Introduction: Muscle Strain and the Quest for Faster Healing
Muscle strains are among the most common injuries encountered by athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and even everyday individuals. Characterized by overstretching or tearing of muscle fibers, strains can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain that halts daily activities. Traditionally, muscle strain recovery relies on rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), which can be frustratingly slow and often insufficient for complete healing. In recent years, shockwave therapy has emerged as a promising treatment modality in sports medicine and rehabilitation. Its non-invasive nature and ability to accelerate tissue repair have sparked growing interest among clinicians and patients alike. This article explores the science behind muscle strain, the challenges in recovery, and how shockwave therapy offers a cutting-edge solution.
What Is Muscle Strain and Why It Happens
A muscle strain occurs when muscle fibers are overstretched or torn due to excessive force or tension. This injury primarily affects the muscle belly or the musculotendinous junction—the area where muscle meets tendon. Strains often result from acute incidents such as sudden movements, lifting heavy loads improperly, or overstressing the muscle beyond its capacity. Microscopic tears in the muscle fibers trigger an inflammatory response, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced function. Understanding the biomechanical forces involved and the biological response to injury is crucial for devising effective treatment strategies. The severity of the strain influences both the symptom intensity and the duration of recovery.
Traditional Muscle Recovery Is Slow and Frustrating
Conventional management of muscle strains typically revolves around conservative approaches like RICE, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity. Although these methods provide symptomatic relief, they often do not directly accelerate tissue regeneration. Muscle healing is an inherently slow process due to the complex sequence of inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling phases at the cellular level. Additionally, inadequate treatment or premature return to activity can lead to incomplete healing, chronic pain, and susceptibility to re-injury. Many patients find themselves frustrated with slow progress and seek therapies that can shorten downtime without compromising long-term outcomes.
Why Shockwave Therapy Is Gaining Ground in Sports Medicine
Shockwave therapy, or extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), utilizes acoustic waves to stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Initially developed for breaking down kidney stones, its application in musculoskeletal injuries has expanded due to its ability to promote tissue regeneration non-invasively. Unlike pharmacological treatments or invasive procedures, shockwave therapy encourages physiological repair through mechanical stimulation, enhancing blood flow and cellular metabolism. The technique has been increasingly adopted in sports medicine for managing chronic tendinopathies, muscle strains, and other soft tissue injuries, thanks to growing clinical evidence supporting its efficacy. This novel approach aligns with modern demands for effective, rapid, and minimally invasive recovery options.
Understanding Muscle Strains and Recovery Challenges
To appreciate how shockwave therapy benefits muscle strain recovery, it is essential to understand the injury’s nature, classification, and biological hurdles involved in healing.
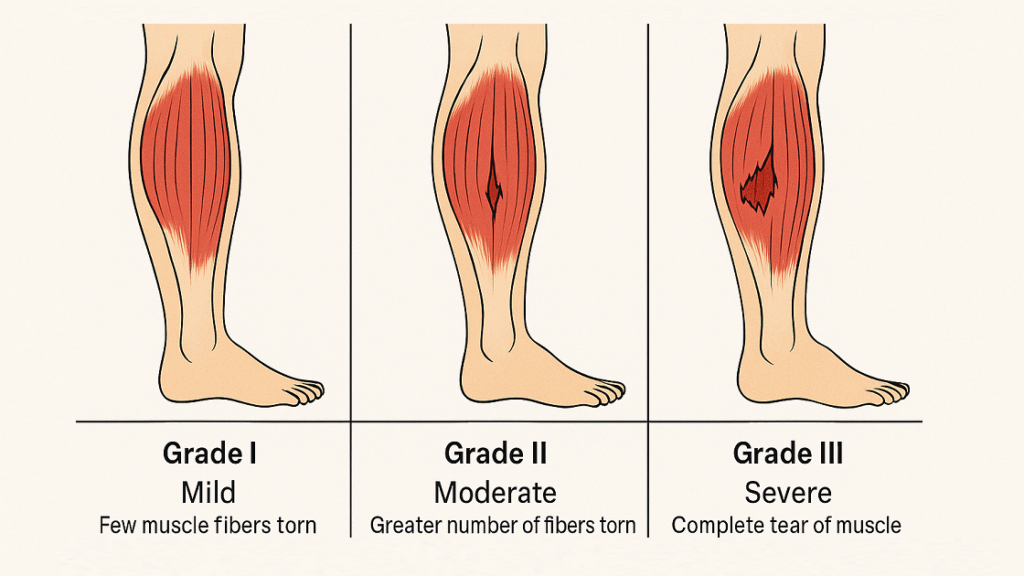
Grading Muscle Strains: Mild to Severe
Muscle strains are classified into three grades based on the extent of fiber damage. Grade I strains involve mild overstretching without significant fiber tearing, resulting in minor pain and minimal functional loss. Grade II strains include partial tears of muscle fibers, accompanied by moderate pain, swelling, and weakness, often limiting activity. Grade III strains represent complete rupture of the muscle or musculotendinous unit, causing severe pain, complete loss of function, and often requiring surgical intervention. The grade directly influences treatment choices and prognosis, with higher grades demanding longer recovery and more intensive rehabilitation.
Common Causes: Overuse, Improper Technique, Sudden Movements
Muscle strains typically arise from a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Overuse injuries occur when repetitive muscle contractions exceed the tissue’s capacity to recover, leading to microtrauma accumulation. Improper technique during sports or manual labor can place abnormal stress on muscles, increasing the risk of strain. Sudden, forceful movements—such as sprinting, jumping, or abrupt directional changes—can cause acute muscle overload and tearing. Additional risk factors include muscle fatigue, inadequate warm-up, poor flexibility, and muscle imbalances. Recognizing these causes is vital for preventive strategies and tailored treatment.
Key Symptoms: Pain, Swelling, Weakness, Limited Motion
The hallmark symptoms of muscle strain include localized pain at the injury site, which typically worsens with muscle use. Swelling and bruising may develop due to bleeding within the muscle tissue. Patients often experience muscle weakness and a noticeable reduction in range of motion. Palpation may reveal tenderness and sometimes a palpable defect in severe cases. Functional impairments vary depending on the injury’s severity and location. These symptoms significantly impact daily activities, athletic performance, and quality of life, underscoring the need for effective treatment approaches.
Why Muscle Healing Takes Time Without Intervention
Muscle healing is a biologically intricate process involving overlapping phases: inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Initially, damaged muscle fibers release chemical signals that attract inflammatory cells to clear debris. Subsequently, satellite cells—muscle stem cells—activate to proliferate and differentiate into new muscle fibers. Finally, the tissue remodels to restore strength and function. This entire process can take weeks to months, especially in severe strains. Without targeted intervention, healing may stall or result in excessive scar tissue formation, impairing muscle elasticity and increasing reinjury risk. Hence, accelerating these natural repair mechanisms is a major therapeutic goal.
What Is Shockwave Therapy for Muscle Injuries?
Shockwave therapy harnesses focused acoustic waves to stimulate tissue repair and modulate pain, providing an innovative tool for muscle strain treatment.
ESWT Explained: How Shockwave Therapy Works
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) delivers high-energy sound waves into injured tissues via a handheld applicator. These waves generate mechanical pressure pulses that propagate through soft tissues, inducing microtrauma at the cellular level. This controlled microtrauma acts as a stimulus for the body’s natural repair processes, triggering a cascade of biological responses. Unlike ultrasound therapy, shockwaves have a higher energy density and reach deeper tissues, making them especially effective for musculoskeletal injuries. Treatment parameters—such as frequency, energy flux density, and session duration—are customized according to injury severity and patient tolerance.
Acoustic Energy and Soft Tissue Regeneration
The core therapeutic effect of ESWT lies in the transmission of acoustic energy that enhances cellular activity. When shockwaves interact with muscle tissue, they increase cell membrane permeability and promote the release of signaling molecules like growth factors. These biochemical signals encourage the recruitment and proliferation of progenitor cells essential for tissue regeneration. Moreover, shockwaves stimulate angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels—improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to damaged areas. This enhanced microcirculation accelerates removal of metabolic waste and fosters an optimal environment for healing.
Core Mechanisms Behind Faster Muscle Recovery
Shockwave therapy promotes muscle repair through several synergistic mechanisms that together accelerate recovery and restore function.
Stimulating Blood Flow (Neovascularization)
One of the pivotal effects of shockwave therapy is neovascularization, the process of new capillary growth within injured tissue. Acoustic waves induce mechanical stress that activates endothelial cells lining blood vessels, leading to the secretion of angiogenic factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The resulting increase in blood vessel density enhances tissue perfusion, delivering vital oxygen and nutrients while expediting waste clearance. Improved vascularization is critical in muscle healing, as it sustains the energy-demanding processes of cellular proliferation and matrix remodeling.
Triggering Collagen Repair and Muscle Remodeling
Collagen, the main structural protein in muscles and connective tissues, plays a crucial role in restoring tensile strength after injury. Shockwave therapy stimulates fibroblasts—collagen-producing cells—to increase synthesis and deposition of organized collagen fibers. This promotes remodeling of the extracellular matrix, replacing disorganized scar tissue with functional muscle architecture. Additionally, ESWT enhances satellite cell activation, facilitating regeneration of contractile muscle fibers. Together, these processes rebuild the injured muscle’s mechanical integrity and flexibility.
Controlling Inflammation and Pain Signals
While inflammation is essential for healing, excessive or prolonged inflammatory responses can delay recovery and exacerbate pain. Shockwave therapy modulates inflammation by regulating cytokine release and immune cell activity, shifting the balance towards resolution. Furthermore, acoustic stimulation affects nociceptors—pain-sensing nerve endings—reducing their excitability and interrupting pain transmission pathways. This dual anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect not only accelerates healing but also improves patient comfort during recovery.
Benefits: How Shockwave Therapy Speeds Up Muscle Recovery
By targeting the fundamental biological processes of muscle repair, shockwave therapy offers several tangible benefits for patients suffering from muscle strains.
Rapid Inflammation Reduction and Pain Relief
Shockwave therapy’s capacity to modulate the inflammatory cascade translates into faster reduction of swelling and pain. Patients frequently report decreased discomfort shortly after treatment, enabling earlier engagement in rehabilitation exercises. This analgesic effect is partly attributed to the desensitization of peripheral nerves and the release of endogenous opioids. Faster pain relief reduces dependency on medications such as NSAIDs, which may have adverse effects when used long-term.
Improved Healing of Torn or Pulled Muscles
Clinical data indicate that shockwave therapy enhances the biological healing of muscle tears by promoting regeneration rather than scar formation. This results in more functional muscle tissue restoration, minimizing weakness and the risk of future injury. The therapy is particularly beneficial in partial muscle tears (Grade II strains), where stimulating intrinsic repair mechanisms can significantly shorten recovery timelines compared to rest alone.
Elimination of Scar Tissue and Adhesions
One common complication of muscle strain is the development of fibrotic scar tissue and adhesions that limit elasticity and cause chronic discomfort. Shockwave therapy facilitates remodeling of these pathological tissues by breaking down excessive collagen deposits and enhancing collagen realignment. This restores normal muscle pliability and prevents stiffness, improving both passive and active range of motion.
Restored Range of Motion and Flexibility
The combined effects of reduced inflammation, pain relief, and scar tissue remodeling lead to improved joint and muscle mobility. Patients experience greater flexibility and strength, enabling a safer and more effective return to daily activities or athletic performance. Enhanced range of motion also reduces compensatory movement patterns that might otherwise cause secondary injuries.
Reduced Downtime: Back to Training Faster
Ultimately, the goal of any muscle strain treatment is to minimize downtime and accelerate return to normal function. Shockwave therapy’s multifaceted biological effects can significantly shorten recovery periods, allowing athletes and active individuals to resume training sooner. This advantage not only improves patient satisfaction but also supports long-term musculoskeletal health by preventing deconditioning.
Shockwave Therapy vs Conventional Treatments
Comparing shockwave therapy with traditional approaches helps clarify its unique value proposition in muscle strain management.
Shockwave vs RICE Method: Faster Relief?
While the RICE protocol remains a first-line response for acute muscle strain, it primarily addresses symptoms rather than underlying tissue repair. Shockwave therapy complements and surpasses RICE by actively stimulating regeneration at the cellular level. Unlike passive rest and ice application, ESWT accelerates biological healing and reduces inflammation more efficiently. Patients often achieve faster pain reduction and functional recovery with shockwave treatment integrated into their rehabilitation plan.
How It Compares to Physiotherapy, Massage, and Steroid Injections
Physiotherapy and massage improve muscle flexibility, strength, and circulation but rely heavily on mechanical manipulation without directly enhancing cellular regeneration. Steroid injections reduce inflammation but carry risks such as tissue weakening and systemic side effects. Shockwave therapy offers a non-pharmacologic, minimally invasive alternative that not only reduces inflammation and pain but also promotes intrinsic tissue repair without adverse effects associated with steroids. Combining ESWT with physiotherapy can yield synergistic benefits.
Evidence-Based Recovery: What the Research Tells Us
Multiple clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of shockwave therapy in muscle strain recovery. Randomized controlled trials report significant improvements in pain scores, muscle strength, and functional outcomes compared to control groups. Meta-analyses confirm faster return to sport and lower reinjury rates. The growing body of evidence supports shockwave therapy as a scientifically validated adjunct or alternative to conventional treatments, underscoring its emerging role in musculoskeletal medicine.
Cost, Session Frequency, and Accessibility
Shockwave therapy is typically administered in outpatient settings with sessions lasting 15–20 minutes. Treatment frequency varies but generally involves 3 to 6 sessions spaced weekly. While the upfront cost may be higher than basic care, the reduced recovery time and improved outcomes can translate into long-term savings by preventing complications and lost productivity. Accessibility is increasing as more clinics adopt shockwave devices and insurance coverage expands.
Who Benefits Most from Shockwave Therapy for Muscle Strain?
Identifying the ideal candidates for shockwave therapy is crucial for tailoring treatment protocols and optimizing patient outcomes. Different populations experience muscle strain for various reasons, and shockwave therapy offers targeted benefits depending on individual needs and injury types. Understanding which groups respond best helps clinicians prioritize this innovative therapy and integrate it effectively into rehabilitation programs.
Athletes with Sports Injuries
Athletes frequently subject their muscles to intense physical loads, rapid directional changes, and high-impact forces that predispose them to acute and chronic muscle strains. These injuries can significantly disrupt training schedules and competitive seasons. Shockwave therapy provides a non-invasive treatment that accelerates tissue repair through enhanced blood flow, collagen synthesis, and inflammation reduction. Its ability to speed up recovery while reducing pain allows athletes to return to their sport faster with decreased risk of reinjury. Moreover, because ESWT sessions are relatively brief and require no downtime, athletes can maintain their conditioning and modify training rather than stopping completely. This combination of efficacy and convenience has made shockwave therapy increasingly popular in professional sports medicine and athletic rehabilitation.
Office Workers with Chronic Muscle Tension
Prolonged sitting, poor posture, and repetitive micro-movements common among office workers can lead to chronic muscle tension and microstrains, especially in the neck, shoulders, and lower back. These subtle but persistent muscle issues often cause discomfort, stiffness, and reduced productivity. Shockwave therapy addresses these problems by breaking down fibrotic tissue and adhesions that develop from chronic muscle overload. By stimulating neovascularization and enhancing circulation, ESWT improves tissue oxygenation and metabolism, which facilitates muscle relaxation and repair. This results in not only pain relief but also improved muscle elasticity and posture correction. Consequently, office workers experience enhanced comfort during daily activities and a lowered risk of progression to more severe musculoskeletal disorders.
Seniors with Age-Related Muscular Issues
Aging brings physiological changes such as decreased muscle mass (sarcopenia), reduced regenerative potential, and increased tissue stiffness, all of which increase vulnerability to muscle strains and slower recovery. Shockwave therapy offers a promising intervention to mitigate these age-related challenges. Through the stimulation of collagen remodeling and the promotion of new capillary growth, ESWT helps restore the structural integrity and functional capacity of aging muscles. Additionally, by modulating inflammatory processes and reducing fibrosis, it enhances mobility and decreases chronic pain. For elderly patients, this translates to improved muscle health, greater independence, and a better quality of life. Incorporating shockwave therapy into comprehensive geriatric rehabilitation can thus be pivotal in maintaining functional ability and preventing disability.
Post-Operative Rehab Patients
Post-surgical patients often face muscle strains and soft tissue complications during their rehabilitation due to disuse, immobilization, or surgical trauma. These factors can delay functional recovery by causing persistent pain, scar tissue formation, and limited range of motion. Integrating shockwave therapy into post-operative rehab protocols has shown to enhance healing by accelerating tissue regeneration and minimizing scar adhesions. The mechanical stimulation provided by ESWT encourages cellular repair mechanisms and improves blood supply to the operated area, facilitating a more efficient rehabilitation process. This helps patients regain muscle strength and joint flexibility sooner, leading to faster restoration of daily activities and reduced reliance on pain medications. Therefore, shockwave therapy can be an invaluable adjunct in optimizing post-surgical recovery outcomes.
What to Expect: The Patient Experience
For patients considering shockwave therapy, understanding the treatment process and anticipated outcomes is key to setting realistic expectations and ensuring adherence.
Consultation and Physical Assessment
The journey begins with a comprehensive clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging diagnostics like ultrasound or MRI to determine the injury’s severity and exclude contraindications. This assessment helps the clinician identify the precise location and extent of muscle damage and tailor a treatment plan specific to the patient’s needs. The personalized protocol includes deciding on shockwave energy levels, treatment frequency, and adjunct therapies. This initial phase is crucial for optimizing safety and efficacy, and it also provides an opportunity to educate patients about the benefits, potential discomforts, and the expected timeline for recovery.
What a Session Feels Like: Pressure or Discomfort?
During the shockwave therapy session, patients usually experience rhythmic pulses of mechanical pressure or a tapping sensation at the treatment site. The intensity can feel like mild to moderate pressure or tingling but is generally well-tolerated. Some patients may report transient discomfort, especially when treating more sensitive or inflamed areas, but this is typically brief and manageable. Therapists can adjust the energy settings and applicator placement to maximize comfort without compromising treatment effectiveness. Sessions typically last 15 to 20 minutes, allowing for focused treatment of affected muscles. This short duration and minimal discomfort contribute to the therapy’s high patient acceptance.
Number of Sessions Needed for Noticeable Results
While individual responses vary, most patients begin to notice improvements in pain levels, mobility, and muscle function after approximately 3 to 6 weekly sessions. Mild strains may respond sooner, with some patients experiencing relief after just one or two treatments. However, complete tissue remodeling and regeneration require sustained biological processes, so adherence to the recommended course is vital. Practitioners continuously monitor patient progress and may adjust the treatment plan accordingly, combining ESWT with physical therapy or other modalities as needed. Patience and consistency are key, as gradual improvements ultimately lead to full functional recovery.
Are There Any Side Effects or Risks?
Shockwave therapy is widely regarded as a safe treatment with a low risk profile. Common side effects are mild and temporary, including localized redness, minor bruising, swelling, or tenderness at the application site. These symptoms generally resolve within hours to a few days and do not require special intervention. However, certain contraindications exist, such as pregnancy, coagulation disorders, malignancies near the treatment area, or implanted electronic devices like pacemakers. Patients should disclose their full medical history during consultation. Compared to invasive procedures or long-term pharmacotherapy, ESWT’s minimal side effects and non-invasive nature make it an attractive option for many patients.

Clinical Evidence and Medical Opinions
Strong scientific backing and professional endorsements are foundational to shockwave therapy’s increasing adoption in musculoskeletal care.
Published Studies on Shockwave for Muscle Repair
A growing number of peer-reviewed studies demonstrate that shockwave therapy positively influences muscle healing at the cellular and tissue levels. Research shows enhanced regeneration of muscle fibers, decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines, and improved extracellular matrix remodeling following ESWT. Controlled trials comparing shockwave therapy with placebo or standard care report statistically significant improvements in pain reduction, muscle strength, and function. Animal studies further elucidate the mechanisms by which acoustic waves promote angiogenesis and satellite cell activation. Collectively, this robust evidence base validates shockwave therapy as a scientifically supported modality for muscle strain management.
Evidence of Shorter Recovery Time and Lower Pain Levels
Clinical trials have consistently shown that patients receiving shockwave therapy experience shorter recovery periods compared to those treated with conventional methods alone. Pain scores assessed using standardized scales (e.g., Visual Analog Scale) decrease more rapidly, enabling earlier resumption of activities. Functional outcome measures, including range of motion and strength tests, also improve faster with ESWT. These advantages translate into higher patient satisfaction, better adherence to rehabilitation programs, and reduced socioeconomic costs associated with prolonged disability or repeated injuries.
What Sports Doctors and Physiotherapists Recommend
Sports medicine physicians and physiotherapists increasingly incorporate shockwave therapy into comprehensive rehabilitation protocols for muscle injuries. They recognize its role in enhancing biological healing and managing pain without the risks of steroids or surgery. Many experts recommend early implementation of ESWT alongside active rehabilitation exercises to prevent chronic inflammation and fibrosis. Professional guidelines and consensus statements from orthopedic and sports organizations are progressively acknowledging shockwave therapy as a valuable adjunct, especially for athletes and active populations seeking rapid recovery.
Testimonials and Recovery Stories
Beyond clinical data, real-world patient experiences highlight the transformative potential of shockwave therapy. Athletes often recount accelerated return to training and competition, attributing their recovery to the therapy’s ability to reduce pain and improve muscle function. Everyday patients describe relief from persistent muscle tension and chronic discomfort, noting improved quality of life and mobility. These personal stories provide tangible evidence of ESWT’s effectiveness, fostering trust among new patients and clinicians. Testimonials complement scientific research by illustrating the therapy’s impact on diverse populations with varying injury severities.
FAQs About Shockwave Therapy and Muscle Strain
Shockwave therapy is most effective when combined with physical therapy. While ESWT accelerates tissue healing, rehabilitation exercises restore strength and flexibility, ensuring comprehensive recovery.
Shockwave therapy penetrates deep tissues and is effective for both superficial and deep muscle strains, though treatment parameters may vary.
Return timelines depend on injury severity and treatment response but are generally shorter with shockwave therapy. Your clinician will guide safe progression.
Some mild discomfort during sessions is normal, and transient soreness afterward may occur but usually resolves within a day or two.
Missing a session may slow progress but usually does not compromise overall outcomes if treatment resumes promptly.
Conclusion: Is Shockwave Therapy Worth It for Muscle Strains?
Muscle strains represent a significant hurdle for many active individuals, often accompanied by prolonged pain and functional limitations. Shockwave therapy presents a scientifically validated, non-invasive modality that accelerates biological healing, reduces inflammation, and restores muscle function. Its ability to shorten recovery time and decrease pain makes it an appealing option alongside conventional treatments. While individual responses vary, the growing clinical evidence and expert endorsements position shockwave therapy as a valuable addition to muscle strain management protocols. Patients seeking faster, safer recovery should consider discussing ESWT with their healthcare provider to optimize their rehabilitation journey.
References
- Shockwave Therapy for Muscle Strain Healing
- Shockwave Therapy’s Role in Muscle Strain Management
- The Science Behind Shockwave Therapy for Muscle Repair
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders
- The Role of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Muscle Injuries: A Systematic Review
