Morton’s neuroma is a common condition that affects the foot, causing pain, discomfort, and even limitations in daily activities. Fortunately, advancements in non-invasive treatment options, such as shockwave therapy, are providing promising relief for those suffering from this painful condition. In this blog, we’ll explore what Morton’s neuroma is, how shockwave therapy works to treat it, and the potential success rates of this revolutionary treatment. We’ll also take a closer look at Swave-200, an advanced shockwave therapy device from Rhein Laser, designed to provide effective relief for Morton’s neuroma.
Difference Between a Neuroma and Morton’s Neuroma
Understanding the nature of Morton’s neuroma begins with knowing the difference between a general neuroma and the specific characteristics of Morton’s neuroma.
What Makes Morton’s Neuroma Special?
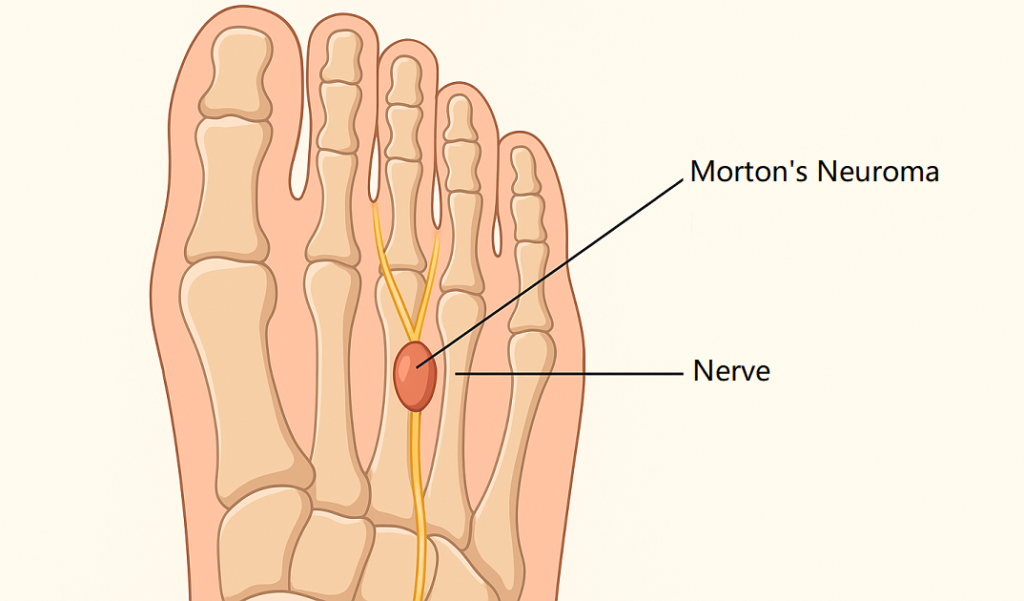
A neuroma is an abnormal growth of nerve tissue, often occurring between the toes. It can be caused by pressure, irritation, or trauma to the nerves in the foot. Morton’s neuroma, however, is a specific type of neuroma that typically develops between the third and fourth toes. It is characterized by thickening and irritation of the tissue surrounding the nerve, leading to pain, burning sensations, and even numbness in the affected area. This condition is more common in women, often due to the wearing of high heels or tight footwear, which puts excessive pressure on the toes.
The Role of Nerves in Morton’s Neuroma
The nerve involved in Morton’s neuroma is the digital nerve, which supplies sensation to the toes. When the nerve is compressed or irritated, it leads to the formation of thickened tissue, which can put further pressure on the nerve and cause severe discomfort. The condition can be exacerbated by activities that involve repetitive pressure on the feet, such as running or wearing inappropriate footwear.
Symptoms and Signs to Watch For
Common symptoms of Morton’s neuroma include:
- Sharp, burning pain between the toes, particularly when walking or standing.
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the toes.
- A feeling of a pebble or something stuck in the shoe.
- Pain relief when taking the weight off the affected foot.
If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to seek early treatment to prevent the condition from worsening.
Living With Morton’s Neuroma
Living with Morton’s neuroma can significantly impact a person’s daily life. The constant discomfort, especially when walking, standing, or exercising, can be draining. Fortunately, non-surgical treatments like shockwave therapy are helping many people find relief.
Common Triggers and Aggravating Factors
Certain activities and lifestyle choices can trigger or worsen Morton’s neuroma. These include:
- High-heeled shoes that crowd the toes and increase pressure on the nerve.
- Tight footwear that doesn’t provide adequate arch support or cushioning.
- Repetitive activities like running or jumping, which can aggravate the pressure on the feet.
- Flat feet or high arches, which can alter the mechanics of walking and increase foot strain.
Footwear and Foot Care Tips for Relief
Proper footwear plays a crucial role in alleviating the pain of Morton’s neuroma. Look for shoes that:
- Provide wide toe boxes to reduce pressure on the affected area.
- Have soft insoles to cushion the foot and absorb shock.
- Offer arch support to promote proper foot alignment.
- Consider using orthotic insoles to provide added support and reduce pressure on the nerve.
Additionally, elevating the foot, applying ice packs, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or walking can provide temporary relief.
Impact on Quality of Life
Morton’s neuroma can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. Daily activities like walking, exercising, or even standing for long periods can become painful. This condition can also lead to frustration, emotional distress, and limitations in work or social life. Early intervention with non-invasive treatments like shockwave therapy can help restore mobility and reduce the emotional toll caused by chronic pain.
Understanding Shockwave Therapy
What Is Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-energy acoustic waves to treat musculoskeletal injuries and conditions. These waves are directed to the affected tissue, where they stimulate healing by enhancing cellular regeneration and improving circulation. Shockwave therapy is particularly effective for conditions involving tendons, muscles, ligaments, and joints, as it helps promote the body’s natural healing process without the need for surgery or medication. The therapy works by transmitting energy into the tissue via an applicator that emits shockwaves. These shockwaves create pressure and mechanical forces within the affected area, stimulating the body’s healing mechanisms. It’s a highly effective alternative for patients looking to avoid invasive procedures like surgery, offering a lower risk of complications while providing meaningful pain relief and promoting tissue regeneration.
The Science Behind Shockwave Therapy
At the core of shockwave therapy is its ability to activate biological processes in the tissue. When the shockwaves penetrate deep into the tissue, several key effects occur:
- Increased Blood Flow: The shockwaves improve circulation in the treated area by promoting the dilation of blood vessels. This enhanced blood flow brings vital nutrients and oxygen to the damaged tissue, which accelerates the healing process. Increased circulation also helps remove toxins from the area, further aiding recovery.
- Cellular Stimulation and Collagen Production: Shockwave therapy stimulates fibroblasts, the cells responsible for producing collagen. Collagen is essential for tissue repair, as it helps form the scaffolding that tissues need to heal. By encouraging collagen production, shockwave therapy speeds up the recovery process and improves the overall strength and integrity of the tissue.
- Reduction of Pain: The acoustic waves have an analgesic effect, helping to reduce pain in the affected area. They do so by desensitizing nerve endings and disrupting the transmission of pain signals to the brain, making the area feel less painful over time.
- Scar Tissue Breakdown: In chronic conditions, scar tissue can form in the affected area, which can hinder movement and contribute to ongoing pain. Shockwave therapy helps break down this scar tissue, improving flexibility and reducing stiffness in the affected region.
These combined effects make shockwave therapy an effective treatment for various musculoskeletal conditions, especially those related to soft tissues and chronic pain.
History and Evolution of Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy was initially developed in the 1980s for lithotripsy — a procedure to break up kidney stones using shockwaves. This technique was highly successful, leading researchers to explore its potential in treating other types of tissue injuries. In the 1990s, the use of shockwave therapy expanded into the realm of musculoskeletal treatments. The therapy gained widespread use in orthopedics and rehabilitation as clinical studies demonstrated its ability to treat conditions like tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, and calcific shoulder tendinopathy. Over the years, the technology has evolved, with improvements in the delivery system, treatment protocols, and understanding of its biological effects. Today, shockwave therapy is a well-established treatment in physical therapy clinics, sports medicine centers, and pain management practices worldwide.
What Does Shockwave Therapy Treat?
Shockwave therapy is an effective treatment for numerous musculoskeletal and soft tissue conditions, offering a non-surgical option for individuals seeking relief from chronic pain and injury. Below, we’ll look at some of the most common conditions that shockwave therapy treats:
Musculoskeletal Conditions
One of the most common uses for shockwave therapy is in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. Conditions such as tendonitis, bursitis, and rotator cuff injuries respond well to shockwave therapy. By promoting circulation and stimulating collagen production, shockwaves can help speed up the healing process for damaged tendons, ligaments, and joints. Tendonitis (inflammation of the tendon) and tendinopathies (degenerative changes in the tendon) are commonly treated with shockwave therapy, which promotes the regeneration of healthy tendon tissue and reduces inflammation. Calcific Tendonitis is another condition where shockwave therapy can be highly effective. This condition involves the buildup of calcium deposits in the tendons, and shockwave therapy can help break down these deposits and promote healing.
Chronic Pain Relief
Chronic pain, especially in the joints, tendons, and soft tissues, can be debilitating. Shockwave therapy offers an alternative to pain medications and invasive surgeries. It works by stimulating healing and reducing pain at the source, making it ideal for conditions like chronic low back pain, plantar fasciitis, and Achilles tendonitis. Studies have shown that shockwave therapy significantly reduces the intensity of chronic pain by desensitizing nerve endings and stimulating the production of natural pain-relieving chemicals, such as endorphins.
Sports Injuries and Recovery
Shockwave therapy is widely used in the treatment of sports injuries. Whether it’s a sprain, strain, or muscle tear, athletes benefit from faster recovery times and enhanced healing. Shockwave therapy can help treat acute injuries like tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, and runner’s knee, as well as chronic conditions caused by overuse or repetitive motions. By improving circulation and speeding up tissue repair, shockwave therapy enables athletes to return to their activities faster and with reduced pain. It’s also used as a preventive measure to reduce the risk of future injuries.
Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries, including ligament sprains, muscle strains, and bursitis, are among the most common conditions treated with shockwave therapy. The therapy helps break down scar tissue, promotes collagen production, and accelerates healing in muscle and connective tissue. Whether it’s an acute muscle tear or a chronic injury, shockwave therapy helps to restore normal function and flexibility. Conditions like shin splints and plantar fasciitis, where the fascia and soft tissues are inflamed or injured, also respond well to shockwave therapy.
Post-Surgical Pain
After surgery, the body often faces challenges with tissue repair, scar tissue formation, and residual pain. Shockwave therapy can be used post-surgically to help break down scar tissue, improve circulation, and alleviate pain. It has been effectively used for conditions such as knee surgery recovery, hip replacement rehabilitation, and shoulder surgery recovery. In addition to reducing pain, shockwave therapy also promotes faster healing and helps restore flexibility in the affected area.
How Shockwave Therapy Works for Morton’s Neuroma
Morton’s neuroma is a painful condition caused by the thickening of the tissue around one of the nerves leading to the toes, typically between the third and fourth toes. It results in sharp, burning pain, tingling, and numbness in the affected area, often aggravated by walking or wearing tight shoes. Shockwave therapy can be a highly effective treatment for this condition, addressing both the underlying causes and the painful symptoms.

Targeting the Affected Nerve and Tissue
The shockwaves are precisely directed at the affected nerve and the surrounding tissue. Morton’s neuroma often involves nerve compression, leading to swelling and thickening of the nerve’s tissue. Shockwave therapy directly targets this thickened tissue, applying mechanical forces that help break it down. This reduction in tissue thickening helps relieve the pressure on the nerve, leading to a reduction in the sharp, burning pain associated with Morton’s neuroma. By targeting both the nerve and the surrounding tissue, shockwave therapy addresses not just the symptoms, but also the underlying structural issues that contribute to the condition. Over time, this reduces both inflammation and nerve irritation, allowing for long-lasting pain relief.
Increasing Blood Flow and Promoting Healing
One of the key benefits of shockwave therapy is its ability to increase blood flow to the affected area. Improved circulation is essential for tissue repair, as it delivers oxygen and nutrients that promote healing. In the case of Morton’s neuroma, poor circulation can delay the body’s natural healing process, especially around the nerve and the surrounding inflamed tissue. Shockwave therapy stimulates blood flow to these areas, accelerating recovery and helping the body repair the damage more quickly. By enhancing blood circulation, shockwave therapy ensures that the tissues in the affected area receive all the necessary resources to heal properly. This not only helps relieve pain, but it also aids in preventing the condition from becoming chronic.
Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is a major factor in Morton’s neuroma, as it causes swelling and pressure on the nerve, intensifying the pain. Shockwave therapy has been shown to significantly reduce inflammation in the treated area. The shockwaves work by stimulating the body’s natural anti-inflammatory responses. They help break down inflammatory markers and promote the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn reduces swelling and discomfort. By addressing the inflammation at its source, shockwave therapy helps create an environment where healing can occur more effectively, allowing patients to experience longer-lasting pain relief.
Pain Reduction and Nerve Desensitization
Pain reduction is one of the primary reasons patients seek shockwave therapy for Morton’s neuroma. The shockwaves delivered during treatment interact with the nerve endings, helping to desensitize them. This process essentially reduces the ability of the nerves to transmit pain signals to the brain, providing significant relief from the burning and tingling sensations that are characteristic of Morton’s neuroma. Additionally, the shockwaves disrupt the pain pathways, leading to a decrease in overall pain perception. This provides immediate relief, which, when combined with the other effects of shockwave therapy, contributes to a significant improvement in the patient’s quality of life.
Breaking Down Scar Tissue
Over time, Morton’s neuroma can lead to the formation of scar tissue around the affected nerve. Scar tissue can contribute to ongoing pain and stiffness, and it can further restrict the function of the foot. Shockwave therapy is highly effective at breaking down scar tissue and fibrotic tissue. The mechanical forces of the shockwaves help to break apart the dense fibrous tissue, promoting tissue remodeling and healing. By breaking down scar tissue, shockwave therapy helps restore flexibility to the affected area, reduces the risk of future complications, and improves the overall function of the foot. This effect is particularly important for patients with chronic Morton’s neuroma who have developed significant scar tissue around the nerve.
What Is the Success Rate of Shockwave Therapy for Morton’s Neuroma?
The effectiveness of shockwave therapy in treating Morton’s neuroma has been extensively researched and shown to yield positive results in many cases. The success rate of this treatment varies depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and how consistently the therapy is applied.
Clinical Research and Studies
Numerous clinical studies have examined the effectiveness of shockwave therapy for treating Morton’s neuroma, and the results consistently suggest that it is a viable treatment option. Research has demonstrated that shockwave therapy significantly reduces pain and improves foot function in patients with Morton’s neuroma. For example, a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research found that patients receiving shockwave therapy reported a significant reduction in pain intensity and an improvement in their quality of life compared to those who received placebo treatments.
Additionally, a meta-analysis of multiple studies indicated that shockwave therapy has an overall success rate of around 70-80% in patients with Morton’s neuroma, with the greatest improvements observed in patients with less severe forms of the condition. Most patients who undergo this therapy experience significant pain relief, increased mobility, and a reduction in other symptoms associated with the condition, such as tingling and numbness.
Success Rate Based on Severity
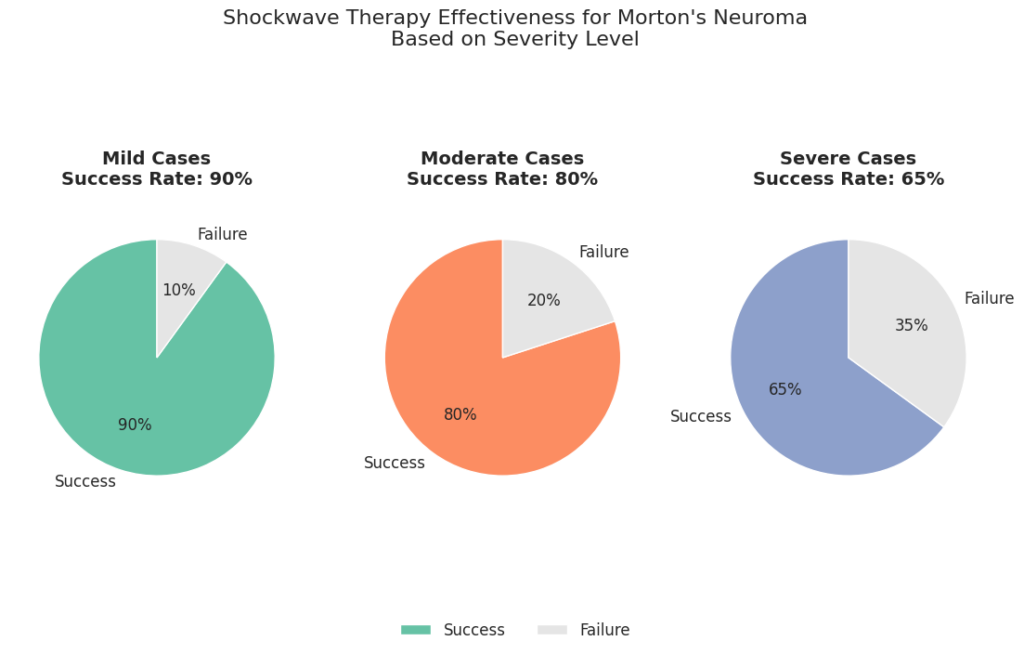
The success rate of shockwave therapy for Morton’s neuroma can vary based on the severity of the condition. Studies suggest that patients with mild to moderate Morton’s neuroma have higher success rates compared to those with advanced or severely fibrotic neuromas. In milder cases, shockwave therapy can reduce inflammation and improve blood flow to the nerve, leading to substantial pain relief and tissue healing. For more severe cases, the success rate may be lower, and the patient may require additional treatments or a combination of therapies to achieve optimal results. However, even in advanced cases, many patients report reduced symptoms and better management of their condition, allowing them to avoid invasive surgical procedures.
Factors Influencing Success
Several factors can influence the success of shockwave therapy for Morton’s neuroma, including:
- Treatment Frequency and Duration: The number of shockwave therapy sessions a patient undergoes can significantly impact the outcome. While some patients may experience relief after just a few treatments, others may require several sessions over a longer period to see improvements.
- Patient’s Response to Treatment: Each patient responds differently to shockwave therapy, with some experiencing faster results than others. Factors such as age, overall health, and lifestyle can affect how quickly the body responds to the treatment.
- Adherence to Aftercare Recommendations: Aftercare plays a crucial role in the success of shockwave therapy. Patients who follow their provider’s recommendations, including rest, proper footwear, and other post-treatment care, tend to have better outcomes.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Patients with additional foot or nerve-related conditions may experience a slower or less complete recovery. Treating underlying health issues can contribute to the overall success of the therapy.
Real-World Success Rates
In real-world settings, the success rate of shockwave therapy for Morton’s neuroma is generally high, with many patients reporting significant pain relief and improvement in their ability to walk and engage in normal activities. According to several studies, between 70-85% of patients experience substantial improvement in symptoms, while some patients achieve complete pain relief. The success of shockwave therapy often leads to a reduction in the need for more invasive treatments, such as injections or surgery.
Learn About Swave-200 Treatment from Rhein Laser
The Swave-200 is an advanced shockwave therapy device from Rhein Laser, designed to effectively treat chronic musculoskeletal pain and promote tissue healing. With its compact design and cutting-edge electromagnetic technology, the Swave-200 delivers powerful energy outputs of up to 210mJ, allowing for deep tissue penetration of up to 8 cm. This makes it suitable for a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions. The Swave-200 comes equipped with seven different applicator heads to cater to various treatment needs, ensuring versatility for different body parts and conditions. Additionally, the device maintains a comfortable temperature range of 31°C to 42°C during treatment, enhancing patient comfort throughout the session.
Weighing just 3 kilograms, the Swave-200 is lightweight and easy to use, making it a perfect option for both clinic and home use. Its high energy efficiency and compact design allow for convenient handling, while still providing optimal results in pain relief and tissue repair. Clinical studies have shown that the Swave-200 has an impressive success rate of up to 90%, making it an excellent choice for practitioners and rehabilitation centers. Whether treating plantar fasciitis, tendonitis, or sports injuries, the Swave-200 consistently delivers effective outcomes. It is a powerful, easy-to-use shockwave therapy device that offers high energy output, deep tissue penetration, and versatile treatment options. It’s a reliable and cost-effective solution for non-invasive pain management and tissue healing.
Conclusion Part
Shockwave therapy offers a promising solution for patients suffering from Morton’s neuroma, providing a non-invasive, effective alternative to surgery. With its ability to reduce pain, improve circulation, and promote healing, shockwave therapy addresses the root causes of the condition and can help patients regain their quality of life. Clinical studies have shown high success rates, particularly in mild to moderate cases, with many patients experiencing lasting relief. The Swave-200 from Rhein Laser is an excellent option for those seeking targeted, effective shockwave therapy. Its precision and adjustability make it ideal for treating Morton’s neuroma, as well as other musculoskeletal conditions. With a growing body of evidence supporting its efficacy, shockwave therapy remains one of the best non-surgical options for managing Morton’s neuroma and other related conditions.
FAQs about This Blog
Q1: How long does it take to see results from shockwave therapy for Morton’s neuroma?
A1: While some patients notice improvement after just one or two sessions, it typically takes around 3-5 sessions over a period of weeks to see significant relief.
Q2: Are there any side effects of shockwave therapy for Morton’s neuroma?
A2: Side effects are minimal and may include mild soreness or redness at the treatment site, but these effects are generally short-lived.
Q3: How long do the results of shockwave therapy last?
A3: Many patients experience lasting relief for months or even years, especially when combined with proper aftercare and lifestyle adjustments.
Q4: Can shockwave therapy be used as a sole treatment for Morton’s neuroma?
A4: Yes, for many patients, shockwave therapy can be effective as a standalone treatment. However, in more severe cases, it may be combined with other therapies, such as corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention, if necessary.
References
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in Patients with Morton’s Neuroma A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27031544
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for interdigital neuroma: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial:
