Введение
Achilles tendinopathy is one of the most common overuse injuries among athletes, particularly runners, basketball players, and other high-intensity sport participants. The injury is characterized by pain, swelling, and stiffness along the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Traditional treatments, such as rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in severe cases, surgery, often require long recovery periods and may not fully restore tendon function. Recently, ударно-волновая терапия (SWT) has emerged as a non-invasive, scientifically supported treatment that accelerates tissue healing, reduces pain, and improves function. This blog explores how shockwave therapy works for Achilles tendinopathy in athletes, its clinical applications, recovery timelines, and frequently asked questions. By understanding this advanced therapy, athletes and clinicians can make informed decisions about tendon rehabilitation.
1. Understanding Achilles Tendinopathy
1.1 What Is Achilles Tendinopathy?
Achilles tendinopathy is a chronic condition resulting from microtears in the tendon fibers, collagen degeneration, and local inflammation. Unlike acute injuries, tendinopathy develops gradually, often due to repetitive stress and overuse. It can affect either the mid-portion of the tendon or its insertion at the heel bone, with each location presenting slightly different symptoms and rehabilitation challenges. Understanding the underlying pathology is crucial for selecting an effective treatment modality, as conventional therapies may only address symptoms rather than tissue repair. Shockwave therapy offers a biological approach by stimulating natural healing processes at the cellular level, providing athletes with an innovative alternative to traditional methods.
1.2 Causes and Risk Factors for Athletes
Athletes are particularly prone to Achilles tendinopathy due to repetitive high-impact activities. Risk factors include:
- Overtraining: Sudden increases in intensity, volume, or frequency of training.
- Biomechanical issues: Poor running form, flat feet, or high arches increasing tendon strain.
- Age: Tendon elasticity decreases with age, making it more susceptible to microtears.
- Previous injuries: Past tendon or calf injuries can predispose athletes to recurrence.
Recognizing these risk factors is essential for prevention and rehabilitation planning. Shockwave therapy is especially beneficial for athletes because it addresses the tendon at a cellular level, improving collagen synthesis and tissue remodeling, which are critical for both recovery and future injury prevention.
2. How Shockwave Therapy Works for Tendinopathy
2.1 The Science Behind ESWT
Shockwave therapy utilizes high-energy acoustic waves to target damaged tendon tissue. These waves stimulate several physiological responses:
- Increased blood flow: Enhanced microcirculation delivers more oxygen and nutrients to the injured site.
- Collagen synthesis: Activation of fibroblasts promotes tendon remodeling and structural repair.
- Pain modulation: Shockwaves reduce the concentration of inflammatory mediators and stimulate the release of endorphins.
This combination of mechanical and biological effects helps accelerate tendon healing, reduce chronic pain, and restore function. ESWT differs from traditional therapies in that it directly influences tissue regeneration rather than merely alleviating symptoms.
2.2 Benefits Over Traditional Treatments
Compared to rest, physical therapy, or anti-inflammatory medications, shockwave therapy offers multiple advantages:
- Non-invasive: No incisions, anesthesia, or injections required.
- Accelerated recovery: Promotes tissue regeneration at a faster rate than conventional methods.
- Reduced risk of re-injury: Strengthens the tendon through improved collagen organization.
- Complementary therapy: Can be combined with stretching, strengthening, and proprioceptive training for optimal results.
For athletes, these benefits mean a faster return to training and competition with reduced downtime, making shockwave therapy an appealing option for both amateur and professional sports participants.
3. Clinical Application for Athletes
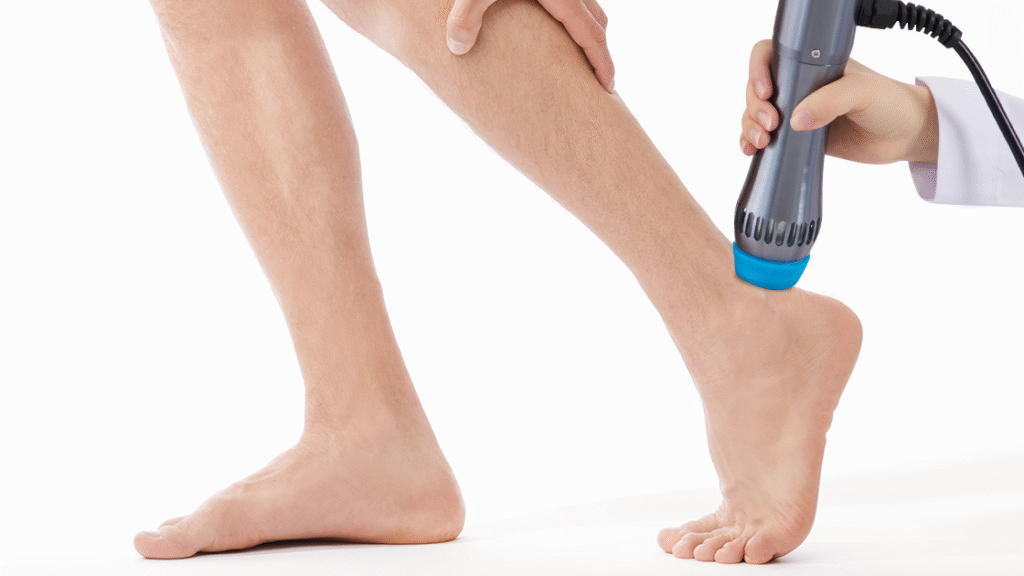
3.1 Typical Treatment Protocol
A standard shockwave therapy protocol for Achilles tendinopathy involves:
- Frequency: Typically 1–2 sessions per week.
- Duration: Each session lasts approximately 15–20 minutes, depending on the injury location and severity.
- Energy settings: Clinicians adjust intensity and frequency based on the tendon’s condition and patient tolerance.
Mid-portion tendinopathy may require slightly different parameters compared to insertional injuries. Athletes can often begin light mobility exercises between sessions, allowing early engagement without compromising tendon healing. By targeting the tendon directly with focused acoustic waves, shockwave therapy promotes structural remodeling, pain relief, and improved tendon function.
3.2 Pre-Treatment and Post-Treatment Care
To maximize efficacy, proper preparation and aftercare are essential:
- Pre-treatment: Keep the area clean and avoid applying creams or lotions. Athletes should avoid high-intensity training immediately before sessions.
- Post-treatment: Light stretching, hydration, and avoiding strenuous activity for 24–48 hours are recommended. Gradual return to sport-specific exercises ensures safe progression.
Combining shockwave therapy with physical therapy, eccentric calf exercises, and proper footwear enhances long-term outcomes. Athletes are often able to resume low-impact training soon after treatment while continuing tendon remodeling under reduced pain conditions.
4. Recovery and Expected Outcomes
4.1 Pain Reduction and Function Improvement
Clinical studies and anecdotal evidence show that ESWT effectively reduces tendon pain and improves functional outcomes in athletes. The therapy targets the entire tendon structure, including microtears that conventional methods might overlook. Many athletes report noticeable pain relief after just a few sessions, with gradual improvements in strength, flexibility, and mobility.
Moreover, the biological stimulation provided by shockwaves helps restore the tendon’s natural mechanical properties, allowing athletes to perform high-impact movements with confidence. By improving tissue quality, ESWT not only alleviates symptoms but also addresses the root cause of chronic tendinopathy.
4.2 Timeline for Returning to Training
Recovery timelines vary based on injury severity, athlete age, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols:
- Mild tendinopathy: Return to full training in 4–6 weeks.
- Moderate tendinopathy: Approximately 6–10 weeks with combined physical therapy.
- Severe or chronic cases: May require 10–12 weeks of treatment with structured progressive loading exercises.
During this period, ESWT sessions are typically spaced 1–2 times per week. Athletes should follow a gradual training ramp-up, integrating flexibility and eccentric strengthening exercises to ensure optimal tendon adaptation and prevent recurrence.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is Shockwave Therapy painful for Achilles tendinopathy?
Most patients feel mild discomfort or tingling during treatment. Pain is usually temporary and well-tolerated.
How many sessions are required for athletes?
Typically 3–6 sessions are needed, depending on injury severity and response to treatment.
Are there any side effects or contraindications?
Minor bruising, redness, or tenderness may occur. Contraindications include pregnancy, active infections, cancerous lesions, and blood clotting disorders.
Can ESWT replace physical therapy entirely?
No, it is most effective when combined with stretching, strengthening, and functional rehabilitation programs.
6. Conclusion
Shockwave therapy is a powerful, non-invasive treatment for Achilles tendinopathy in athletes. By stimulating collagen synthesis, enhancing blood flow, and reducing inflammation, ESWT accelerates tendon healing and improves function. When integrated with structured rehabilitation programs, athletes can achieve faster pain relief, reduced risk of re-injury, and a safe return to high-intensity sports. For professional and amateur athletes alike, shockwave therapy offers an evidence-based alternative to prolonged rest, medication, or invasive surgery.
Ссылки
Shockwave Machines. “Indications for Shockwave Therapy.”
https://www.shockwavemachines.com/indications
Gerdesmeyer L, et al. “Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis.” Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 2008.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18378843
Rompe JD, et al. “Shock wave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial.” The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 2007.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17122321
Speed C. “Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy in the management of chronic soft-tissue conditions.” Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 2004.
