report high satisfaction with treatment convenience and effectiveness.
Middle-Aged Adults with Chronic Tendinopathy
Degenerative tendon changes common in 40-60 year age group benefit significantly from shockwave therapy’s regenerative properties. Calcific deposits, tendon thickening, and reduced elasticity improve through mechanotransduction effects. Success rates remain high despite chronic symptom duration exceeding 6-12 months. Treatment outcomes correlate positively with patient compliance and concurrent lifestyle modifications.
Older Adults with Degenerative Shoulder or Cervical Pain
Age-related tissue changes including reduced vascularity and collagen quality respond well to shockwave therapy’s circulatory enhancement. Modified treatment parameters account for decreased tissue tolerance and slower healing responses. Combination with gentle exercise programs optimizes outcomes while preventing overexertion. Safety profiles remain excellent with appropriate patient selection and treatment modification.
Post-Surgical Patients in Rehabilitation
Patients experiencing delayed healing, scar tissue formation, or persistent pain following shoulder or cervical surgery benefit from shockwave intervention. Treatment promotes tissue remodeling and addresses surgical adhesions effectively. Protocols begin 6-8 weeks post-operatively following surgical clearance. Enhanced rehabilitation outcomes reduce overall recovery time and improve functional restoration.
Final Thoughts: Shockwave Therapy as a Modern Pain Relief Solution
Shockwave therapy is transforming musculoskeletal medicine by offering a non-invasive, scientifically validated alternative to traditional pain management. This technology addresses the root causes of chronic pain, promoting sustainable healing instead of masking symptoms. Unlike pharmaceuticals or surgery, shockwave therapy provides targeted benefits with minimal risk and faster recovery. As healthcare systems prioritize cost-effective, evidence-based treatments, shockwave therapy stands out for its clinical efficacy and economic advantages. The treatment’s continued technological advancements promise even more precise and comfortable outcomes, expanding its applications for musculoskeletal disorders. For individuals with chronic neck and shoulder pain, shockwave therapy offers an opportunity for active, pain-free living. Integrated into comprehensive rehabilitation programs, it addresses underlying issues, maximizing long-term recovery. As clinical experience grows, shockwave therapy will continue to play a central role in modern pain management, offering hope for those suffering from debilitating conditions.
Références
- La révolution de la thérapie par ondes de choc pour les douleurs cervicales
- Bannir les douleurs cervicales grâce à la thérapie par ondes de choc
- Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Cervical Myofascial Pain Following Neck Dissection Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Mécanismes de la thérapie extracorporelle par ondes de choc dans la médecine régénérative musculo-squelettique
- The Effectiveness of Ergonomic Training and Therapeutic Exercise in Chronic Neck Pain in Accountants in the Healthcare System: A Review
