Pain management has evolved significantly over the past decades, with healthcare professionals increasingly seeking effective, non-invasive treatment modalities that address the root causes of chronic pain rather than merely masking symptoms. Among these emerging therapies, extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) has gained considerable recognition for its ability to provide lasting pain relief while promoting natural tissue healing. This comprehensive guide explores the therapeutic potential of shockwave therapy and its transformative impact on modern pain management practices.
Introduction: Understanding Pain Management Challenges Today
The landscape of pain management faces unprecedented challenges as healthcare systems worldwide grapple with the complex needs of millions suffering from chronic pain conditions. Understanding these challenges provides essential context for appreciating why innovative therapies like shockwave therapy have become increasingly valuable in clinical practice.
The Burden of Chronic Pain Worldwide
Chronic pain affects approximately 1.5 billion people globally, representing one of the most significant healthcare challenges of our time. This pervasive condition impacts individuals across all demographics, with musculoskeletal disorders accounting for nearly 30% of all disability-adjusted life years worldwide. The economic burden extends beyond direct medical costs, encompassing lost productivity, reduced quality of life, and substantial psychological impacts on patients and their families. The prevalence of chronic pain conditions continues to rise, particularly in developed nations where sedentary lifestyles, repetitive stress injuries, and aging populations contribute to increasing incidence rates. Conditions such as plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis, and chronic tendinopathies have become commonplace, affecting millions of workers, athletes, and aging adults who struggle to find effective, long-term relief from conventional treatment approaches.
Growing Demand for Alternative and Non-Invasive Therapies
The opioid crisis has fundamentally shifted healthcare providers’ approach to pain management, creating urgent demand for safe, effective alternatives to pharmaceutical interventions. Patients increasingly seek treatment modalities that address underlying pathophysiology rather than providing temporary symptom relief, driving interest in regenerative medicine approaches that promote natural healing processes. Contemporary pain management emphasizes multimodal treatment strategies that combine various therapeutic approaches to optimize outcomes while minimizing risks. Non-invasive therapies have gained particular attention due to their favorable safety profiles, reduced recovery times, and ability to complement other treatment modalities. This paradigm shift has positioned advanced technologies like extracorporeal shockwave therapy at the forefront of modern pain management protocols.
衝撃波治療とは? An Expert Overview
Shockwave therapy represents a sophisticated medical technology that harnesses the therapeutic potential of acoustic waves to stimulate healing and provide pain relief. Understanding the fundamental principles and mechanisms underlying this treatment modality is essential for appreciating its clinical applications and therapeutic benefits in various pain conditions.
Definition, History, and Medical Background
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy involves the application of shock waves to injured tissues, stimulating healing and providing pain relief. These high-energy sound waves interact with the body, promoting regeneration and reparative processes of bones, tendons, and other soft tissues. The technology originated in the 1980s as a treatment for kidney stones (lithotripsy) before evolving into a therapeutic modality for musculoskeletal conditions. Modern shockwave therapy utilizes sophisticated devices that generate controlled acoustic waves with specific energy levels, frequencies, and penetration depths. These devices are classified into focused and radial shockwave systems, each offering distinct therapeutic characteristics and clinical applications. The technology has received FDA approval for various conditions, including plantar fasciitis and lateral epicondylitis, establishing its credibility within mainstream medical practice.
Mechanism of Action: How Shockwaves Promote Healing
Shockwave therapy’s therapeutic effects arise from mechanotransduction, where high-energy acoustic waves interact with cells and tissues. These pulses create mechanical stress, triggering biological responses that promote healing, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain. At the cellular level, shockwaves activate mechanosensitive ion channels, increasing intracellular calcium and stimulating signaling pathways. This boosts the production of growth factors such as VEGF, TGF-β, and BMPs, essential for tissue repair and regeneration. The therapy also encourages neovascularization by promoting angiogenic factors, enhancing blood flow and nutrient delivery to damaged areas. Additionally, shockwaves help break down calcific deposits and scar tissue, while stimulating collagen synthesis and extracellular matrix production, vital for tissue remodeling. Together, these effects support accelerated healing and functional recovery in treated tissues.
Conditions Effectively Treated with Shockwave Therapy
The versatility of shockwave therapy extends across numerous musculoskeletal and soft tissue conditions, making it a valuable treatment option for diverse patient populations. Clinical evidence supports its efficacy in treating both acute injuries and chronic degenerative conditions, with particularly strong outcomes observed in specific diagnostic categories.
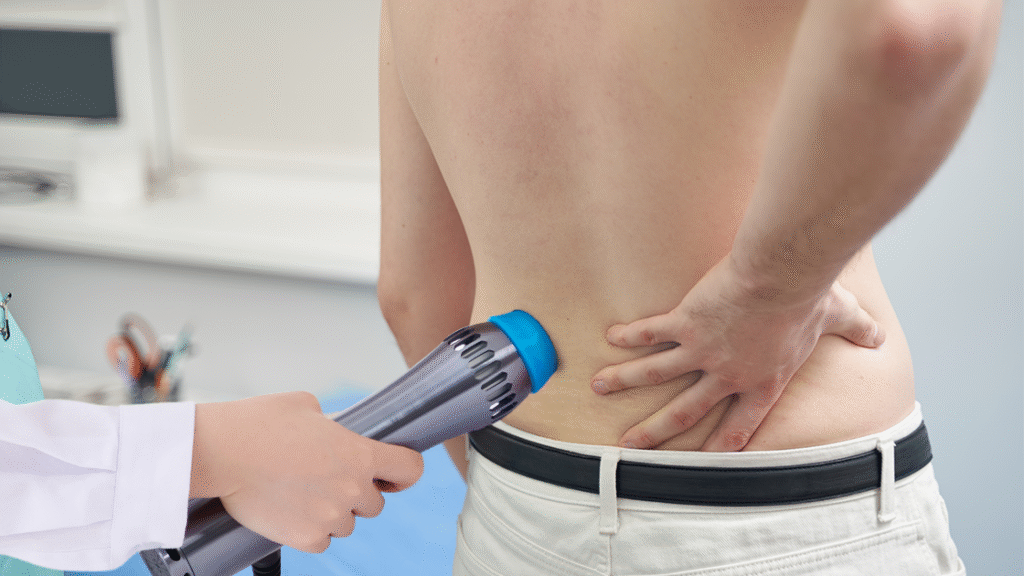
Common Musculoskeletal Disorders
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) effectively treats chronic conditions like tendonitis, 足底筋膜炎そして アキレス腱炎, which commonly affect athletes and active individuals. Plantar fasciitis is among the most successfully treated, with studies showing significant pain relief and improved function, especially in patients unresponsive to conservative treatments. Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) also responds well, with multiple trials demonstrating better outcomes than placebo. ESWT targets tendinopathic changes by promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation, easing pain and restoring function. Additionally, shockwave therapy is highly effective for calcific tendinitis of the shoulder. The acoustic waves mechanically break down calcium deposits and stimulate their resorption, resulting in pain reduction and better shoulder mobility. Success rates for calcific tendinitis treatment often exceed 80% in well-selected patients, making ESWT a valuable non-invasive option for various musculoskeletal disorders.
Joint and Soft Tissue Conditions
Osteoarthritis and other degenerative joint conditions benefit from shockwave therapy’s ability to stimulate cartilage metabolism and reduce subchondral bone sclerosis. The treatment can improve joint function and reduce pain in knee osteoarthritis, particularly when conventional therapies have provided limited relief. Clinical studies demonstrate sustained improvements in pain scores and functional assessments following shockwave therapy protocols. 筋筋膜性疼痛症候群 and trigger point-related conditions respond well to focused shockwave therapy, which can effectively deactivate trigger points while addressing underlying tissue restrictions. The therapy’s ability to improve tissue extensibility and reduce muscular tension makes it particularly valuable for treating complex myofascial pain patterns that often resist conventional treatment approaches.
Sports Injuries and Overuse Syndromes
Athletic populations frequently benefit from shockwave therapy due to the high prevalence of overuse injuries and the need for rapid, effective treatment that allows return to activity. Patellar tendinopathy (jumper’s knee) represents a common condition in jumping athletes that responds well to shockwave therapy, with studies showing significant improvements in pain and function scores. Achilles tendinopathy, both insertional and mid-portion varieties, demonstrates excellent response rates to shockwave therapy. The treatment addresses the degenerative changes within the tendon while promoting healing of the surrounding peritendinous tissues. Athletes often experience faster return to sport compared to traditional rehabilitation approaches, making shockwave therapy particularly valuable in competitive sports medicine settings.
Nerve Pain and Myofascial Trigger Points
Multiple randomized control trials have concluded that ESWT is beneficial in reducing spasticity, reducing pain, improving range of motion, and improving function in conditions including cerebral palsy and stroke with both upper and lower limb spasticity. This neurological application extends the therapeutic potential of shockwave therapy beyond traditional musculoskeletal indications. Myofascial trigger points respond effectively to focused shockwave therapy, which can mechanically disrupt trigger point activity while promoting local circulation and reducing referred pain patterns. The therapy’s ability to address both peripheral and central sensitization mechanisms makes it particularly valuable for treating complex chronic pain conditions involving trigger point activity and myofascial restrictions.
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Pain Management Backed by Science
The scientific foundation supporting shockwave therapy continues to expand, with numerous clinical studies demonstrating its efficacy across various pain conditions. Understanding these evidence-based benefits helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about incorporating this therapy into comprehensive pain management strategies.
Non-Invasive, Drug-Free Alternative to Surgery and Medication
Shockwave therapy offers a compelling alternative to surgical interventions and long-term pharmaceutical management, particularly for patients seeking to avoid the risks and complications associated with invasive procedures. The therapy provides therapeutic benefits without the need for incisions, anesthesia, or prolonged recovery periods, making it an attractive option for patients with multiple comorbidities or contraindications to surgery. The drug-free nature of shockwave therapy eliminates concerns about medication interactions, side effects, and dependency issues that often accompany chronic pain management with pharmaceuticals. This characteristic makes the therapy particularly valuable for elderly patients, individuals with multiple medications, and those seeking to reduce their reliance on pain medications while maintaining effective symptom control.
Accelerated Tissue Repair and Natural Regeneration
The use of ESWT in CLBP patients results in significant and quantifiable reductions in pain and disability in the short term. The regenerative effects of shockwave therapy extend beyond immediate pain relief, promoting actual tissue healing and structural improvements in treated areas. This regenerative capacity distinguishes shockwave therapy from purely symptomatic treatments, offering patients the potential for lasting improvement rather than temporary relief. The therapy stimulates endogenous stem cell recruitment and activation, enhancing the body’s natural healing responses in damaged tissues. Growth factor upregulation, including increased production of VEGF, PDGF, and TGF-β, supports angiogenesis, fibroblast proliferation, and extracellular matrix synthesis essential for tissue repair and remodeling processes.
Reduction of Chronic Inflammation and Scar Tissue Breakdown
Chronic inflammation represents a key pathological process in many pain conditions, perpetuating tissue damage and impeding natural healing responses. Shockwave therapy modulates inflammatory cascades through multiple mechanisms, including the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the promotion of anti-inflammatory mediators that support tissue healing and pain resolution. The mechanical effects of acoustic waves can effectively break down fibrotic scar tissue and adhesions that contribute to pain and functional limitations. This tissue remodeling effect is particularly beneficial in conditions involving chronic tendinopathies, where abnormal collagen organization and scar tissue formation impede normal tissue function and perpetuate pain symptoms.
Enhanced Blood Circulation Supporting Long-Term Recovery
Neovascularization represents a crucial component of the healing process that is often impaired in chronic pain conditions. Shockwave therapy stimulates angiogenesis through the upregulation of angiogenic growth factors, leading to improved blood supply in treated tissues. Enhanced circulation facilitates nutrient delivery, waste product removal, and the transport of healing factors essential for tissue recovery. The improved vascular supply has lasting benefits that extend beyond the immediate treatment period, supporting ongoing tissue health and reducing the likelihood of symptom recurrence. This vascular enhancement is particularly important in conditions affecting poorly vascularized tissues, such as tendons and ligaments, where limited blood supply often impedes natural healing processes.
Convenience: Short Sessions, Minimal Discomfort, and Downtime
Treatment convenience represents a significant advantage of shockwave therapy, with typical sessions lasting only 10-15 minutes and requiring no special preparation or post-treatment restrictions. Patients can return to normal activities immediately following treatment, making the therapy compatible with busy schedules and active lifestyles without disrupting daily routines or work commitments. The minimal discomfort associated with shockwave therapy, described by most patients as tolerable pressure or mild discomfort, eliminates the need for anesthesia or pain medications during treatment. This comfort profile makes the therapy accessible to patients of all ages and pain tolerance levels, while the absence of significant side effects allows for repeated treatments as needed to achieve optimal outcomes.
What to Expect During Your Shockwave Therapy Treatment
Understanding the treatment process helps patients prepare for their shockwave therapy experience and sets appropriate expectations for treatment outcomes. The systematic approach to shockwave therapy ensures safety, maximizes therapeutic benefits, and provides patients with comprehensive care throughout their treatment journey.
Initial Assessment by Certified Healthcare Professionals
Comprehensive patient evaluation forms the foundation of successful shockwave therapy treatment, beginning with detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging review when appropriate. Healthcare providers assess pain patterns, functional limitations, previous treatments, and contraindications to ensure appropriate patient selection and treatment planning. The assessment process includes evaluation of pain intensity using validated scales, functional assessments specific to the affected area, and identification of contributing factors that may influence treatment outcomes. Providers also discuss treatment goals, expectations, and alternative options to ensure patients make informed decisions about their care and understand the expected treatment timeline.
Treatment Protocol: Duration, Frequency, and Procedure
Standard shockwave therapy protocols typically involve 3-6 treatment sessions spaced 1-2 weeks apart, though specific protocols may vary based on the condition being treated and individual patient factors. Each session involves the application of a predetermined number of shockwave pulses at specific energy levels and frequencies determined by the treatment protocol and patient tolerance. During treatment, patients are positioned comfortably with the affected area accessible for shockwave application. Ultrasound gel is applied to enhance acoustic coupling between the device and skin surface, ensuring optimal energy transmission to target tissues. The healthcare provider systematically treats the affected area using predetermined treatment parameters while monitoring patient comfort and response.
Patient Experience: Sensations and Common Reactions During Therapy
Most patients describe shockwave therapy sensations as rhythmic pressure or tapping, with intensity varying based on energy levels and individual sensitivity. The treatment is generally well-tolerated, with any discomfort typically subsiding immediately after the session ends. Some patients may experience mild soreness or tenderness in the treated area for 24-48 hours following treatment. Common immediate reactions include mild skin redness at the treatment site, which typically resolves within hours, and occasional temporary increase in symptoms as the body responds to the therapeutic stimulus. These reactions are considered normal physiological responses and generally indicate appropriate tissue stimulation and treatment effectiveness.
Post-Treatment Care Guidelines and Recovery Tips
Most patients can resume normal activities immediately after the session.
Avoid intense physical activities for 24–48 hours to optimize tissue response and reduce soreness.
Maintain adequate hydration to support healing.
Apply ice to the treated area if experiencing soreness or discomfort.
Continue any prescribed exercises or physical therapy routines as advised.
Attend scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor progress, assess treatment effectiveness, and determine if additional sessions are needed based on symptom relief and functional improvement
Safety, Risks, and Considerations
Shockwave therapy boasts an excellent safety profile with minimal reported adverse effects, making it suitable for most patients seeking non-invasive pain management options. However, understanding potential risks and contraindications ensures appropriate patient selection and optimal treatment outcomes while maintaining the highest safety standards.
Common Side Effects and How They Are Managed
Temporary skin redness at the treatment site
Mild swelling around the treated area
Transient soreness lasting 24–48 hours
Mild pain during treatment, generally well tolerated
Rare “flare reaction” — temporary worsening of symptoms within the first few days, which resolves on its own
Management recommendations:
Rest and avoid overexertion
Apply ice to reduce soreness and inflammation
Use over-the-counter pain relievers if necessary
Important Contraindications and When to Avoid Shockwave Therapy
Absolute Contraindications:
妊娠
Presence of pacemakers or other electronic implants near the treatment area
Active infections at the treatment site
Relative Contraindications (Require Careful Evaluation):
Bleeding disorders or use of anticoagulant medications
Malignancy (cancer) in the treatment area
Certain cardiac conditions
Severe osteoporosis
Recent corticosteroid injections in the targeted area
Comparing Shockwave Therapy with Other Pain Management Modalities
Understanding how shockwave therapy compares to other treatment options helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about optimal treatment approaches. Each modality offers distinct advantages and limitations that must be considered within the context of individual patient needs and treatment goals.
Medication: Pros, Cons, and When to Avoid
Pharmaceutical pain management provides rapid symptom relief and is readily accessible, making it a common first-line treatment for many pain conditions. However, medications typically provide temporary relief without addressing underlying pathophysiology, often requiring long-term use with associated risks of side effects, dependency, and diminishing effectiveness over time. Shockwave therapy offers complementary benefits by promoting actual tissue healing while providing pain relief, potentially reducing the need for long-term medication use. The combination of both approaches may be optimal in certain cases, allowing for symptom management during the healing process while addressing underlying tissue pathology through regenerative mechanisms.
Surgery: Risks, Recovery, and Alternatives
Surgical interventions often provide definitive treatment for structural problems but carry inherent risks including infection, scarring, prolonged recovery, and potential complications. Surgery may be necessary for severe structural damage or when conservative treatments have failed, but many patients prefer exploring non-invasive alternatives first. Shockwave therapy can serve as an effective alternative to surgery for many conditions, particularly chronic tendinopathies and calcific deposits where conservative treatments have failed. The therapy’s ability to promote tissue healing and structural improvements without surgical risks makes it an attractive option for patients seeking to avoid invasive procedures while achieving meaningful symptom improvement.
Physical Therapy and Manual Techniques: Complement or Substitute?
Physical therapy and manual treatment techniques provide valuable benefits through exercise, education, and hands-on interventions. These approaches excel at addressing movement patterns, strength deficits, and functional limitations that contribute to pain conditions. However, they may be limited in their ability to address underlying tissue pathology in chronic conditions. Shockwave therapy complements physical therapy by addressing tissue-level pathology while physical therapy addresses functional and biomechanical factors. The combination of both approaches often provides synergistic benefits, with shockwave therapy enhancing tissue healing capacity while physical therapy optimizes movement patterns and prevents symptom recurrence through improved function and strength.
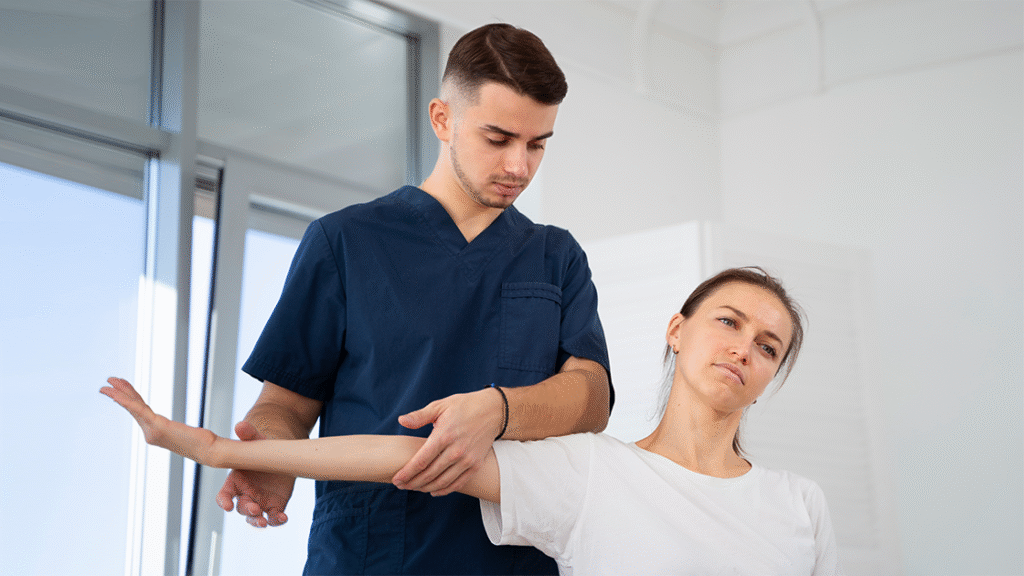

Clinical Evidence and Expert Endorsements
The growing body of scientific evidence supporting shockwave therapy has led to increased acceptance among healthcare professionals and integration into clinical practice guidelines. This evidence base provides the foundation for informed treatment decisions and supports the therapy’s role in modern pain management protocols.
Summary of Key Peer-Reviewed Studies and Meta-Analyses
The findings of the present meta-analysis indicate that the utilization of ESWT may yield positive outcomes in terms of pain reduction in patients with LE. Multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses have demonstrated significant improvements in pain and function across various conditions treated with shockwave therapy, with effect sizes often exceeding those observed with conventional treatments. The results of our study have shown that ESWT had a statistically significant superiority over placebo for improvement in the parameters of pain, disability, depression, anxiety, and quality of life in the patients with CLBP. These findings extend beyond simple pain reduction to include meaningful improvements in functional capacity and quality of life measures that are important to patients’ overall well-being.
Recommendations from Professional Medical Associations
Professional medical organizations have increasingly recognized shockwave therapy as an evidence-based treatment option for specific conditions. Physical medicine and rehabilitation specialists are using extracorporeal shock wave therapy to treat an evolving list of musculoskeletal and neurological diagnoses. This growing acceptance reflects the accumulating evidence base and clinical experience supporting the therapy’s efficacy and safety. Clinical practice guidelines from various medical societies now include shockwave therapy as a recommended treatment option for conditions such as plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis, and calcific tendinitis. These endorsements provide healthcare providers with confidence in recommending the therapy and support insurance coverage decisions for appropriate patients.
Real Patient Outcomes and Verified Testimonials
Patient satisfaction rates with shockwave therapy are consistently high, with many individuals reporting significant improvements in pain and function that have lasted months to years following treatment. These real-world outcomes complement clinical trial data and provide valuable insights into the therapy’s effectiveness in diverse patient populations and clinical settings. Long-term follow-up studies demonstrate sustained benefits in many patients, with low recurrence rates and high satisfaction scores supporting the therapy’s value as a treatment option. Patient testimonials frequently emphasize the convenience, tolerability, and effectiveness of shockwave therapy compared to previous treatment experiences, contributing to growing patient demand for this therapeutic modality.
衝撃波治療を考慮すべき人
Identifying appropriate candidates for shockwave therapy ensures optimal treatment outcomes while maximizing the therapy’s therapeutic potential. Understanding patient profiles and clinical scenarios where shockwave therapy provides maximum benefit helps guide treatment selection and patient counseling.
Ideal Candidates: Profiles and Case Examples
Individuals with chronic pain unresponsive to conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, and medications
Patients with specific conditions like plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow), and calcific tendinitis
Symptoms persisting for several months despite proper conservative care
Athletes and active individuals motivated to recover and comply with post-treatment care
Patients with overuse injuries or training-related conditions
Candidates who seek regenerative treatment while maintaining activity levels
When Alternative or Complementary Treatments Are Recommended
Patients with acute injuries may benefit from conservative care before shockwave therapy
Complex chronic pain sufferers may require multimodal treatment plans
Those with significant biomechanical issues or movement dysfunction should consider physical therapy before or alongside shockwave therapy, addressing underlying causes to improve outcomes and prevent recurrence
Combining shockwave therapy with other modalities often leads to better results in complex cases
よくある質問 (FAQ)
Shockwave therapy uses acoustic waves to stimulate cellular processes—like activating ion channels and growth factors—that promote tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and interrupt pain signals. It’s like giving your body a gentle nudge to heal itself faster.
Chronic tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, calcific shoulder tendinitis, sports overuse injuries, and even nerve-related pain respond well. It’s especially effective when traditional treatments like meds or rest haven’t worked.
Many patients notice improvements within a few sessions, but the full benefits often develop over weeks as tissue regenerates. It’s a natural healing process rather than instant numbing.
Unlike surgery, shockwave therapy is non-invasive with no downtime. It also avoids the risks of long-term medication, offering a drug-free alternative that supports healing instead of just masking pain.
Sessions typically last 10–20 minutes with mild tapping sensations. Most people can resume daily activities right away but should avoid intense exercise for 24–48 hours to optimize recovery. Ice and hydration may help with any temporary soreness.
Conclusion: Unlocking Lasting Pain Relief with Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy marks a breakthrough in pain management by offering a non-invasive, scientifically supported treatment that targets the root causes of pain. Unlike traditional methods focused mainly on symptom relief, it promotes natural healing, reduces chronic inflammation, and delivers lasting benefits. Supported by growing clinical evidence and boasting a strong safety record, shockwave therapy is becoming a valuable tool in modern, personalized pain care. Its high patient satisfaction and minimal side effects make it an appealing alternative to drugs and surgery. For those with chronic pain unresponsive to conventional treatments, shockwave therapy offers renewed hope for long-term relief and improved quality of life. Convenient and well-tolerated, it empowers patients to regain active lifestyles and overcome the challenges of persistent pain.
