1. Introduction to Shockwave Therapy
Ударно-волновая терапия, также известная как экстракорпоральная ударно-волновая терапия (ESWT), is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy acoustic waves to treat various musculoskeletal conditions. Widely used for лечение боли, muscle and tendon injuries, and inflammation, this therapy has become a popular alternative to more invasive procedures like surgery.
Despite its growing popularity, a common question remains: Does shockwave therapy hurt? In this article, we will explore this question by looking at how it works, its potential for discomfort, and its overall effectiveness. Let’s dive into the world of this therapy to better understand its impact on the body.
2. How Shockwave Therapy Works
2.1 The Science Behind Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy involves delivering rapid, high-energy acoustic waves to targeted areas of the body. These waves stimulate healing by increasing blood flow, accelerating tissue repair, and reducing pain. It has been shown to be particularly effective in treating conditions like plantar fasciitis, calcific shoulder tendinopathy, and chronic tendon injuries.
The energy generated by the shockwaves penetrates deeply into the tissue, causing micro-trauma that encourages the body’s natural healing response. This mechanism promotes faster recovery times, enhanced circulation, and better tissue regeneration. While the treatment is non-invasive, understanding how it works helps us address the common concern about pain during the procedure.
2.2 Types of Shockwave Therapy
There are two main types of shockwave therapy commonly used in medical settings:
2.2.1 Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSWT)
Focused shockwave therapy targets specific areas with high precision, delivering energy deep into the tissues. It is typically used for conditions like deep muscle and tendon injuries, where concentrated energy is needed to break down calcifications and stimulate tissue repair.
2.2.2 Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT)
Unlike focused shockwaves, radial shockwaves spread out as they travel, making them effective for treating more superficial conditions. This method is commonly used for conditions like muscle tension, fascia pain, and conditions that affect the surface layers of muscle or tendon.
Both forms of therapy have proven to be effective, although the sensation and depth of treatment differ.
3. Does Shockwave Therapy Hurt?
3.1 Sensation During the Treatment
One of the key concerns for individuals considering shockwave therapy is the potential for pain. During treatment, patients may feel a pulsing or tapping sensation as the shockwaves are applied to the targeted area. The level of discomfort can vary significantly based on the area being treated, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s pain tolerance.
For some people, the treatment may feel slightly uncomfortable or mildly painful, while others may experience more intense sensations. However, the pain is typically short-lived and subsides once the treatment ends. Most individuals report that the discomfort is bearable and that the benefits of the therapy far outweigh the temporary sensations during the procedure.
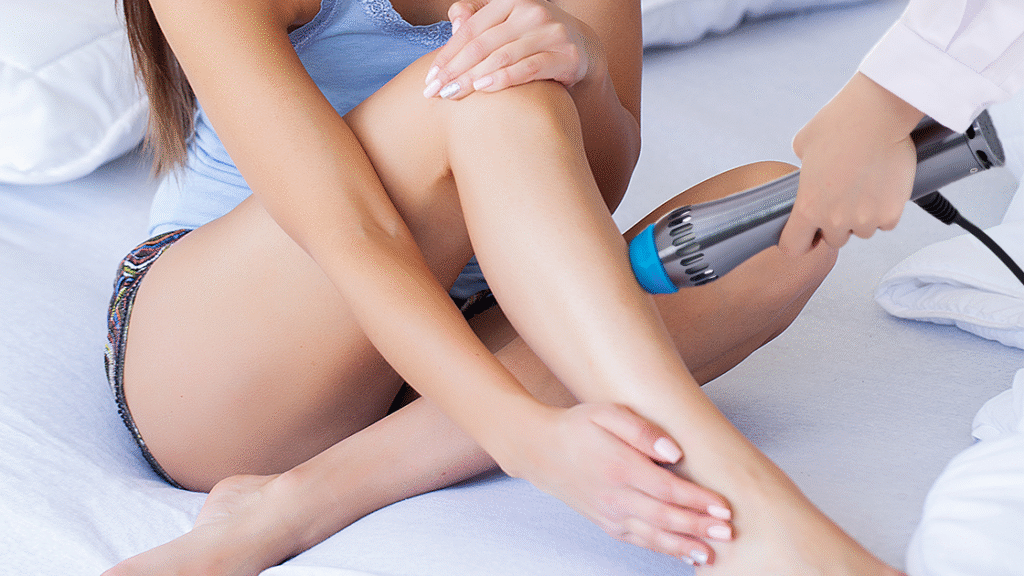
3.2 Factors That Affect Pain Levels
The level of discomfort during shockwave therapy can be influenced by several factors:
3.2.1 Treatment Area
Areas with more muscle or fat may experience less discomfort, while bony areas or tendons may cause more sensitivity. For example, treating a bony prominence like the elbow or knee can be more uncomfortable than treating larger muscle groups like the thigh.
3.2.2 Type of Injury Being Treated
Chronic injuries or conditions like calcific tendinopathy or plantar fasciitis may cause the treatment to feel more intense, especially if the tissue is inflamed or stiff. For individuals with long-standing pain, the body’s sensitivity might also affect the level of discomfort during therapy.
3.2.3 Patient’s Pain Tolerance
Pain perception is highly subjective. Some patients may have a higher pain tolerance and find the therapy tolerable, while others may perceive the treatment as more uncomfortable. Your healthcare provider can adjust the intensity of the shockwaves to ensure a more comfortable experience.
3.3 Minimizing Pain During Treatment
To make the experience more comfortable, therapists can adjust the intensity of the shockwave applied, giving the patient a more controlled and comfortable treatment. Local anesthesia or pain-relieving creams may also be used in some cases to minimize discomfort.
4. Benefits of Shockwave Therapy
Despite concerns about discomfort, shockwave offers several compelling benefits, making it a worthwhile treatment option for many individuals.
4.1 Pain Relief and Muscle Recovery
Shockwave therapy is highly effective at alleviating chronic pain. The acoustic waves stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, helping to reduce inflammation and improve tissue regeneration. This is particularly beneficial for those suffering from conditions like tendonitis, bursitis, and plantar fasciitis. Many patients report significant reductions in pain after just a few sessions.
4.2 Non-Invasive Solution
Unlike surgery or injections, shockwave therapy is non-invasive and does not require any recovery time. It provides a safe alternative to more aggressive treatments, and it can be performed on an outpatient basis. This makes it a highly attractive option for people who wish to avoid the risks and downtime associated with more invasive procedures.
4.3 Speeding Up Healing and Tissue Repair
One of the most remarkable benefits of shockwave is its ability to accelerate tissue healing. By stimulating circulation and promoting collagen production, shockwave helps the body heal damaged tissue more quickly, reducing the recovery time for injuries. This makes it an effective treatment for both acute injuries and chronic conditions.
5. Is Shockwave Therapy Right for You?
5.1 Considerations Before Undergoing Treatment
Before opting for shockwave therapy, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional. This therapy may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with certain medical conditions like blood clotting disorders or infections. Your doctor will assess your condition and determine whether it is the right treatment for you.
5.2 Post-Treatment Care
After undergoing shockwave therapy, patients may experience mild soreness or tenderness in the treated area. This is a normal response and typically resolves within a few hours to a day. It is advisable to avoid strenuous physical activities for a short period following treatment to allow the body to heal.
6. Conclusion: Is Shockwave Therapy a Good Choice?
In conclusion, while shockwave therapy may cause mild to moderate discomfort during the procedure, it is generally well-tolerated and offers numerous benefits, including pain relief, faster recovery times, and a non-invasive solution to chronic injuries. The sensation during treatment can vary, but with proper adjustments and careful consideration, most patients find the therapy to be manageable.
Shockwave therapy provides an effective alternative to surgery and medication, especially for musculoskeletal pain and injuries. As always, consult with your healthcare provider to determine if it is the right option for your specific needs.
7. References
“A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms and Applications,” Journal of Musculoskeletal Medicine.
(https://www.journals.sagepub.com)
“Efficacy of Shockwave in Treating Chronic Tendon and Fascia Disorders,”
“Shockwave Therapy in Orthopedics: An Overview,” Orthopedic Research and Reviews. https://www.dovepress.com
