Understanding Plantar Fasciitis
The Anatomy of the Plantar Fascia
The plantar fascia is a thick band of fibrous connective tissue located on the underside of the foot. It originates from the medial tubercle of the calcaneus and extends to the proximal phalanges of the toes. Acting like a bowstring, it supports the medial longitudinal arch and plays a critical role in the biomechanics of walking, absorbing shocks and distributing loads during gait. When subjected to repetitive stress or mechanical overload, microtears can develop, leading to inflammation and degeneration—a condition referred to as plantar fasciitis or plantar fasciopathy.
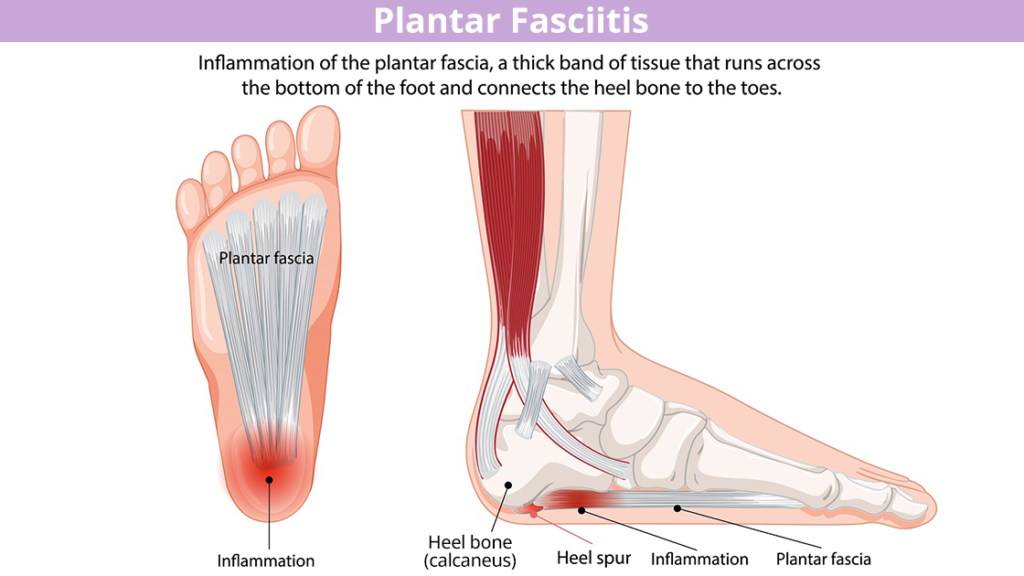
Risk Factors for Heel Pain
Several intrinsic and extrinsic factors increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis:
- Biomechanical Abnormalities: Overpronation, flat feet, or high arches can alter load distribution.
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases strain on the plantar fascia.
- Occupational Stress: Jobs that require prolonged standing or walking on hard surfaces elevate risk.
- Age: Middle-aged adults (40–60 years) are commonly affected.
- Improper Footwear: Lack of arch support or cushioning contributes to excessive strain.
- Tight Posterior Chain Muscles: Reduced flexibility in the Achilles tendon and calf muscles restricts normal dorsiflexion, increasing fascial tension.
Signs and Symptoms of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis
Patients typically report the following clinical features:
- Sharp Heel Pain: Especially pronounced during the first steps after waking (post-static dyskinesia).
- Localized Tenderness: At the medial calcaneal tubercle.
- Pain After Activity: Symptoms may worsen after, rather than during, physical activity.
- Stiffness: Particularly in the morning or after periods of rest.
- Gait Alterations: To offload the painful heel, patients may develop compensatory walking patterns, leading to further musculoskeletal issues.
The Rise of Shockwave Therapy in Foot Pain Management
What Is Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)?
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is a treatment modality that delivers acoustic pressure waves to damaged tissue from outside the body. It can be classified into two types: focused shockwaves and radial shockwaves. Both stimulate biological healing responses but differ in penetration depth and energy delivery. ESWT is FDA-approved and has transitioned from urological applications to orthopedic and sports medicine fields for treating chronic musculoskeletal disorders, particularly when conservative treatments fail.
Mechanism of Action
Promoting Blood Flow and Collagen Production
The mechanical energy delivered by shockwaves induces controlled microtrauma, which stimulates angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) and enhances local blood circulation. The influx of oxygen and nutrients fosters cellular repair. Fibroblasts—the key cells responsible for collagen synthesis—are activated, facilitating structural restoration of the fascia.
Breaking Down Scar Tissue and Calcification
Chronic inflammation can lead to fibrotic tissue and calcium deposits (enthesophytes). Shockwaves exert mechanical shear forces that fragment calcifications and remodel disorganized collagen fibers. This improves fascial elasticity and reduces nociceptive stimulation.
Triggering Natural Inflammatory Response
ESWT elicits a reparative inflammatory reaction by stimulating the release of key mediators such as Substance P, nitric oxide (NO), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). This cytokine-mediated response initiates a regenerative cascade, including macrophage activity, stem cell recruitment, and matrix remodeling.
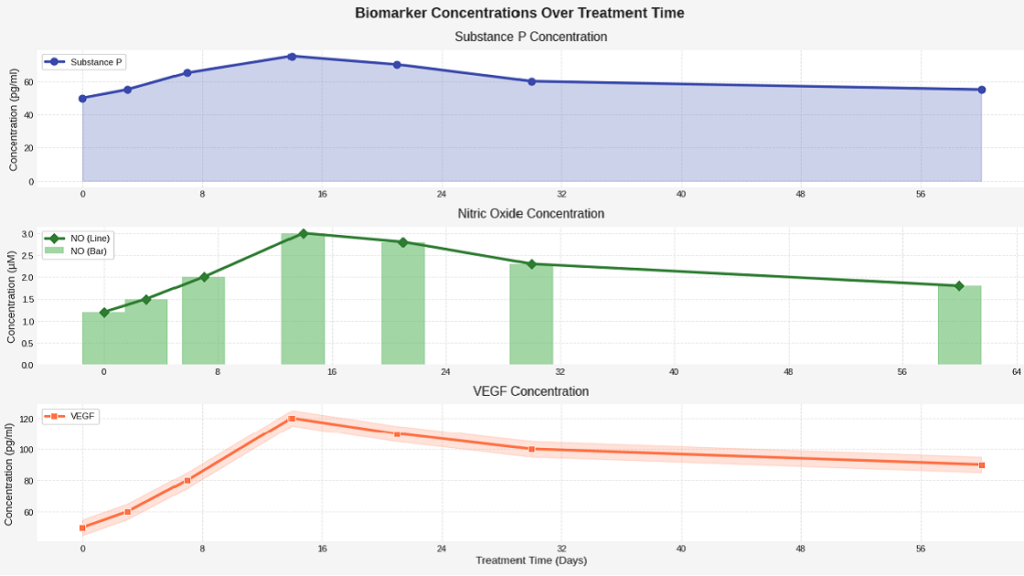
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis
Non-Invasive and Drug-Free Treatment
Shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a non-surgical procedure that doesn’t require anesthesia, incisions, or pharmaceuticals. This makes it ideal for patients who want to avoid the side effects of medication or the risks and downtime associated with surgery. It works by delivering acoustic waves to the damaged tissue, stimulating natural healing without introducing foreign substances into the body.
Fast Pain Relief and Functional Recovery
Many patients begin to notice improvements in pain levels after just one or two sessions. The mechanical stimulation promotes blood flow, reduces inflammation, and interrupts pain signaling in the nervous system. As tissue regeneration kicks in, patients often regain mobility, improve gait, and return to normal activities faster than with traditional conservative treatments alone.
Reduced Risk of Recurrence
Unlike temporary solutions such as corticosteroid injections, shockwave therapy addresses the underlying tissue damage. It enhances the healing of the plantar fascia, encourages collagen regeneration, and corrects biomechanical deficits over time. With improved tissue integrity and load tolerance, the chances of plantar fasciitis recurring are significantly lower.
Complementary to Other Modalities
ESWT can be easily combined with physical therapy, stretching exercises, orthotic devices, and lifestyle modifications. It doesn’t interfere with other treatments, making it a powerful addition to multi-modal rehabilitation plans. This flexibility ensures a holistic recovery path tailored to each patient’s needs.
What to Expect During and After Treatment
The Treatment Session Experience
During a session, the clinician applies gel to the affected area and uses a handheld applicator to deliver shockwaves. Patients may feel tapping or mild discomfort, especially over sensitive or inflamed tissue. The intensity can be adjusted based on patient tolerance. Each session typically lasts 15–20 minutes and doesn’t require downtime.
Treatment Frequency and Duration
Most patients undergo 3 to 5 sessions, spaced about one week apart. The number of treatments depends on the severity and duration of symptoms. Chronic cases may need additional sessions. Improvements often begin after the second treatment and continue to build in the following weeks as tissue healing progresses.
Side Effects and Safety
Shockwave therapy is generally safe with minimal side effects. Some patients experience temporary redness, swelling, or bruising at the treatment site. Mild soreness similar to post-exercise fatigue may occur. These effects usually resolve within 24–48 hours. Serious complications are rare when performed by trained professionals.
Aftercare and Recovery Tips
Post-treatment care is simple:
- Rest the treated foot for a day or two
- Avoid high-impact activity (e.g., running or jumping)
- Use ice if discomfort occurs
- Wear cushioned, supportive shoes
- Follow any prescribed stretching or rehab routines
- Staying consistent with aftercare helps maximize treatment effectiveness and prevent re-injury.
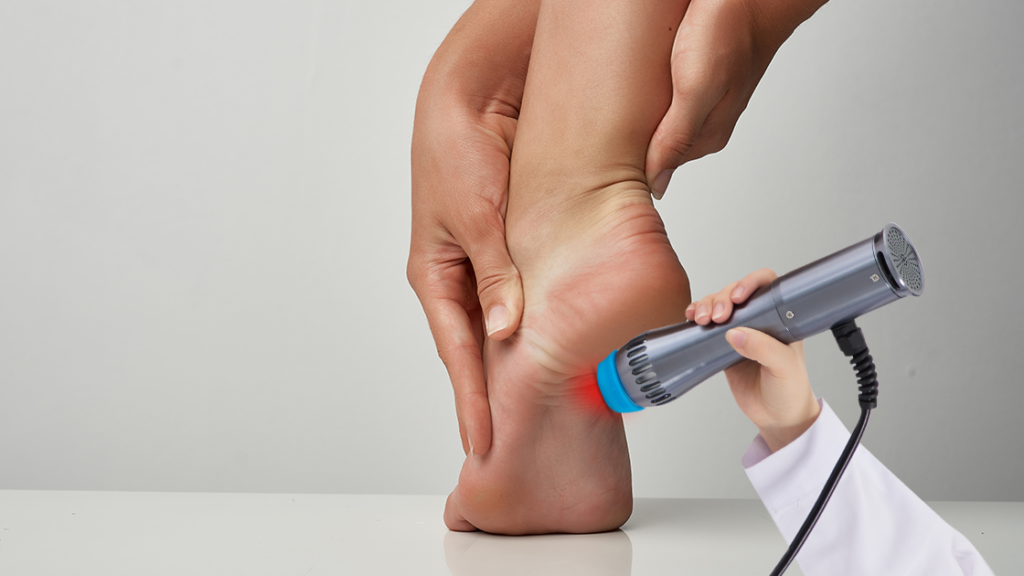
Beyond Plantar Fasciitis: Other Conditions ESWT Treats
Achilles Tendinopathy
Achilles tendinopathy results from overuse, repetitive motion, or strain on the Achilles tendon, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. It’s common in athletes, especially in running or jumping sports. Shockwave therapy effectively treats this condition by stimulating tendon healing, promoting collagen production, and improving blood circulation. It helps reduce inflammation and activates the body’s natural healing response, easing pain and improving mobility. ESWT can be an effective alternative to surgery, which involves long recovery times and risks.
Heel Spurs
Heel spurs are bony growths on the heel bone, often linked to chronic plantar fasciitis. While the spurs themselves aren’t painful, they can cause discomfort by irritating surrounding tissues. Shockwave therapy targets these tissues, reducing inflammation, breaking down scar tissue, and enhancing blood flow, leading to pain relief. ESWT is especially useful for patients who have not responded to treatments like physical therapy or orthotics. While it doesn’t remove the spur, it alleviates the pain and inflammation associated with it.
Other Tendinopathies and Soft Tissue Conditions
ESWT is beneficial for treating a range of tendon and soft tissue injuries, accelerating healing by improving circulation, collagen production, and tissue regeneration. Conditions treated with shockwave therapy include:
- Patellar Tendinopathy (Jumper’s Knee): Pain in the knee tendon, often due to repetitive jumping or running, can be treated with ESWT to stimulate tendon regeneration.
- Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow: ESWT effectively relieves pain and aids healing by targeting the tendons in the forearm muscles.
- Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: Shockwave therapy promotes healing in the shoulder tendons by encouraging collagen production and tendon repair.
- Gluteal Tendinopathy: Pain in the hip area caused by tendon damage can be alleviated by ESWT, promoting healing and reducing pain.
Myofascial Pain and Trigger Points
Myofascial pain syndrome is characterized by muscle pain and trigger points—painful spots within muscles that cause discomfort when pressed. Shockwave therapy deactivates these points by delivering mechanical waves that stimulate muscle tissue, improve blood flow, and release muscle tension. This helps reduce pain, restore muscle function, and improve range of motion. ESWT is particularly effective for chronic muscle knots and stiffness caused by injury or overuse, providing significant relief after just a few sessions.
Scientific Evidence and Further Reading
Clinical Trials Supporting Shockwave Therapy
There is substantial clinical evidence supporting shockwave therapy (ESWT) for musculoskeletal conditions, particularly plantar fasciitis. A 2020 meta-analysis in Pain Medicine reviewed over 1,000 patients, finding ESWT significantly reduced pain and improved function compared to treatments like corticosteroid injections and physical therapy. Another study in The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery showed ESWT outperformed corticosteroid injections for chronic plantar fasciitis. Additionally, research in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research highlighted that ESWT’s benefits, such as pain relief and improved function, lasted up to 12 months. These findings reinforce ESWT as a leading, non-invasive solution for chronic pain.
Guidelines from Authoritative Bodies
Several healthcare authorities endorse shockwave therapy for chronic conditions. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) supports ESWT for plantar fasciitis unresponsive to conservative treatments. The American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons also recommends it for chronic heel pain, citing its proven benefits. The International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment (ISMST) affirms ESWT’s effectiveness for musculoskeletal disorders, further validating its clinical success. These endorsements solidify shockwave therapy as a mainstream treatment option.
Final Thoughts: Walk Free Again
If you’re struggling with the daily pain of plantar fasciitis or another chronic musculoskeletal issue, shockwave therapy might be the solution you’ve been searching for. This non-invasive, drug-free treatment offers a scientifically backed approach to healing, providing long-term relief from pain and inflammation. Unlike medications or surgeries, shockwave therapy targets the root causes of your condition, promoting tissue repair, increasing circulation, and improving collagen production. Whether you’re a runner who can’t get back to your routine or someone who simply wants to walk without pain, shockwave therapy offers the chance to regain your mobility and quality of life. Take the first step toward healing and walk pain-free again.
FAQs: Shockwave Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis
Q1. Can Shockwave Therapy Help If I’ve Tried Everything Else?
If you’ve hit a dead-end with traditional treatments like physical therapy, insoles, or cortisone shots, shockwave therapy might be your breakthrough. It’s ideal for those who haven’t had lasting success with other methods, offering a non-invasive alternative that works on a deeper level to heal the tissue and reduce pain.
Q2. Is Shockwave Therapy Just for Athletes, or Can Anyone Benefit?
Absolutely anyone can benefit! While athletes may turn to shockwave therapy for overuse injuries, it’s also highly effective for office workers, busy parents, or anyone dealing with plantar fasciitis, no matter their activity level. Whether you’re on your feet all day or sitting behind a desk, shockwave therapy can ease your heel pain.
Q3. How Does Shockwave Therapy Compare to Foot Surgery for Plantar Fasciitis?
Surgery is a big step, and shockwave therapy is often a safer, more conservative alternative. It’s non-invasive, requires no recovery time, and can work wonders on chronic plantar fasciitis. While surgery might be the last resort, ESWT gives you the chance to heal naturally without the risk and long recovery.
Q4. Can Shockwave Therapy Prevent Future Plantar Fasciitis Flare-Ups?
While it’s not a crystal ball, shockwave therapy can significantly reduce the chances of a flare-up. By improving the health of your tendons, enhancing circulation, and promoting long-term healing, it helps create a more resilient foundation for your feet, lowering the odds of future pain.
Q5. What Happens If I Don’t Follow Up With Post-Treatment Care?
After your treatment, follow-up care is key to getting the best results. Not following through on stretching, resting, or using any recommended orthotics might slow down recovery. Think of the aftercare like watering a plant—it’s an essential part of helping your foot stay healthy and pain-free.
Q6. Will I Need Ongoing Treatments After Completing My Sessions?
Once you’ve completed the recommended sessions, many patients report long-lasting relief. However, depending on your lifestyle or specific foot condition, some individuals may benefit from occasional “touch-up” treatments. It’s all about keeping your feet in tip-top shape!
References
Long Term Effectiveness of ESWT in Plantar Fasciitis in Amateur Runners:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9737564
Effectiveness of shockwave therapy in the treatment of plantar fasciitis:
