Introduction: The Lower Back Pain Crisis
Lower back pain is a global health crisis, affecting over 619 million people in 2020—a number expected to reach 843 million by 2050. With a lifetime prevalence nearing 84% in developed countries, it’s the leading cause of disability worldwide. The burden extends beyond pain, affecting work productivity, mental health, and quality of life, while driving over $100 billion in annual healthcare costs in the U.S. alone. Traditional treatments like painkillers, physical therapy, and surgery often provide incomplete relief or come with significant risks. As frustration grows with limited outcomes, innovation in pain management is accelerating. One promising advancement is extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT)—a non-invasive technique that stimulates the body’s natural healing response. Once used for kidney stones, ESWT now offers a mechanical, regenerative approach to treating chronic lumbar back pain, aiming to break the cycle of pain without surgery or long-term medication reliance.
Understanding Shockwave Therapy: Science Made Simple
To appreciate the therapeutic potential of shockwave therapy for lumbar back pain, it’s essential to understand the fundamental principles underlying this innovative treatment modality. The science behind ESWT combines advanced physics with biological healing mechanisms to create a unique therapeutic approach.
What is Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)?
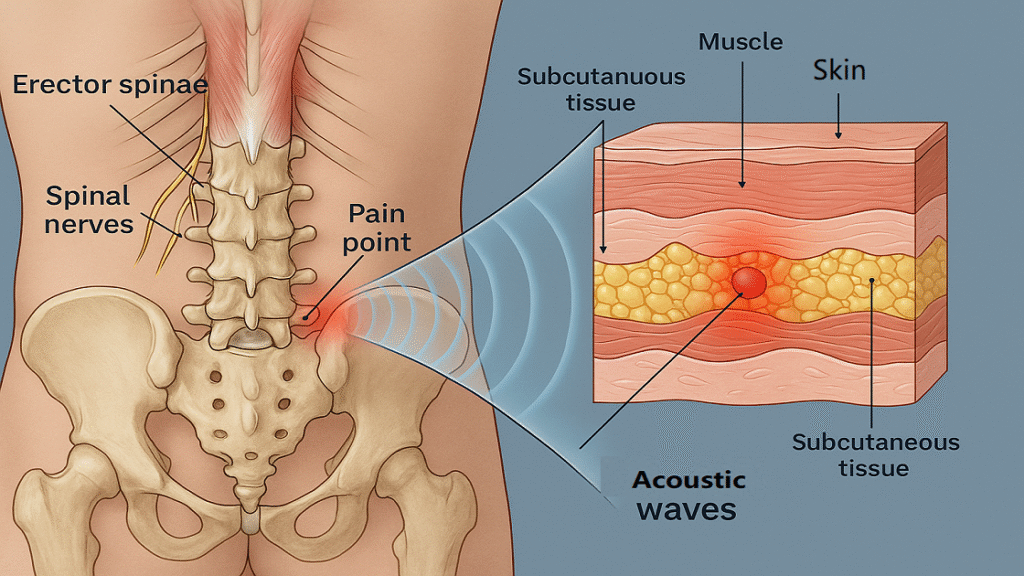
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy utilizes high-energy acoustic waves generated outside the body and transmitted through skin and soft tissues to target specific anatomical structures. These acoustic waves are characterized by rapid pressure changes that create mechanical stress within tissues, triggering various biological responses. The term “extracorporeal” literally means “outside the body,” distinguishing this approach from invasive procedures. Modern ESWT devices can generate focused or radial shockwaves, each with distinct penetration depths and energy distributions suitable for different clinical applications.
How Shockwave Therapy Works for Lower Back Pain
The therapeutic mechanisms of shockwave therapy for lower back pain involve complex interactions between mechanical energy and biological tissues. Understanding these processes provides insight into why ESWT can be effective where other treatments may fail.
Acoustic Wave Penetration and Tissue Stimulation
It represents the primary mechanism through which shockwave therapy exerts its therapeutic effects. When high-energy acoustic waves penetrate lumbar tissues, they create controlled mechanical stress that stimulates cellular metabolism and tissue regeneration. The waves can penetrate up to 12 centimeters deep, reaching muscles, fascia, ligaments, and even bone structures within the lumbar spine. This deep penetration allows treatment of structures that are typically difficult to access through conventional physical therapy techniques.
Neovascularization and Tissue Regeneration
It occur as direct responses to shockwave stimulation. The mechanical stress induced by acoustic waves triggers the release of growth factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). These growth factors promote the formation of new blood vessels (neovascularization) within treated tissues, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to previously hypoxic areas. Enhanced circulation facilitates tissue repair, reduces inflammation, and promotes healing of degenerative structures commonly associated with chronic lower back pain.
The Pain Gate Theory and Neurological Effects
They explain how ESWT can provide immediate and long-term pain relief. According to the gate control theory of pain, non-painful stimuli can inhibit pain signal transmission to the brain. Shockwave therapy activates large-diameter nerve fibers that effectively “close the pain gate,” reducing pain perception. Additionally, ESWT may influence substance P levels and other neurotransmitters involved in pain processing, creating both immediate analgesic effects and long-term pain modulation.
Biological Mechanisms Behind Pain Relief
The biological mechanisms underlying ESWT’s pain-relieving effects involve multiple interconnected pathways that address both symptoms and underlying pathophysiology of chronic lower back pain.
Anti-Inflammatory Response Activation
It occurs through several mechanisms following shockwave treatment. ESWT stimulates the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines while simultaneously reducing pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). This shift in the inflammatory milieu helps resolve chronic inflammation that often perpetuates lower back pain. Additionally, shockwave therapy may influence macrophage polarization, promoting the transition from pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages to anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages, which facilitate tissue repair and healing.
Collagen Synthesis and Tissue Repair
They represent crucial mechanisms for addressing structural abnormalities associated with chronic lower back pain. Shockwave therapy stimulates fibroblast activity and collagen production, leading to improved tissue quality and mechanical properties. This is particularly important in treating conditions involving fascia, tendons, and ligaments that support the lumbar spine. Enhanced collagen synthesis can help restore normal tissue architecture and improve the load-bearing capacity of spinal support structures.
Endogenous Pain Modulation Pathways
They are activated through ESWT’s influence on the nervous system. Treatment can stimulate the release of endorphins and other endogenous opioids, providing natural pain relief without the side effects associated with pharmaceutical opioids. Furthermore, shockwave therapy may influence central pain processing mechanisms, potentially reducing central sensitization that often complicates chronic pain conditions. This neuroplasticity effect can lead to lasting improvements in pain perception and functional capacity.
Clinical Evidence: What Research Says About ESWT for Back Pain
The clinical evidence supporting shockwave therapy for lower back pain has grown substantially over the past decade, with numerous high-quality studies demonstrating its efficacy and safety. This body of research provides the foundation for evidence-based clinical decision-making and helps establish ESWT as a viable treatment option for appropriate patients.
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have provided comprehensive evaluations of ESWT effectiveness for lower back pain. A 2023 systematic review analyzing 15 randomized controlled trials involving over 1,200 patients found significant improvements in pain intensity and functional outcomes following ESWT treatment. The pooled analysis demonstrated a mean reduction in Visual Analog Scale (VAS) pain scores of 3.2 points compared to control groups, representing clinically meaningful improvement. Additionally, functional disability scores improved by an average of 12.4 points on standardized outcome measures, indicating substantial enhancement in daily living activities and work capacity.
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
Multiple high-quality randomized controlled trials have specifically examined ESWT for chronic lower back pain, providing robust evidence for its therapeutic benefits. A landmark study published in the Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine randomized 120 patients with chronic non-specific lower back pain to receive either ESWT or sham treatment over a 4-week period. Results demonstrated significant improvements in pain intensity, functional capacity, and quality of life measures in the ESWT group compared to controls. Importantly, these improvements persisted at 3-month and 6-month follow-up evaluations, suggesting lasting therapeutic benefits. Treatment response rates exceeded 70% in the active treatment group, with over 40% of patients experiencing greater than 50% pain reduction.
Comparative Studies: ESWT vs. Traditional Treatments
Comparative effectiveness research has evaluated ESWT against established treatment modalities, providing valuable insights into its relative benefits and positioning within comprehensive pain management strategies. Studies comparing ESWT to conventional physical therapy have shown superior outcomes for shockwave treatment in terms of pain reduction and functional improvement. When compared to corticosteroid injections, ESWT demonstrated comparable short-term pain relief with superior long-term outcomes and fewer adverse effects. Notably, combination approaches incorporating ESWT with traditional therapies often yielded the best overall results, suggesting synergistic therapeutic effects rather than replacement of existing treatments.
Conditions Treated: When Shockwave Therapy Works Best
Understanding the specific conditions and patient populations that respond optimally to shockwave therapy is crucial for maximizing treatment success and patient satisfaction. Clinical experience and research evidence have identified several lower back pain conditions that demonstrate particularly favorable responses to ESWT.

Chronic Non-Specific Lower Back Pain
Chronic non-specific lower back pain represents the most common indication for ESWT treatment, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. This condition is characterized by persistent pain lasting longer than 12 weeks without identifiable structural pathology on imaging studies. Patients typically experience deep, aching pain that may be accompanied by muscle stiffness, reduced range of motion, and functional limitations. ESWT has shown remarkable efficacy in this population, with success rates ranging from 65-80% across multiple clinical studies. The treatment appears particularly effective for patients who have failed to respond adequately to conservative management including physical therapy, medications, and activity modification.
Mechanical Lower Back Pain Syndromes
Mechanical lower back pain syndromes encompass a group of conditions related to abnormal movement patterns, postural dysfunction, and biomechanical imbalances within the lumbar spine and surrounding structures. These conditions often involve fascial restrictions, muscle imbalances, and joint dysfunction that create pain and movement limitations. ESWT’s ability to address soft tissue restrictions while promoting tissue remodeling makes it particularly well-suited for treating mechanical pain syndromes. Clinical outcomes in this population demonstrate significant improvements in spinal mobility, movement quality, and functional capacity following ESWT treatment protocols.
Myofascial Pain and Trigger Points
Myofascial pain syndrome involving the lumbar region presents with characteristic trigger points within affected muscles and associated referred pain patterns. These hyperirritable spots within muscle tissue can perpetuate pain cycles and contribute to movement dysfunction. ESWT has demonstrated exceptional efficacy in treating myofascial trigger points, with studies showing rapid deactivation of trigger points and resolution of referred pain patterns. The mechanical disruption of trigger point pathophysiology through shockwave energy appears to break the cycle of muscle contraction and ischemia that maintains these painful spots.
Post-Surgical and Injury-Related Back Pain
Patients experiencing persistent pain following lumbar spine surgery or traumatic injury represent a challenging clinical population that often demonstrates favorable responses to ESWT. Post-surgical pain may result from scar tissue formation, altered biomechanics, or incomplete healing of soft tissues. ESWT’s ability to promote tissue remodeling and improve circulation can help address these underlying factors contributing to persistent pain. Similarly, injury-related back pain involving soft tissue damage, muscle strains, or fascial tears may benefit from the regenerative effects of shockwave therapy, particularly when conventional treatments have provided limited relief.
Treatment Protocol: What to Expect During ESWT
Understanding the comprehensive treatment protocol for ESWT helps patients prepare for therapy and establishes realistic expectations regarding the treatment process and timeline. A structured approach to ESWT delivery maximizes therapeutic benefits while ensuring patient safety and comfort throughout the treatment course.
Pre-Treatment Assessment and Patient Selection
Comprehensive pre-treatment assessment forms the foundation of successful ESWT outcomes and begins with detailed medical history evaluation and physical examination. Healthcare providers conduct thorough pain history documentation, including pain onset, duration, intensity, aggravating and relieving factors, and previous treatment responses. Physical examination focuses on postural assessment, range of motion testing, palpation for trigger points and areas of tissue restriction, and functional movement screening. Imaging studies may be reviewed to rule out contraindications and identify specific anatomical targets for treatment. Patient selection criteria emphasize individuals with chronic pain conditions lasting longer than 12 weeks who have failed to respond adequately to conservative management approaches.
Treatment Session Breakdown
Individual ESWT sessions follow a standardized protocol designed to optimize therapeutic outcomes while maintaining patient comfort and safety. Treatment begins with patient positioning to ensure optimal access to target tissues while maintaining comfort throughout the procedure. Ultrasound gel application facilitates acoustic wave transmission and allows for precise targeting of affected areas. The shockwave applicator is systematically moved across treatment zones, delivering prescribed energy levels and pulse frequencies according to established protocols. Sessions typically last 15-20 minutes, with patients experiencing mild to moderate discomfort during treatment that resolves quickly following session completion. Real-time communication between provider and patient ensures appropriate energy adjustments and optimal treatment delivery.
Complete Treatment Course Planning
Evidence-based treatment protocols typically involve 3-6 ESWT sessions scheduled at weekly intervals, allowing adequate time for biological responses to develop between treatments. Treatment course planning considers individual patient factors including pain severity, chronicity, previous treatment responses, and functional limitations. Energy levels and pulse frequencies may be gradually increased throughout the treatment course as tissues adapt and tolerance improves. Response monitoring occurs at each session through pain assessment and functional evaluation, allowing for protocol modifications as needed. Some patients may require additional sessions beyond the standard protocol, particularly those with severe or long-standing conditions.
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery Guidelines
Post-treatment care guidelines optimize therapeutic responses and minimize potential adverse effects following ESWT sessions. Patients receive specific instructions regarding activity modification, typically avoiding high-impact activities for 24-48 hours following treatment while maintaining normal daily activities and gentle movement. Ice application may be recommended for localized soreness or mild swelling that occasionally occurs after treatment. Patients are educated about expected treatment responses, including potential temporary pain increase during the first 48-72 hours as healing processes are activated. Follow-up communication ensures appropriate recovery progression and addresses any concerns that may arise between treatment sessions.
Effectiveness and Success Rates: Real-World Results
Clinical effectiveness and success rates provide crucial insights into ESWT’s therapeutic potential and help establish realistic expectations for patients considering this treatment option. Real-world outcomes data demonstrates the practical benefits and limitations of shockwave therapy in diverse patient populations.
Pain Reduction Outcomes and Statistics
Pain reduction represents the primary outcome measure for evaluating ESWT effectiveness in lower back pain treatment. Clinical studies consistently demonstrate significant pain reductions following ESWT protocols, with average VAS score improvements ranging from 40-60% compared to baseline measurements. Approximately 70-80% of treated patients experience clinically meaningful pain reduction defined as greater than 30% improvement from baseline scores. More impressive outcomes show that 40-50% of patients achieve greater than 50% pain reduction, representing substantial functional improvement and enhanced quality of life. These pain reduction benefits typically begin during the treatment course and continue to improve for 3-6 months following treatment completion.
Treatment Response Timelines
Understanding treatment response timelines helps patients maintain realistic expectations and compliance throughout the therapy course. Initial treatment responses may be observed within 2-3 sessions, with progressive improvement continuing throughout the complete treatment protocol. Peak therapeutic benefits typically occur 6-12 weeks following treatment completion, as biological healing processes require time to fully develop. Some patients experience immediate pain relief following individual sessions, while others demonstrate gradual improvement over several weeks. Long-term follow-up studies indicate that treatment benefits can persist for 12-24 months or longer in responsive patients, particularly when combined with appropriate maintenance strategies and lifestyle modifications.
Factors Affecting Treatment Success
Multiple factors influence treatment success rates and help identify patients most likely to benefit from ESWT interventions. Patient age appears to correlate with treatment outcomes, with younger patients generally demonstrating superior responses compared to older individuals. Pain chronicity significantly impacts treatment success, with patients experiencing pain for less than 2 years showing better outcomes than those with longer-duration symptoms. Baseline functional capacity and activity levels predict treatment response, with more active patients typically achieving better results. Concurrent medical conditions, medication use, and psychological factors including depression and anxiety can influence treatment outcomes and may require additional management strategies.
Patient-Reported Outcomes and Satisfaction
Patient-reported outcome measures provide valuable insights into the real-world impact of ESWT beyond traditional pain and functional assessments. Quality of life improvements are frequently reported following successful ESWT treatment, including enhanced sleep quality, improved mood, and increased social participation. Work productivity and employment status often improve significantly in responsive patients, with reduced absenteeism and enhanced job performance. Patient satisfaction rates with ESWT treatment consistently exceed 80% in published studies, with high levels of treatment acceptability and willingness to recommend the therapy to others. Return to previously enjoyed activities and recreational pursuits represents a meaningful outcome for many patients who had limited participation due to chronic pain.
Safety Profile: Side Effects and Contraindications
A comprehensive understanding of ESWT’s safety profile is essential for informed clinical decision-making and appropriate patient counseling. While generally considered safe when properly administered, shockwave therapy does carry potential risks and contraindications that must be carefully evaluated for each patient.
Common Side Effects and Management
Common side effects following ESWT are typically mild and self-limiting, requiring minimal intervention for resolution. Local skin redness and mild swelling at treatment sites occur in approximately 10-15% of patients and typically resolve within 24-48 hours without specific treatment. Temporary pain increase during the first 2-3 days following treatment affects approximately 20-30% of patients as healing processes are activated, but this response often indicates appropriate therapeutic stimulation. Mild bruising may occur in sensitive individuals, particularly those with bleeding tendencies or anticoagulant use. These side effects are managed through patient education, ice application, and temporary activity modification as needed.
Rare but Serious Complications
Serious complications from ESWT are extremely rare when appropriate protocols and contraindications are observed. Severe pain exacerbation requiring medical intervention occurs in less than 1% of patients and typically resolves with conservative management. Infection at treatment sites is exceptionally rare due to the non-invasive nature of the procedure, but appropriate skin preparation and sterile techniques minimize this risk. Vascular complications including hematoma formation may occur in predisposed individuals, emphasizing the importance of thorough medical screening. Nerve injury or neurological complications are theoretical risks that have not been reported in clinical literature when appropriate energy levels and targeting protocols are followed.
Absolute and Relative Contraindications
Absolute contraindications to ESWT must be strictly observed to ensure patient safety and prevent potential complications. Pregnancy represents an absolute contraindication due to unknown effects on fetal development and potential risks to maternal health. Active infection or malignancy in the treatment area prevents ESWT application due to theoretical risks of spreading pathological processes. Severe coagulopathy or active anticoagulation therapy increases bleeding risks and contraindicate treatment. Relative contraindications require careful risk-benefit analysis and may include cardiac pacemakers, severe cardiovascular disease, and certain neurological conditions requiring individualized assessment.
Patient Safety Protocols and Monitoring
Comprehensive safety protocols ensure appropriate patient selection, treatment delivery, and post-treatment monitoring to minimize risks and optimize outcomes. Pre-treatment screening includes detailed medical history review, physical examination, and evaluation of contraindications and risk factors. Treatment protocols specify appropriate energy levels, pulse frequencies, and session durations based on individual patient factors and clinical presentation. Real-time monitoring during treatment includes patient communication, vital sign assessment when indicated, and immediate response to adverse events. Post-treatment follow-up protocols ensure appropriate recovery monitoring and early identification of any delayed complications or unexpected responses.
Combination Therapies: Maximizing Treatment Outcomes
Integrating ESWT with complementary therapeutic approaches often yields superior outcomes compared to monotherapy, creating synergistic effects that address multiple aspects of chronic lower back pain. This multimodal approach recognizes the complex nature of chronic pain and the benefits of comprehensive treatment strategies.
ESWT with Physical Therapy Integration
Combining ESWT with physical therapy creates a powerful therapeutic synergy that addresses both tissue healing and functional restoration. Physical therapy evaluation and treatment can identify movement dysfunctions, muscle imbalances, and biomechanical abnormalities that contribute to ongoing pain and disability. ESWT treatment helps prepare tissues for physical therapy interventions by reducing pain, improving tissue quality, and enhancing healing responses. Sequential treatment protocols typically begin with ESWT to address tissue pathology and pain, followed by progressive physical therapy to restore normal movement patterns and functional capacity. This integrated approach demonstrates superior outcomes compared to either treatment alone.
Shockwave Therapy with Injection Therapies
Strategic combination of ESWT with targeted injection therapies can provide complementary benefits for complex lower back pain conditions. Trigger point injections may be performed prior to ESWT treatment to optimize tissue preparation and reduce treatment discomfort. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or regenerative injection therapies may be combined with ESWT to enhance healing responses and tissue regeneration. The mechanical stimulation from shockwave therapy can improve the distribution and uptake of injected substances, potentially enhancing their therapeutic effects. Timing and sequencing of these combination treatments require careful consideration to optimize synergistic benefits while minimizing potential complications.
Lifestyle Modification and Wellness Integration
Comprehensive treatment approaches incorporate lifestyle modifications and wellness strategies that support long-term treatment success and prevent symptom recurrence. Ergonomic assessment and workplace modifications address environmental factors that may contribute to ongoing pain and dysfunction. Nutritional counseling focuses on anti-inflammatory dietary approaches that support tissue healing and overall health. Sleep hygiene optimization addresses the bidirectional relationship between pain and sleep disturbances. Stress management techniques including mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation training help address psychosocial factors that influence pain perception and treatment responses.
Technology-Enhanced Treatment Approaches
Advanced technology integration can enhance ESWT effectiveness and provide more comprehensive treatment approaches for complex lower back pain conditions. Ultrasound imaging guidance improves treatment precision and allows for real-time visualization of target tissues and treatment effects. Electromagnetic field therapy or low-level laser therapy may be combined with ESWT to provide additional tissue stimulation and healing enhancement. Biofeedback and movement analysis technologies help optimize treatment protocols and monitor progress objectively. Telemedicine and remote monitoring capabilities allow for enhanced patient support and treatment optimization between clinic visits.
Conclusion
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) offers a promising, non-invasive solution for chronic lower back pain—especially for those unresponsive to traditional treatments. Backed by systematic reviews, randomized trials, and real-world data, ESWT demonstrates success rates of 65–80%, significantly reducing pain and improving function. Its benefits go beyond symptom relief. ESWT stimulates tissue repair through acoustic waves, promotes neovascularization, reduces inflammation, and modulates pain pathways, targeting the root causes of chronic pain. With a strong safety profile and minimal side effects, it presents a compelling alternative to surgery and long-term medication. When integrated with physical therapy, injections, or wellness strategies, ESWT can deliver even greater outcomes. This multimodal approach reflects the complex nature of chronic back pain and enhances overall treatment effectiveness. As technology evolves and clinical knowledge expands, ESWT’s role in back pain care will likely grow. For patients seeking lasting relief and restored quality of life, ESWT is a worthy, science-backed option in the pain management toolbox.
References and Scientific Sources
- SWAVE-200-best shockwave therapy machine
- Shockwave Therapy for Back Pain
- How Effective Is Shockwave Therapy?
- Efficacy and safety of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in chronic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 632 patients
- Effects of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain and Their Dynamic Balance Ability
