はじめに
Manual laborers often face chronic musculoskeletal pain due to repetitive motions, heavy lifting, and prolonged strain. These cumulative injuries, known as overuse injuries, can significantly impact work efficiency and may progress into chronic conditions. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) has emerged as a non-invasive rehabilitation method that helps manual laborers manage pain, accelerate tissue repair, and improve function. By delivering high-energy acoustic waves to affected tissues, shockwave therapy enhances blood circulation, stimulates cellular regeneration, and supports recovery from tendon, ligament, and muscle damage. This article explores the application of shockwave therapy for manual laborers, including indications, treatment mechanisms, therapy sessions, candidate suitability, and expected outcomes.
1. Understanding Overuse Injuries in Manual Laborers
1.1 Common Types of Overuse Injuries
Manual laborers are prone to injuries in tendons, ligaments, and muscles. Common types include:
- Tendonitis: Examples include rotator cuff tendonitis, patellar tendonitis, and Achilles tendonitis.
- Muscle strains and micro-tears: Repetitive work can cause small fiber damage and chronic strain.
- Repetitive strain injuries (RSI): Often affect the wrist, elbow, and shoulder due to repetitive tasks.
These injuries typically develop gradually, presenting as localized pain, tenderness, and limited range of motion, sometimes affecting daily activities and work performance.
1.2 Causes and Risk Factors
Key factors contributing to overuse injuries include:
- Repetitive lifting or carrying motions: Continuous load on the hands, arms, and back.
- Poor ergonomics: Non-ergonomic work postures increase stress on tendons and joints.
- Age-related tissue degeneration: Tendons and ligaments lose elasticity with age, slowing natural healing.
Understanding these mechanisms is essential for designing effective rehabilitation plans. Shockwave therapy targets these cumulative, chronic injuries in a non-invasive manner.
2. How Shockwave Therapy Works
2.1 Mechanism of Action
Shockwave therapy uses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate healing in injured tissues. Its effects include:
- Promoting tissue regeneration: Stimulates cell proliferation and collagen synthesis, accelerating tendon and ligament repair.
- Improving blood circulation: Enhances local microcirculation, supplying oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissue.
- Reducing inflammation and pain: Modulates nerve sensitivity, alleviating pain caused by chronic inflammation.
This therapy addresses both symptoms and tissue quality, providing deep tissue repair that traditional physical therapy alone cannot achieve.
2.2 Comparison to Traditional Therapies
- Physical therapy alone: Improves flexibility and muscle strength but may have limited effects on deep tendon pathology.
- Medication (NSAIDs or corticosteroid injections): Offers short-term pain relief but does not promote tissue regeneration and carries potential side effects.
- Shockwave therapy: Non-invasive, drug-free, and promotes tissue repair and functional recovery, making it ideal for manual laborers.
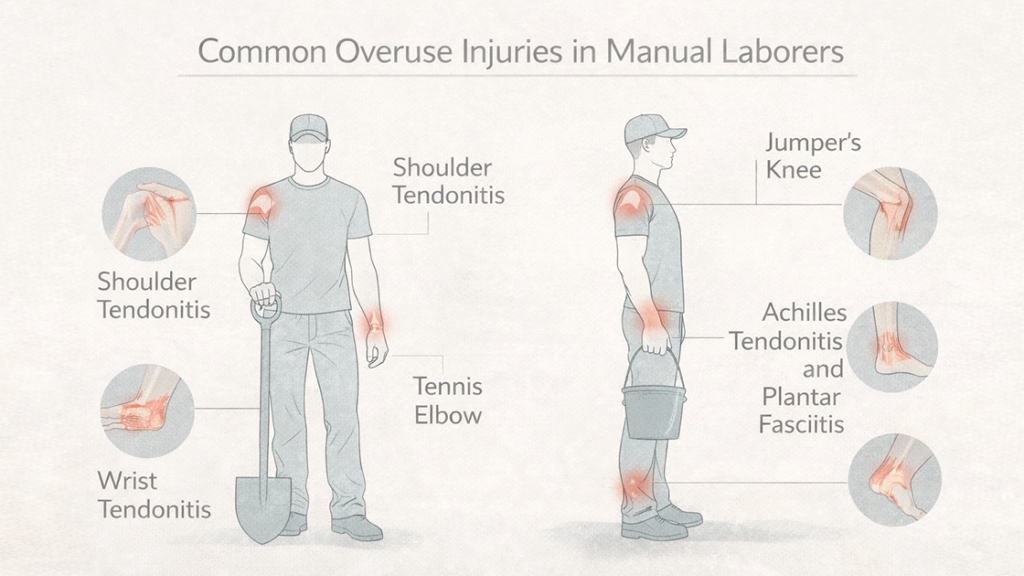
3. Common Injuries Treated in Manual Laborers
3.1 Shoulder and Rotator Cuff Injuries
Shoulder pain and limited range of motion are frequent among laborers who repeatedly lift or overhead press. Shockwave therapy can:
- Reduce calcifications in tendons
- Stimulate tendon cell regeneration
- Relieve inflammation and pain while improving shoulder mobility
3.2 Elbow and Wrist Overuse Injuries
- Tennis elbow (Lateral epicondylitis): Pain along the outer elbow, common in workers who lift or use tools repetitively.
- Wrist tendonitis: Common in workers performing repetitive hand tasks or mechanical operations.
Shockwave therapy enhances tendon blood flow, accelerates micro-damage repair, and reduces pain.
3.3 Knee and Lower Limb Tendinopathies
- Jumper’s knee (Patellar tendonitis): Common in workers performing repeated squats or heavy lifting.
- Achilles tendonitis and plantar fasciitis: Frequently affect workers who stand for extended periods.
Shockwave therapy promotes collagen remodeling and strengthens tendons and ligaments, enabling faster recovery of walking, running, and load-bearing capacity.
4. Who Is a Good Candidate?
4.1 Ideal Candidates
- Manual laborers with chronic or cumulative overuse injuries
- Patients unresponsive to conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, or medications
- Individuals seeking non-surgical, drug-free treatment
4.2 Contraindications
- Active infection or malignancy at the treatment site
- Blood clotting disorders
- Pregnancy (specific areas require caution)
- Patients with severe intolerance to treatment
Professional evaluation ensures safety and maximizes treatment effectiveness.
5. What to Expect During Treatment
5.1 Treatment Procedure
- Each session typically lasts 5–15 minutes
- Treatment plans usually involve 4–8 sessions spaced 3–7 days apart
- Can be combined with physical therapy or functional training for better results
5.2 Pain Relief and Recovery Timeline
- Some patients feel mild improvement after 1–2 sessions
- Chronic or severe injuries may require the full course for significant pain reduction
- Post-treatment, patients can usually perform light work immediately
6. Key Benefits for Manual Laborers
6.1 Accelerated Recovery
Shockwave therapy stimulates tendon, ligament, and soft tissue repair, reducing downtime and enabling workers to return to full activity sooner.
6.2 Non-Invasive Advantage
No surgery, minimal side effects, and no long-term medication dependence, making it safe for long-term occupational rehabilitation.
FAQ
Does shockwave therapy hurt?
Most patients experience mild tingling or vibration; generally well-tolerated.
How soon can I return to work?
Light work may resume the same day, heavy labor should be gradually reintroduced.
Can shockwave therapy prevent future injuries?
It improves tendon and ligament quality but should be combined with proper ergonomics and strengthening exercises.
How many sessions are required?
Typically 4–8 sessions, spaced 3–7 days apart, depending on severity.
Is it suitable for chronic or acute injuries?
Effective for chronic and cumulative injuries; acute injuries require professional assessment.
結論
Shockwave therapy offers a non-invasive, effective solution for manual laborers with overuse injuries. By promoting tissue healing, reducing inflammation, and relieving pain, it enables workers to recover safely and restore functional capacity. Combined with professional assessment and rehabilitation exercises, shockwave therapy is a valuable tool for managing chronic occupational musculoskeletal injuries.
参考文献
Gerdesmeyer L, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic tendinopathies.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12590617
Speed C. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16909768
Shockwave Machines. Indications for Shockwave Therapy.
