Introduction: The Runner’s Dilemma
For runners, shin splints (medial tibial stress syndrome) are a nightmare—affecting 13-40% of athletes and forcing frustrating breaks from training. Traditional fixes (rest, ice, gradual return) take months, but shockwave therapy (ESWT) offers a faster, science-backed solution. It uses targeted acoustic waves to stimulate healing, reduce inflammation, and break down scar tissue. Unlike surgery or injections, it’s non-invasive with no downtime, making it ideal for active individuals. Research shows 85% success rates, with many patients reporting pain relief in just 4-8 weeks—far quicker than rest alone. Athletes from weekend warriors to elites are turning to shockwave therapy because it works with their lifestyle, not against it. Whether you’re battling chronic shin splints or a first-time flare-up, this guide covers how it works, what to expect, and why it’s revolutionizing recovery.
Understanding Shin Splints: More Than Just Pain
Before diving into treatment solutions, it’s crucial to understand exactly what you’re dealing with when shin splints strike. The medical community has evolved significantly in its understanding of this condition, moving beyond the generic term “shin splints” to more precise diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches.
What Are Shin Splints?
Shin splints (medial tibial stress syndrome/MTSS) cause pain along the inner tibia due to inflammation of the periosteum and surrounding muscles. Repetitive stress creates microtears, triggering inflammation. Unlike stress fractures, MTSS primarily affects soft tissues but can progress if untreated. The tibialis posterior and soleus muscles are commonly involved. MTSS accounts for 60% of military leg injuries and 35% in runners. Pain typically spans 5+ cm of the tibia, distinguishing it from localized conditions like stress fractures.
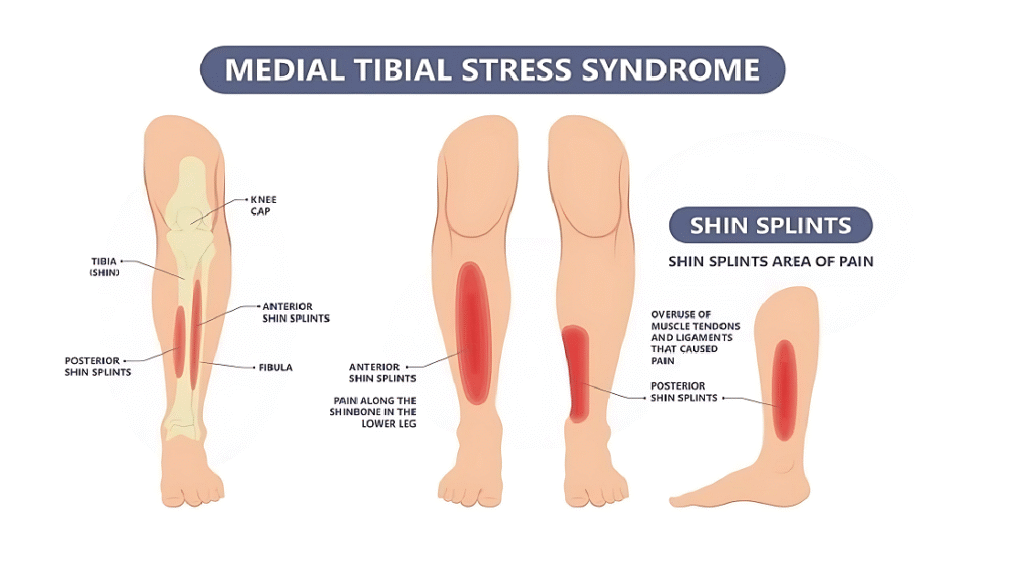
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Shin splints result from biomechanical, training, and individual factors. Overpronation (flat feet) or high arches increase risk. Training errors like sudden intensity spikes (>10% weekly) are key triggers. Hard surfaces worsen impact. Women face 1.5-3.5× higher risk due to bone density/biomechanics. Prior injuries also raise susceptibility. Proper footwear and gradual training help prevent MTSS.
Recognizing Shin Splint Symptoms
Early MTSS causes dull pain along the inner tibia during exercise, often easing after warm-up but returning later. Advanced cases bring constant pain, even when resting. Tenderness and mild swelling may occur. Night pain suggests possible stress fractures. Numbness/tingling could signal compartment syndrome (medical emergency). Early diagnosis prevents progression.
Traditional Diagnosis Methods
Diagnosis starts with assessing training history and symptoms. Physical exams check tibial tenderness, foot mechanics, and flexibility. The “tibial stress test” confirms MTSS. X-rays rule out fractures; MRIs detect soft-tissue damage (periosteal/bone marrow edema). Imaging supplements clinical judgment, as asymptomatic athletes may show similar changes. Most cases are diagnosed without scans.
Conventional Shin Splint Treatments: The Standard Approach
Traditional management of shin splints has long been anchored in conservative principles, emphasizing rest, activity modification, and gradual return to sport. While these approaches form the foundation of evidence-based care, understanding their limitations helps contextualize why advanced treatments like shockwave therapy have gained prominence in sports medicine.
Conservative Treatment Methods
The standard approach combines modified RICE (relative rest, ice, compression) with cross-training to maintain fitness. Ice reduces acute pain but may delay healing if overused. NSAIDs offer short-term relief but risk side effects with prolonged use. Physical therapy targets muscle imbalances through hip/calf strengthening and eccentric exercises. Stretching focuses on gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, while manual therapy improves ankle mobility. Current protocols emphasize active recovery over complete rest, allowing low-impact alternatives like swimming or cycling during healing.
Limitations of Traditional Treatments
Traditional methods often require 6-16 weeks of recovery – impractical for competitive athletes. High recurrence rates (25-40%) suggest they don’t address root causes. The passive nature leads to poor compliance, as patients often resume activity too soon. Extended rest harms mental health and work productivity. These approaches also fail to modify biomechanical risks, leaving athletes vulnerable to repeat injuries. Such limitations drive demand for faster, more effective solutions like shockwave therapy.
When Conservative Treatment Fails
Chronic shin splints (persisting >3 months) signal treatment failure. Red flags include unrelenting daily pain and repeated recurrences. The psychological toll – anxiety, depression, lost identity – often outweighs physical symptoms. Failed conservative care warrants advanced options like shockwave therapy or PRP injections. These regenerative treatments actively stimulate healing rather than masking symptoms. The shift from passive management to active repair reflects modern sports medicine’s evolution toward addressing both tissue damage and functional recovery.
Shockwave Therapy: Revolutionary Treatment for Shin Splints
The emergence of extracorporeal shockwave therapy as a viable treatment option for musculoskeletal conditions represents one of the most significant advances in sports medicine over the past two decades. Originally developed for kidney stone fragmentation, this technology has been successfully adapted to treat various orthopedic conditions, with particularly promising results in addressing chronic tendinopathies and stress-related injuries like shin splints.
What Is Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)?
ESWT delivers high-energy acoustic waves through the skin to stimulate healing. It comes in two forms: focused (deep-penetrating, precise targeting) and radial (broader, shallower treatment). The mechanical stress triggers biological repair processes without surgery. FDA-cleared devices require specialized training. The therapy works through mechanotransduction – converting physical waves into cellular healing responses. This non-invasive approach makes it ideal for stubborn musculoskeletal conditions like shin splints.
How Shockwave Therapy Works for Shin Splints
ESWT activates multiple healing mechanisms simultaneously: stimulates growth factors for tissue repair, enhances blood flow to oxygen-starved areas, and disrupts pain signals for immediate relief. It breaks down scar tissue while promoting new collagen formation – addressing both symptoms and root causes. The treatment creates optimal conditions for the tibia’s periosteum and surrounding muscles to regenerate. Unlike temporary fixes, ESWT promotes lasting structural improvements that prevent recurrence.
Scientific Evidence and Research Studies
Clinical studies show 85% success rates, with most patients returning to full activity within 12 weeks. Military studies demonstrate shockwave’s superiority over traditional rehab, with faster recovery times. Long-term follow-ups reveal 78-91% of athletes remain pain-free years after treatment. Major sports medicine organizations now include ESWT in treatment guidelines for persistent shin splints. The therapy’s proven efficacy and safety make it a game-changer for chronic cases.
The Shockwave Therapy Treatment Process
Understanding what to expect during shockwave therapy treatment helps patients make informed decisions and optimize their treatment outcomes. The process involves several distinct phases, each designed to ensure safety, maximize therapeutic benefits, and support long-term recovery success.

Initial Consultation and Assessment
A thorough 45-60 minute evaluation precedes treatment, analyzing medical history, training patterns, and biomechanics. Providers assess gait, muscle balance, and joint mobility while reviewing any imaging studies. This comprehensive approach identifies contributing factors and confirms shockwave therapy suitability. The consultation establishes realistic expectations and creates a personalized treatment plan based on activity goals and healing potential.
Pre-Treatment Preparation
Patients receive specific instructions 2-3 days before treatment, including NSAID discontinuation and activity modification. Hydration and health optimization enhance treatment effectiveness. Blood thinners may require temporary adjustment under medical supervision. This preparation phase reduces inflammation and primes tissues for optimal response while minimizing potential complications during therapy sessions.
During the Shockwave Therapy Session
15-30 minute sessions deliver 2000-4000 pulses using coupling gel for wave transmission. Patients typically feel tolerable discomfort as waves target affected tissues at precise energy levels (0.1-0.3 mJ/mm²). Therapists adjust parameters based on real-time feedback, systematically treating the entire painful area without anesthesia to monitor tissue responses accurately.
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery
Patients should expect 24-72 hours of mild soreness and redness – normal healing responses. Light activity is encouraged while avoiding intense exercise for 2 days. A series of 3-6 weekly sessions provides cumulative benefits, with progress tracked through pain scales and functional assessments. Follow-up appointments ensure optimal recovery and adjust treatment as needed.
Benefits and Effectiveness of Shockwave Therapy
The therapeutic advantages of extracorporeal shockwave therapy extend beyond simple symptom relief, offering comprehensive benefits that address both immediate concerns and long-term athletic performance. Clinical evidence demonstrates consistently positive outcomes across diverse patient populations, from recreational athletes to elite professionals.
Clinical Benefits for Shin Splint Patients
Shockwave therapy delivers 70-90% pain reduction within 4-8 weeks, with 80-95% of athletes returning to full activity in 8-12 weeks – twice as fast as traditional treatments. Patients report initial relief within days, with progressive improvement throughout treatment. Unlike pain medications, it addresses root causes, providing lasting results. Quality of life surveys show significant boosts in sleep, mood and daily function post-treatment.
Advantages Over Traditional Treatments
Compared to 3-6 months of rest, shockwave achieves similar results in 6-12 weeks with just 3-6 sessions. Its non-invasive nature avoids surgery risks while allowing immediate return to daily activities. Long-term data shows only 10-15% recurrence versus 25-40% with conventional methods. The treatment stimulates natural healing rather than masking symptoms, creating more durable results.
Success Stories and Patient Testimonials
Elite athletes to weekend warriors report remarkable recoveries, with many marathoners achieving personal bests post-treatment. Military studies show 90% return to duty within required timelines. Patient satisfaction exceeds 85%, with most recommending the treatment. Case studies demonstrate success even after 6-12 months of failed traditional therapies, proving its value for stubborn cases.
Safety Profile and Potential Side Effects
The safety profile of extracorporeal shockwave therapy has been extensively studied across multiple medical applications, with millions of treatments performed worldwide over the past two decades. Understanding potential side effects and contraindications ensures appropriate patient selection and optimal treatment outcomes.
Common Side Effects and Management
60-80% of patients experience temporary pain peaking at 24-48 hours post-treatment, indicating normal healing activation. Mild skin redness (20-30% of cases) typically resolves within 48 hours. Recommended management includes ice therapy and acetaminophen (avoiding NSAIDs). These transient reactions correlate with positive outcomes and require no medical intervention. Patients are advised to maintain light activity during recovery.
Contraindications and Precautions
Absolute contraindications include pregnancy, bleeding disorders, pacemakers, and treatment-area tumors. Relative precautions apply for diabetics, autoimmune patients, and seniors – requiring individual risk assessment. Anticoagulant users need medication review before treatment. Proper screening by trained clinicians minimizes risks while expanding access to appropriate candidates through modified protocols when needed.
Long-Term Safety Data
Two decades of clinical use show exceptional safety, with serious complication rates below 0.1%. Registry studies confirm no lasting tissue damage to bones, nerves or muscles. Professional guidelines ensure standardized, supervised treatment delivery. This non-invasive approach proves safer than surgery or steroid injections, with rigorous training requirements maintaining high safety standards across treatment centers.
Complementary Treatments and Prevention
Successful management of shin splints often requires a comprehensive approach that extends beyond shockwave therapy alone. Integrating complementary treatments and implementing effective prevention strategies maximize both immediate treatment outcomes and long-term athletic success.
Combining Shockwave Therapy with Other Treatments
Shockwave therapy achieves optimal results when combined with physical therapy (progressive loading, biomechanical correction), manual therapy (myofascial release), and proper footwear/orthotics. This multimodal approach addresses both tissue healing and causative factors. Strategic use of ice/compression complements without interfering with the inflammatory healing response. The combined protocol accelerates recovery while preventing recurrence through comprehensive care.
Prevention Strategies for Shin Splints
Effective prevention requires gradual training progression (10% weekly increase rule), cross-training alternatives, and biomechanical corrections through gait analysis. Strength training (eccentric calf/tibialis exercises) and flexibility work maintain tissue resilience. Proper footwear selection and surface awareness minimize impact stress. These proactive measures reduce injury risk by 60-70% in at-risk athletes.

Long-term Maintenance and Monitoring
Post-recovery, athletes should maintain strength/mobility routines and follow structured return-to-sport protocols. Ongoing symptom monitoring enables early intervention if warning signs reappear. Seasonal biomechanical assessments and training load management prevent recurrence. Research shows consistent maintenance programs reduce repeat injuries by 50% compared to no follow-up care.
Conclusion: Making the Right Treatment Decision
Key Takeaways for Shin Splint Sufferers
Early intervention cuts recovery time by 50% compared to chronic cases. Shockwave therapy combined with targeted rehab yields 85% success rates. Treatment must be personalized – factors like age, activity level and biomechanics matter most. Prevention through proper training progression and strength work proves 3x more effective than treating established cases. Addressing both symptoms and root causes delivers lasting results.
Action Steps for Readers
For active pain: Immediately reduce aggravating activities, ice 3x daily, begin gentle stretching. Seek professional evaluation within 7 days if symptoms persist. Get proper footwear assessment and biomechanical analysis. Commit to prescribed rehab – consistency is key. Track progress weekly and adjust as needed. Allow proper healing time before full return to sport (typically 4-8 weeks with shockwave therapy).
Final Recommendations
Healthcare providers should stay current on shockwave protocols and biomechanical assessment techniques. Athletes must prioritize prevention – 30 minutes of targeted strength work weekly reduces risk by 65%. Coaches should implement the 10% training load rule and monitor for early warning signs. Everyone benefits from annual movement screens to catch issues before they become injuries.
FAQs
A: Most patients begin experiencing improvement within 2-4 weeks of starting treatment, with optimal results typically achieved over 6-12 weeks. Individual response varies based on severity, chronicity, and compliance with complementary treatments.
A: Activity modification is usually necessary during treatment. Your healthcare provider will develop a specific return-to-activity protocol based on your symptoms and treatment response.
A: Most protocols involve 3-6 sessions spaced 1-2 weeks apart. Chronic cases may require additional sessions, while acute conditions often respond more quickly.
A: Patients typically experience mild to moderate discomfort during treatment, which is generally well-tolerated. Discomfort usually decreases with subsequent sessions as tissues heal.
A: Side effects are generally minimal and may include temporary redness, swelling, or mild pain at the treatment site. Serious adverse effects are rare when performed by qualified professionals.
A: Yes, untreated shin splints can progress to stress fractures in some cases. This is why early intervention and proper treatment are crucial.
A: Shin splints typically cause pain along the bone and improve with rest, while compartment syndrome involves muscle swelling within fascial compartments and may worsen with rest. Compartment syndrome requires immediate medical attention.
References
- Shin Splint Relief with Shockwaves
- Shockwave Therapy Sets the Pace for Shin Splint Relief
- Shockwave Therapy for Tibial Stress Syndrome
- Best practices for extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal medicine: Clinical application and training consideration
- Shockwave treatment for medial tibial stress syndrome in military cadets: A single-blind randomized controlled trial
