Introduction: Why Soft Tissue Healing Matters
Soft tissue injuries—ranging from sprains and strains to post-surgical incisions—are incredibly common and affect people of all ages. These wounds can lead to prolonged pain, limited mobility, and delayed return to work or daily activities. Whether caused by trauma, repetitive strain, or surgery, healing such injuries is a priority in both sports medicine and general healthcare. As we seek faster, less invasive ways to promote tissue recovery, shockwave therapy has emerged as a revolutionary solution. Unlike traditional therapies that rely heavily on medication and rest, shockwave therapy uses acoustic energy to stimulate biological responses that accelerate healing naturally. Understanding this modality’s mechanisms and ideal applications can transform wound care for clinicians and patients alike.
Understanding the Science Behind Shockwave Therapy
What Is Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy (SWT), also known as extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive treatment that delivers acoustic waves into the body’s tissues. These waves carry high energy to pain regions and musculoskeletal tissues with subacute, subchronic, and chronic conditions. Originally developed for breaking kidney stones (lithotripsy), SWT has evolved to treat various orthopedic and soft tissue pathologies due to its regenerative potential. There are two main types:
- Radial Shockwave Therapy (RSWT): Delivers low- to medium-energy waves that disperse radially over a broader area.
- Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSWT): Delivers high-energy waves concentrated on a specific tissue depth for deeper penetration.
Both variants stimulate the body’s natural healing mechanisms by triggering cellular responses and promoting tissue regeneration.
How Shockwaves Interact with Soft Tissues
Shockwave therapy utilizes high-pressure acoustic pulses that penetrate deep into the tissue. These sound waves create microscopic mechanical deformations and vibrations within soft tissues, stimulating the body’s natural healing processes. The primary effects of shockwaves include:
- Microtrauma Creation: Shockwaves induce controlled microtrauma, triggering the body’s repair mechanisms.
- Collagen Production: Shockwaves stimulate fibroblasts to produce collagen, enhancing the extracellular matrix (ECM) and strengthening the tissue.
- Capillary Growth: The therapy promotes angiogenesis, or the formation of new blood vessels, improving circulation and nutrient supply to the wound area.
Biological Effects on Wound Microenvironment
Shockwave therapy has a profound impact on the wound microenvironment, which includes the cells, extracellular matrix (ECM), blood vessels, and biochemical factors surrounding a wound. By influencing these components, shockwave therapy promotes faster and more efficient tissue regeneration, leading to accelerated healing. The key biological effects include stimulating the cells responsible for healing, reducing inflammation, and enhancing oxygenation and metabolism in the affected area.
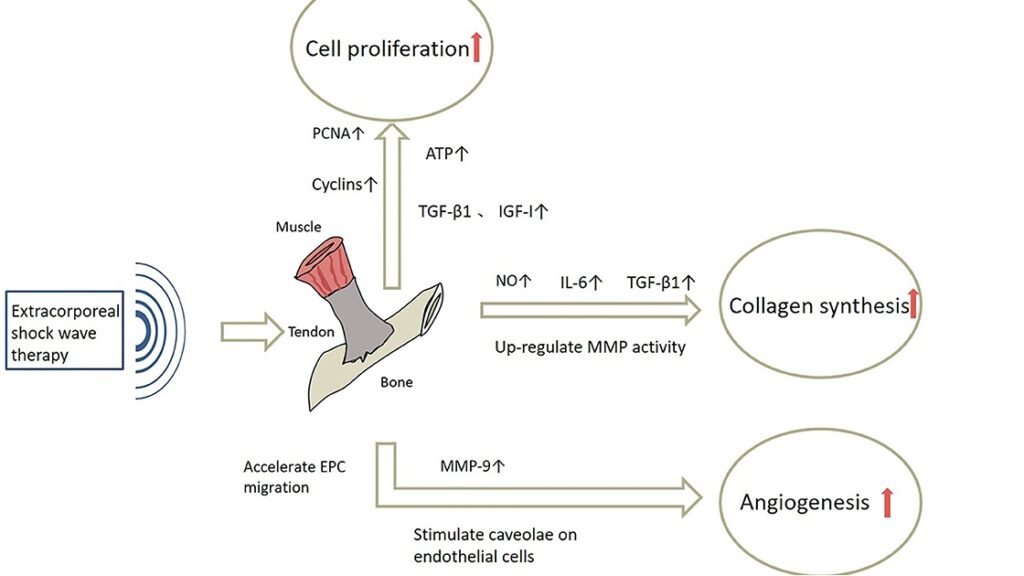
Stimulation of Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes
Fibroblasts and keratinocytes are crucial for wound healing. Fibroblasts are responsible for producing collagen and ECM, which form the structural foundation of the new tissue, while keratinocytes help regenerate the skin layer over the wound. Shockwave therapy stimulates fibroblasts to increase collagen production and ECM synthesis, which accelerates tissue regeneration. This not only promotes faster healing but also reduces scarring by strengthening the newly formed tissue. Similarly, shockwave therapy enhances the proliferation and migration of keratinocytes, leading to a quicker formation of new skin, which is particularly beneficial for treating skin wounds and post-surgical incisions.
Downregulation of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
Chronic wounds often suffer from excessive inflammation, which can significantly delay the healing process. Pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-1β play a key role in regulating this immune response. Shockwave therapy works by downregulating these pro-inflammatory cytokines, which helps to reduce swelling and control the immune response. By decreasing the levels of these inflammatory markers, shockwave therapy not only accelerates healing but also prevents prolonged inflammation that can damage the tissue. This creates a more balanced and favorable environment for wound healing, which is particularly important in chronic wounds where inflammation has become persistent.
Enhanced Oxygenation and Metabolism at the Wound Site
One of the most significant benefits of shockwave therapy is its ability to enhance blood circulation to the wound site by stimulating angiogenesis—the formation of new blood vessels. This increased vascularization improves oxygen and nutrient delivery to the wounded tissue, which is essential for collagen synthesis and the formation of new blood vessels. Additionally, the improved blood flow aids in the removal of metabolic waste products, such as carbon dioxide and lactic acid, which can otherwise hinder tissue regeneration. Shockwave therapy also boosts cellular metabolism in the affected area, speeding up the production of enzymes and proteins essential for tissue repair. These processes contribute to creating an optimal healing environment by improving tissue oxygenation, reducing cellular stress, and enhancing the overall metabolic activity necessary for effective healing.
Key Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Wound Healing
Pain Management Without Drugs
Shockwave therapy can provide significant pain relief without the need for drugs. Chronic wounds and soft tissue injuries are often painful, and traditional pain management methods may involve pharmaceuticals that can have undesirable side effects. Shockwaves have been shown to trigger the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms by promoting the release of endorphins and reducing the sensitivity of pain receptors in the affected area. In addition to providing immediate pain relief, shockwave therapy also reduces the inflammation that often accompanies wound healing, helping to control pain over the long term.
Enhanced Blood Flow and Oxygenation
Improved blood flow and oxygenation are key factors in accelerating wound healing. By stimulating the formation of new blood vessels and increasing the oxygen supply to the injured tissue, shockwave therapy ensures that the wound area receives the necessary nutrients for repair. Increased oxygenation also promotes the production of collagen and other extracellular matrix components that are essential for healthy tissue regeneration. Moreover, this enhanced blood flow reduces the risk of tissue necrosis, which is often a concern in poorly healing wounds.
Scar Minimization & Tissue Remodeling
Shockwave therapy has been found to be effective in reducing scar tissue formation, which is a common issue in the healing of soft tissue injuries. By stimulating the remodeling of collagen fibers and promoting the formation of organized tissue, shockwave therapy helps prevent the formation of hypertrophic or keloid scars. This tissue remodeling process results in smoother, more even skin post-healing, stronger and more flexible tissue that retains its function without excessive scarring. For patients who have undergone surgery or experienced trauma, shockwave therapy can significantly enhance the appearance and functionality of healed tissue, improving both aesthetic and functional outcomes.
Ideal Wound Types for Shockwave Treatment
Acute Soft Tissue Injuries
Shockwave therapy is highly effective in managing acute injuries such as:
- Muscle strains
- Ligament sprains
- Tendon tears
In these cases, SWT helps reduce inflammation, minimize hematoma formation, and promote faster tissue regeneration without the need for invasive intervention.
Chronic Non-Healing Wounds
Patients suffering from conditions such as diabetic foot ulcers, venous stasis ulcers, or pressure sores often have wounds that resist standard care. Shockwave therapy has shown excellent results in restarting the healing cascade in these chronic wounds by breaking down biofilms, promoting angiogenesis, reactivating dormant cells. Clinical studies demonstrate that SWT significantly improves healing rates and reduces recurrence in chronic wound cases.
Post-Surgical Incisions & Tissue Trauma
After surgery, tissues go through an inflammatory phase followed by proliferation and remodeling. Shockwave therapy can be introduced post-operatively to:
- Enhance incision healing
- Prevent adhesions
- Reduce swelling and bruising
- Minimize scar formation
Examples include orthopedic surgeries (ACL repair, meniscectomy), plastic surgeries (abdominoplasty, facelifts), and general surgeries (hernia repair, mastectomy). In these applications, SWT promotes rapid return to baseline activity and improves patient satisfaction with outcomes.
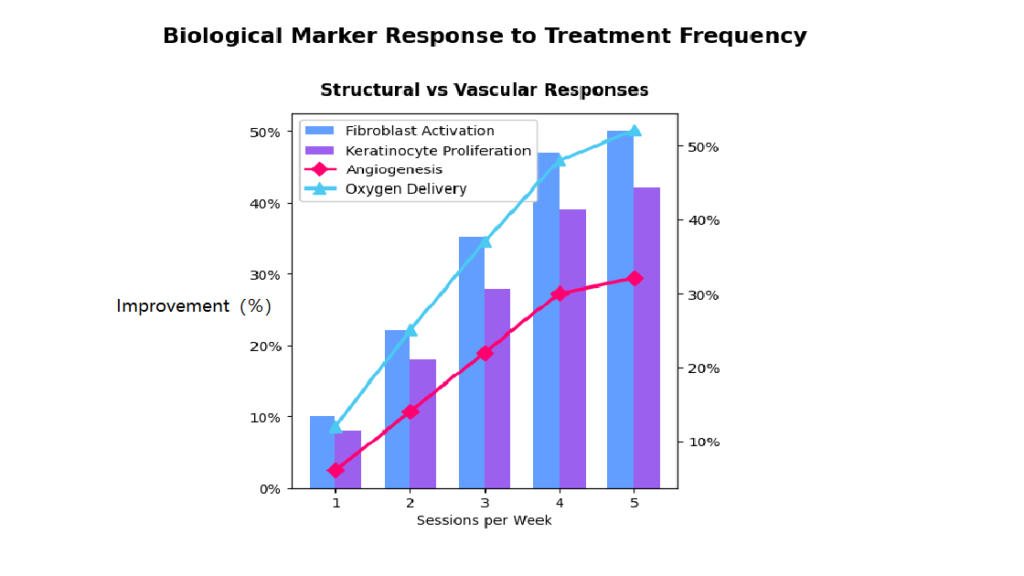
Clinical Evidence and Research Findings
Evidence-Based Outcomes
Shockwave therapy (SWT) for soft tissue wound healing is not just a novel trend—its efficacy is strongly backed by high-level clinical research. Studies consistently report improvements in wound closure rates, granulation tissue formation, revascularization, and pain scores. One randomized controlled trial published in Wound Repair and Regeneration demonstrated that SWT led to a 53% faster healing rate in patients with diabetic foot ulcers compared to standard wound care alone. In another study involving 100 patients with pressure sores, shockwave therapy reduced wound size by an average of 65% within four weeks, significantly outperforming the control group. Meta-analyses have confirmed SWT’s impact on:
- Increased tissue oxygenation (by up to 40%),
- Improved neovascularization, including higher levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF),
- Downregulation of MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases), reducing excessive tissue breakdown in chronic wounds.
Furthermore, evidence supports SWT’s effect on cellular regeneration. A German study using histological staining revealed an increase in fibroblast density and collagen deposition after SWT, contributing to faster and more organized tissue remodeling.
Case Studies and Patient Success Stories
Real-world success stories are equally compelling. A 55-year-old male with a venous leg ulcer that persisted for over 18 months saw complete wound closure in 8 weeks after incorporating radial shockwave therapy into his care plan. Notably, this patient had previously failed hyperbaric oxygen therapy and advanced dressings. In a sports rehab clinic, an elite sprinter recovering from a grade II hamstring tear was treated with focused SWT twice a week. MRI imaging showed significantly accelerated muscle fiber regeneration, and the athlete resumed full training two weeks ahead of schedule compared to the clinic’s average recovery timeline. These cases underscore SWT’s ability to transform stubborn or slow-healing wounds across different patient populations, from diabetics to athletes to post-surgical patients.
Protocols and Best Practices
Treatment Frequency and Duration
Protocols vary depending on the wound type and severity, but best practices generally follow these parameters:
| Wound Type | Frequency | Total Duration |
| Acute soft tissue injury | 2–3 times/week | 2–4 weeks |
| Chronic ulcers | Once every 5–7 days | 4–8 weeks |
| Post-surgical wounds | 1–2 times/week | 3–6 sessions |
Each session typically lasts 5–10 minutes, depending on the wound’s surface area. Energy levels range from 0.1 to 0.25 mJ/mm² for superficial wounds, with radial shockwave therapy preferred for broader regions and focused therapy for deeper or localized lesions.
Integration with Other Modalities
Shockwave therapy achieves best outcomes when integrated into a comprehensive wound care regimen, including:
- Advanced dressings (e.g., hydrocolloids, silver-based)
- Offloading techniques (for foot ulcers)
- Topical growth factors or PRP therapy
- Nutritional support (especially in chronic or elderly patients)
- Laser therapy or electrical stimulation (in multimodal rehab settings)
Safety Guidelines and Contraindications
Shockwave therapy is generally safe and well-tolerated. However, practitioners should adhere to the following contraindications:
- Malignant tumors at or near the treatment site
- Open bone fractures
- Severe coagulopathy or patients on anticoagulants
- Pregnancy
- Infection with abscess formation
Mild erythema, tingling, or temporary soreness may occur post-treatment, but these effects typically resolve within hours. No anesthesia is required, and there is no downtime, which is a major advantage over surgical debridement or other invasive wound healing techniques.
Patient FAQs
Q1: Is shockwave therapy painful?
A: Most patients report a mild tapping or tingling sensation during treatment. The procedure is well-tolerated and doesn’t require anesthesia.
Q2: How quickly will I see results?
A: Many patients notice improvements within 1–2 weeks, particularly in pain relief and wound size reduction. Full healing varies by wound type and compliance.
Q3: Can it replace dressings or other treatments?
A: Shockwave therapy complements—rather than replaces—standard wound care. It’s part of a multimodal healing plan that includes proper hygiene, dressing changes, and in some cases, nutritional or compression therapy.
Q4: Is it covered by insurance?
A: Coverage varies. Some insurance providers approve SWT for chronic wounds like diabetic ulcers. Always check with your healthcare provider or clinic administrator.
Q5: Are there any side effects?
A: Side effects are rare and mild. Temporary redness or minor discomfort may occur, but serious complications are extremely rare when performed by trained professionals.
Conclusion: Healing Reimagined
Shockwave therapy represents a paradigm shift in the treatment of soft tissue wounds. It activates the body’s intrinsic regenerative potential—stimulating fibroblasts, enhancing oxygen supply, and re-establishing microvascular circulation—all without drugs or scalpels. For patients who have suffered from chronic ulcers, surgical wounds, or tendon tears, SWT offers more than just accelerated healing—it offers renewed hope. Its proven safety profile, ease of application, and synergistic compatibility with other treatments make it a top-tier option in modern wound care. Whether you’re a healthcare provider seeking better outcomes or a patient looking for a non-invasive, science-backed solution, shockwave therapy brings wounds one step closer to full recovery—faster than ever before.
References
Shock Wave Therapy for Wound Healing and Scar Treatment:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK586112
Defocused Shock Wave Therapy for Chronic Soft Tissue Wounds in the Lower Limbs: A Pilot Study:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0301562916302745
Shock wave therapy for acute and chronic soft tissue wounds: a feasibility study:
