Introduction: The Rise of Shockwave Therapy in Musculoskeletal Care
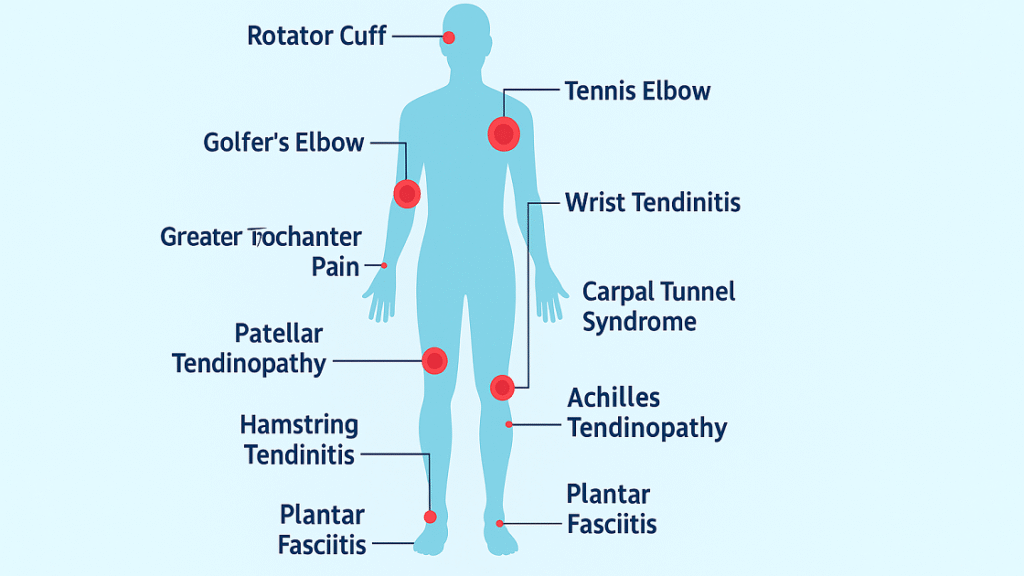
Musculoskeletal injuries in the upper and lower extremities are a leading cause of chronic pain and mobility issues. Traditional treatments—like rest, medications, or surgery—often offer short-term relief without addressing the root cause. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is changing that. This non-invasive technique uses acoustic energy waves to activate the body’s natural healing, targeting tendons and soft tissues effectively. From tennis elbow and rotator cuff problems to plantar fasciitis and Achilles tendinopathy, ESWT has shown excellent results across various conditions. Widely adopted by physical medicine and rehabilitation experts, shockwave therapy is backed by growing clinical research. Its expanding use reflects a shift toward non-surgical, evidence-based care in orthopedic and sports medicine.
How Shockwave Therapy Works: A Science-Backed Healing Mechanism
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of shockwave therapy provides crucial insight into why this treatment has achieved such remarkable clinical success across diverse musculoskeletal pathologies. The therapeutic effects of ESWT are multifaceted, involving complex biomechanical and biochemical processes that work synergistically to promote tissue healing and pain relief.
The Physics Behind It: Focused and Radial Shockwaves
Shockwave therapy uses two energy types: focused and radial. Focused shockwaves (F-SWT) penetrate deeper (up to 12 cm) and target specific tissue points with high precision. They are ideal for deep or chronic tendon injuries. Radial shockwaves (R-SWT), generated pneumatically, disperse outward in a broad pattern and are better suited for superficial or diffuse conditions. Although less intense, radial waves provide wider coverage. The choice between the two depends on injury depth and treatment goals. Focused waves allow deep, pinpoint healing; radial waves cover larger, shallower areas. Both reduce pain and promote healing by delivering acoustic pulses that stimulate recovery pathways without damaging healthy tissue.
Stimulating Natural Healing: Neoangiogenesis and Cell Regeneration
Shockwave therapy goes beyond breaking up scar tissue—it activates healing at the cellular level. The mechanical stress stimulates the release of key growth factors like VEGF and PDGF, triggering neoangiogenesis—the growth of new blood vessels. Better blood flow brings nutrients, clears waste, and accelerates regeneration. It also enhances production of collagen types I and III, restoring tendon structure. By promoting tenocyte (tendon cell) activity, shockwave therapy supports long-term tissue repair. This combination of enhanced vascularization, cellular regeneration, and collagen remodeling helps reverse chronic tendon damage and strengthen soft tissue over time.
Fast-Track to Pain Relief: Breaking the Pain-Spasm Cycle
Shockwave therapy provides fast relief by disrupting chronic pain cycles. It uses mechanical stimulation to block pain signals through the gate control theory, offering immediate analgesia. It also reduces substance P, a neurotransmitter linked to pain, and promotes release of natural opioids. This “hyperstimulation analgesia” effect overwhelms pain pathways, calming irritated nerves. As pain subsides, muscle spasms ease, restoring normal function. This process enables patients to begin rehab sooner, improving outcomes. By reducing both pain and muscle guarding, shockwave therapy restores function without relying on drugs or injections.
Enhancing Mobility Without Surgery or Medication
Shockwave therapy restores mobility by breaking down scar tissue and adhesions that restrict movement. It also addresses calcific deposits without surgery. The mechanical energy disrupts abnormal tissue while promoting new, healthier tissue growth. Combined with anti-inflammatory effects and enhanced collagen remodeling, patients experience improved joint and tendon flexibility. Over time, shockwave therapy helps regain range of motion and functional strength naturally. This drug-free, non-invasive approach offers a safer alternative to injections or surgery—ideal for patients seeking mobility gains without downtime.
Upper Extremity Conditions Treated with Shockwave Therapy
The upper extremity encompasses a complex network of joints, tendons, ligaments, and muscles that work in intricate coordination to provide the remarkable dexterity and strength required for daily activities. When pathology affects these structures, the resulting functional limitations can significantly impact quality of life and occupational performance. Shockwave therapy has demonstrated exceptional efficacy in treating a wide range of upper extremity conditions, offering patients effective non-surgical treatment options.
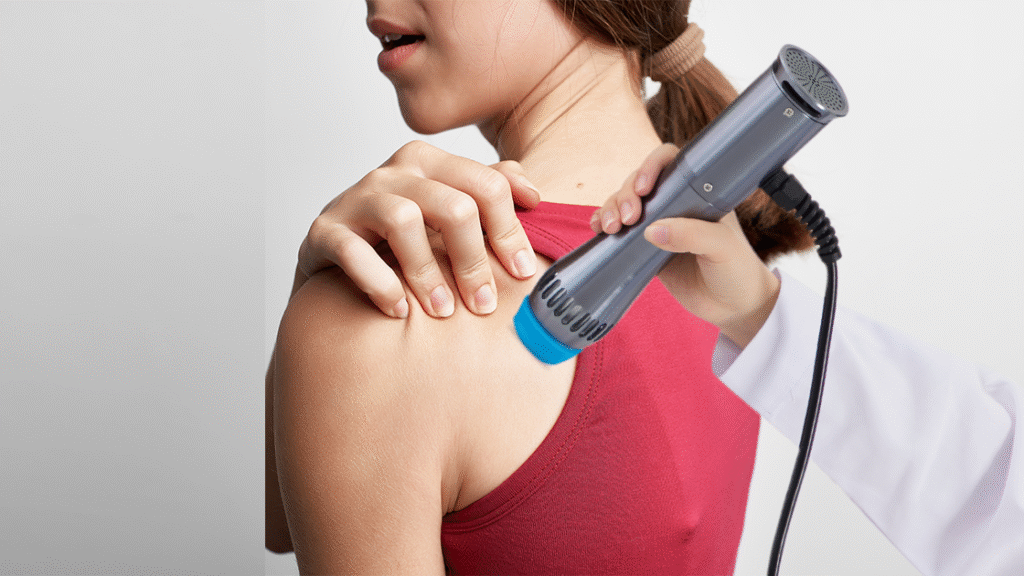
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Tennis elbow is a common overuse injury involving tendon degeneration at the lateral elbow. The condition causes pain, weakness, and limited arm function. Shockwave therapy has strong clinical support for treating lateral epicondylitis by promoting tissue repair and disrupting degenerative areas. NICE guidelines endorse its use in chronic cases. Treatment usually includes 3–5 weekly sessions with energy levels between 0.08–0.25 mJ/mm². Most patients report less pain and better function within 6–12 weeks, with long-term symptom relief. Shockwaves help regenerate collagen, reduce inflammation, and restore tendon strength without the need for injections or surgery.
Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy and Shoulder Bursitis
Rotator cuff tendinopathy and shoulder bursitis often involve calcific deposits, inflammation, and tendon wear. Shockwave therapy improves shoulder function by breaking down calcifications and promoting tissue healing. Clinical trials show clear pain relief and improved mobility—especially for calcific types—with high-energy shockwaves (HE-SWT) proving more effective than low-energy treatments. Shockwaves enhance vascularity, stimulate collagen production, and help resolve chronic inflammation. This dual action restores shoulder biomechanics and reduces impingement. For non-calcific cases, ESWT boosts tendon regeneration, improving shoulder use and quality of life without invasive intervention.
Wrist Tendinitis and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Digital-era overuse has increased wrist issues like tendinitis and carpal tunnel syndrome. Shockwave therapy addresses both inflammatory and degenerative elements. It reduces swelling in tendon sheaths (e.g., in de Quervain’s or FCR tendinitis) and supports tendon healing. For carpal tunnel, studies show ESWT may ease nerve compression by reducing inflammation and improving tissue flexibility. Lower energy settings and precise application are used to protect sensitive wrist anatomy. This non-invasive approach offers pain relief, functional improvement, and avoids surgery or steroid injections, making it ideal for work-related or tech-driven hand injuries.
Lower Extremity Conditions Treated with Shockwave Therapy
The lower extremities bear the constant demands of weight-bearing activities and locomotion, making them particularly susceptible to overuse injuries and degenerative conditions. The complex biomechanics of the lower limb kinetic chain mean that dysfunction in one area can lead to compensatory changes and secondary pathology throughout the extremity. Shockwave therapy has proven highly effective in treating numerous lower extremity conditions, often providing significant relief where other treatments have failed.
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Spurs
Plantar fasciitis is a top cause of heel pain, often linked to stress-related microtears and degeneration at the fascia’s heel insertion. Shockwave therapy is a proven, noninvasive treatment that uses acoustic energy to reduce pain and trigger healing. It disrupts damaged tissue and boosts repair mechanisms within the fascia. Most protocols involve 3–5 weekly sessions with customized energy settings. Studies report significant pain relief and improved foot function within 6–12 weeks post-treatment, helping many avoid surgery.
Achilles Tendinopathy
Achilles tendinopathy, often chronic and hard to treat, involves tendon thickening, degeneration, and calcification due to overuse and poor blood supply. Shockwave therapy enhances healing by promoting new blood vessel growth, collagen remodeling, and reducing inflammation. It’s especially helpful when other treatments fail. Focused or radial waves are applied directly to painful areas, with energy levels tailored to comfort. Long-term outcomes show reduced pain and restored function, allowing many patients to resume normal activities.
Patellar Tendinopathy (Jumper’s Knee)
Patellar tendinopathy causes knee pain due to tendon degeneration, often affecting athletes and active individuals. Repeated stress leads to collagen damage and abnormal nerve growth, resulting in chronic discomfort. Shockwave therapy promotes tendon healing while patients remain active, addressing the root problem without long rest. Treatments focus on the lower patella region with carefully adjusted energy. Clinical studies report marked improvements in pain and mobility, with many patients returning to sports or work.
Hip Bursitis and Gluteal Tendinopathy
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome includes bursitis and gluteal tendinopathy, causing lateral hip pain, tenderness, and activity limitation. These conditions often overlap and stem from overuse, tendon degeneration, and bursae inflammation. Shockwave therapy reduces pain and boosts tendon healing while calming inflamed bursae. It’s especially effective for patients with altered gait or hip mechanics. Treatments target tender zones with tailored energy settings. Clinical results show significant pain reduction and improved mobility within months.
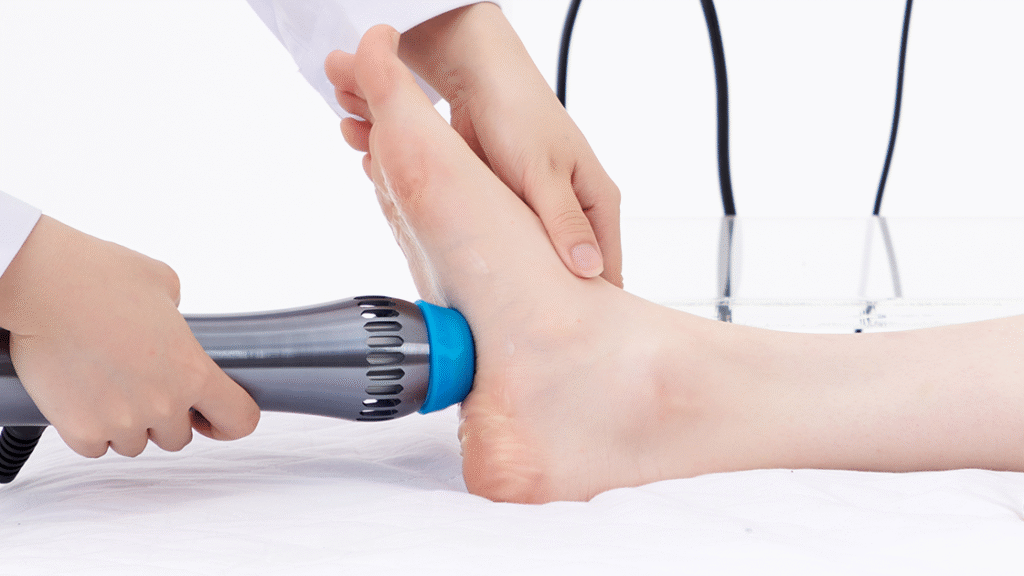
Clinical Evidence and Guidelines: What the Research Says
The clinical efficacy of shockwave therapy in treating musculoskeletal conditions is supported by an extensive body of research evidence that continues to expand as new applications and protocols are developed. This evidence base provides the foundation for evidence-based treatment decisions and helps guide clinical practice in the application of ESWT across various conditions.
Randomized Controlled Trials and Meta-Analyses
RCTs and meta-analyses provide strong evidence supporting shockwave therapy for musculoskeletal pain. These studies confirm its ability to reduce pain, improve function, and promote healing. Meta-analyses show shockwave therapy outperforms placebo and often matches or surpasses treatments like steroid injections and surgery. Research has also helped define optimal protocols, including energy levels and session frequency. Overall, shockwave therapy is a safe and effective option for various upper and lower limb conditions, backed by high-level clinical evidence.
Expert Recommendations and Treatment Protocols
Leading organizations like ISMST have issued evidence-based guidelines on shockwave therapy. These include patient selection criteria, safety measures, and detailed protocols for energy levels, frequency, and number of sessions. Recommendations aim to maximize outcomes and minimize side effects. Accurate diagnosis and follow-up are emphasized to ensure long-term success. Standardized protocols improve treatment consistency across clinics, making shockwave therapy a reliable option in orthopedic and sports medicine.
Long-Term Follow-Ups and Patient Outcomes
Long-term studies show that shockwave therapy offers sustained benefits, with patients reporting pain relief and improved function months or even years later. These lasting results are due to deep tissue healing and restoration of normal movement patterns, not just temporary symptom control. Follow-up data reveal high patient satisfaction, improved quality of life, and low recurrence rates. Unlike quick fixes, shockwave therapy tackles the root cause of chronic pain for durable recovery.
Who Can Benefit? Ideal Candidates for Limb Shockwave Therapy
The success of shockwave therapy depends significantly on appropriate patient selection and accurate diagnosis of suitable conditions. Understanding the characteristics of ideal candidates helps optimize treatment outcomes and ensures that patients receive the most appropriate care for their specific conditions.
Athletes with Overuse Injuries
Athletes often suffer from overuse injuries like tennis elbow, jumper’s knee, or Achilles tendinopathy due to repetitive stress. These injuries are chronic and resistant to rest or standard treatments. Shockwave therapy offers a fast, effective solution, enabling athletes to keep training while recovering. It promotes tissue repair, reduces pain, and avoids the risks of medications or surgery. The mechanical and biological effects of shockwave therapy match the needs of overused tendons and soft tissues, making it a preferred option for sports-related injuries.
Middle-Aged Adults with Chronic Tendon Pain
Chronic tendon pain is common in middle-aged adults due to aging and accumulated stress on tissues. Tendons lose elasticity and healing slows, often leading to long-lasting pain that doesn’t respond to standard care. Shockwave therapy triggers tissue regeneration and reduces inflammation. It’s non-invasive, safe for patients with other health issues, and avoids surgery. Results in this group are typically excellent, with lasting improvements in pain, mobility, and quality of life.
Post-Surgical Patients Needing Rehabilitation
Shockwave therapy aids recovery after orthopedic surgery by reducing scar tissue, easing pain, and speeding healing. It’s especially useful for patients experiencing delayed healing or stiffness. Timing is key—it’s usually started once initial healing is complete to avoid interfering with recovery. Adjusted protocols help address specific surgical sites safely. By enhancing tissue quality and minimizing complications, shockwave therapy supports smoother, faster rehabilitation and a quicker return to normal activity.
Individuals Seeking Alternatives to Injections or Surgery
Many patients want to avoid injections or surgery due to concerns over risks, side effects, or personal preference. Shockwave therapy offers an effective, non-invasive alternative. It works well for patients who haven’t improved with physical therapy or medication but aren’t ready for surgery. Studies show it can match or even outperform corticosteroid injections or surgery for several conditions. It’s a valuable first-line option for those seeking safer, more natural solutions.
Treatment Experience: What to Expect During & After Sessions
Understanding the treatment experience helps patients prepare for shockwave therapy and sets appropriate expectations for the treatment process and recovery timeline. The patient experience encompasses pre-treatment preparation, the actual treatment sessions, immediate post-treatment effects, and the recovery and healing process.
Number of Sessions and Duration
Shockwave therapy usually involves 3–5 sessions over several weeks, with weekly treatments to allow healing. Each session lasts 15–30 minutes depending on the area treated. Clinicians often start with a trial of 2–3 sessions to assess effectiveness. If there’s no improvement, the treatment plan may be adjusted. Many patients notice benefits after the second or third session. Some may need more or fewer treatments depending on condition severity and personal response. The goal is steady improvement without overwhelming the tissue.
Pain Levels During Application
Pain during shockwave therapy varies. Most patients describe the feeling as sharp taps or pulses. Discomfort ranges from mild to moderate but is short-lived and stops after the session. Clinicians adjust energy levels to maintain comfort without sacrificing effectiveness. No anesthesia is needed. A handheld device delivers the waves through the skin to stimulate healing in deep tissues. Most patients tolerate the treatment well and can resume normal activities immediately afterward.
Post-Treatment Recommendations and Recovery Timeline
After treatment, patients are advised to avoid intense activity and anti-inflammatory meds, which may slow healing. Ice and gentle stretching may be recommended. Some people feel sore or notice increased symptoms for a few days, which is normal and temporary. Improvement usually begins within 2–4 weeks, with full benefits seen between 6–12 weeks post-treatment. Recovery continues as tissues regenerate. Pain relief typically comes first, followed by better mobility and overall function.
Safety, Side Effects, and Contraindications
Patient safety represents a paramount concern in the application of any medical treatment, and shockwave therapy has an excellent safety profile when performed by qualified practitioners using appropriate protocols. Understanding potential side effects and contraindications ensures safe and effective treatment delivery.
Is Shockwave Therapy Safe?
Shockwave therapy is widely regarded as safe when applied correctly. It is non-invasive, carries no surgical risks, and avoids drug-related side effects. Clinical studies show that serious complications are rare. Most patients tolerate the treatment well, with only mild and temporary discomfort during sessions. Proper screening, accurate diagnosis, and adherence to treatment protocols are key to minimizing risks. Because it doesn’t involve medication or anesthesia, it’s also suitable for patients with multiple health concerns.
Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
- Mild pain or discomfort at the treatment site
- Skin redness or swelling, usually fades in a few days
- Small bruises (petechiae) may occur
- Temporary soreness or stiffness
Management tips:
- Apply ice to ease discomfort
- Use over-the-counter pain relievers if needed
- Modify activities briefly
- Contact your provider if symptoms persist or worsen
Who Should Avoid Shockwave Treatment?
Absolute contraindications:
- Pregnancy
- Cancer in the treatment area
- Bleeding disorders or use of blood thinners
- Active infection at the treatment site
- Open growth plates in children
Relative contraindications:
- Pacemakers near treatment area
- Severe vascular disease
- Certain neurological conditions
Note: Always undergo professional screening before treatment.
Conclusion: The Future of Extremity Pain Relief is Shockwave
Shockwave therapy is emerging as a leading solution for extremity pain due to its non-invasive nature, strong clinical backing, and high patient acceptance. As technology advances, treatment becomes more precise, with research expanding into areas like nerve repair, wound healing, and regenerative medicine. With integration into broader rehab plans—alongside physical therapy and exercise—shockwave therapy offers a cost-effective, holistic approach that promotes natural healing and long-term relief. Its role in musculoskeletal care is set to grow as more patients and providers recognize its benefits.
FAQs: Quick Answers to Common Patient Questions
It might sting during treatment, but most patients say the long-term pain relief is worth the temporary discomfort.
Many people start feeling better after 2–3 sessions, with full benefits often peaking within 6–12 weeks.
Yes—shockwave therapy doesn’t knock you off your feet. Most return to daily activities right away.
Not likely. Most conditions improve after 3–5 sessions. Your provider will assess your progress to decide.
Often, yes. It’s drug-free, non-surgical, and safe for many who don’t respond to other treatments.
It goes deeper—stimulating healing at the source, not just masking symptoms.
References: Clinical Research & Medical Guidelines
Clinical evidence for shockwave therapy is steadily growing, backed by ongoing research and peer-reviewed studies in orthopedics, sports medicine, and rehabilitation. Guidelines from professional bodies like the International Society for Musculoskeletal Shockwave Therapy (ISMST) and other medical organizations endorse its use for various conditions. Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have reinforced its effectiveness and safety, helping to position it within evidence-based clinical practice. These studies highlight its value in treating musculoskeletal pain, tendinopathies, and soft tissue injuries. Research also explores new indications, refines treatment protocols, and examines combination therapies to enhance outcomes. As the data continues to evolve, shockwave therapy is increasingly recognized as a key non-invasive treatment option in modern musculoskeletal care.
- How Shockwave Therapy Defeats Tendinopathy
- Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopathy
- How Effective Is Shockwave Therapy?
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Best practices for extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal medicine: Clinical application and training consideration
